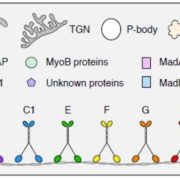
Update on Myosin Motors: Molecular Mechanisms and Physiological Functions
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research Blog By Jennifer M Ryan and Andreas Nebenfuehr
The cytoskeleton is the main organizing principle that defines not only the distribution of cellular components within cells but also the overall shape and growth pattern of cells and entire multicellular organisms. This function is particularly evident in…
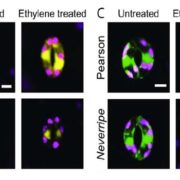
Flavonols Modulate ROS in Tomato Guard Cells
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogAlthough reactive oxygen species (ROS) have historically been considered damaging agents within cells, recent studies have demonstrated that these molecules also serve as second messengers in signaling pathways. The reactive nature of ROS allows these compounds to function as signaling molecules by reversibly…
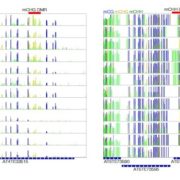
Arabidopsis DNA Methylome Stability under Stress
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogIt has been speculated that DNA methylation could complement genetic variation, as a mode for transferring heritable information, to contribute to phenotypic variation. Indeed, DNA methylation states can be maintained faithfully over both mitotic and meiotic cell division. According to this view, any…

Resistance to Wheat Stripe Rust
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchWheat (Triticum aestivum) yields can be severely reduced by the obligate biotrophic pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst). Currently, approaches to manage this disease rely on cultivar resistance coupled with fungicide application. However, driven by a greater need for wheat production,…

Origin and Role of ABA in Stomatal Regulation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogWhen the vapor pressure difference (VPD) between a leaf and the atmosphere increases (i.e., when air humidity decreases), guard cells lose turgor, thereby leading to stomatal closure. The evolution of this mechanism was an important step in the colonization of land by plants, since it enabled plants…

GA Signaling Increases Cytosolic Calcium
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogGibberellins (GAs) regulate many aspects of plant development, including seed germination, stem elongation, flower induction, and anther development. DELLA proteins, of which there are 5 in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), play a central role in GA signaling. GA triggers DELLA degradation via the…
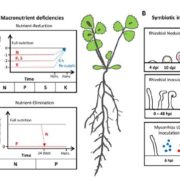
The Small Secreted Peptides of Legumes
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogSmall secreted peptides (SSPs) are peptides of 5 to 50 amino acid residues that are secreted into the apoplast. SSPs are critical regulators of a diverse array of growth and developmental processes in plants, including root growth, nutrient homeostasis, meristem maintenance, stress acclimation, pathogen…
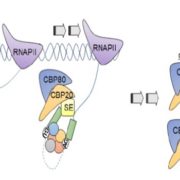
Update: Nuclear Cap-Binding Complex in Abiotic Stress Responses
Blog, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Agata Daszkowska-Golec
The nuclear cap-binding 16 complex (nCBC) in higher eukaryotes specifically binds to the monomethylated (7-methylguanosine (m717 GpppN)) cap structure at the 5¢ end of freshly transcribed mRNA. In addition to protecting mRNAs from degradation by exonucleases, the nCBC functions…
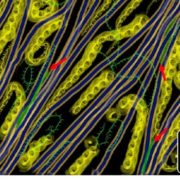
Update: Diffuse growth of plant cell walls
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Daniel J. Cosgrove
Introduction
The primary wall of a growing cell is a versatile, subtle and dynamic structure, with unique properties and functions in the life of the plant (Burton et al., 2010). When a cell grows, its wall stretches irreversibly as the cell enlarges in volume. Cells can start…

