How Does a Plant Tolerate Prolonged Darkness?
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe exposure of plants to prolonged darkness leads to the exhaustion of starch reserves and carbon and energy starvation. In such cases, plants must use alternative nutrient and energy sources to survive. Autophagy is an important mechanism that breaks down proteins and lipids and thereby provides the…

Update: Cation/H+ transporters affect membrane trafficking
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: UpdatesBy Heven Sze and Salil Chanroj.
Plants remodel their cells through the dynamic endomembrane system. Intracellular pH is important for membrane trafficking, but the determinants of pH homeostasis are poorly defined in plants. Electrogenic proton (H+) pumps depend on counter-ion fluxes to establish…
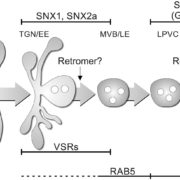
Turnover of Tonoplast Proteins
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBy Rumen Ivanov and David G. Robinson
Our knowledge of vacuole biogenesis and the transport of proteins to the vacuole has advanced consistently over the last 30 years. In meristematic cells, the tonoplast appears to develop directly out of the endoplasmic reticulum (Viotti et al., 2013). Once it is…
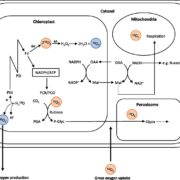
Photosynthetic Oxygen Production: New Method Brings to Light Forgotten Flux
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchOxygen (O2) is evolved during photosynthetic electron transport when water is split by the oxygen-evolving complex to provide protons and electrons to the chloroplastic electron chain, thereby generating ATP and NADPH—the energy source and reducing power for plant metabolism. The majority of this chemical…

Improving on the Humble Spud
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchThe humble spud. Simple, unassuming, yet vital in supporting a large proportion of the world’s population. Historically speaking, much of the research performed on potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) has gone into enhancing their disease resistance, justifiably so given the severe famines brought about through…
Intra-Organ Regulation of Shade Responses
Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlants beneath a canopy compete with neighboring plants for light by triggering various physiological responses, collectively known as shade avoidance syndrome. Because of the selective absorption of red (R) light by plants in the upper canopy, plants in the shade are exposed to low R to far-red (FR)…

A MicroRNA Regulating Lateral Root Growth in Response to Salt
Plant Physiology: On The InsideSoil salinity is a major threat to crop yields around the world. Salt generally damages plants through osmotic stress in the rhizosphere, interfering with water and nutrient uptake and causing cells to be subjected to ionic toxicity Developmental plasticity in the root system is an important strategy…
Drugs Triggering Oil Accumulation in a Diatom
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideOils composed of triacylglycerols (TAGs) have a broad range of applications, ranging from foods to biofuels. Microalgae are promising feedstocks for the production of (TAGs) but obtaining high yields of TAGs is challenging. Conte et al. (10.1104/pp.17.01804) have developed a phenotypic assay for the…

Mechanisms of Long-Distance mRNA Movement
Plant Physiology: On The InsidePhloem has long been recognized as a tissue that transports carbohydrates and amino acids. In recent years, however, it has also been found that this tissue serves as a conduit for signals, e.g., mRNAs, small RNAs, proteins, small peptides, and hormones. Several classical studies have shown that certain…

