Review: Naphthylphthalamic acid and the mechanism of polar auxin transport ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTeale and Palme give an overview of what the last 60 years of using synthetic chemicals inhibitors of polar auxin transport has really taught us. Key among inhibitors is Naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA) that interferes with polar auxin transport and can mimic PIN gene mutant phenotypes. These inhibitors…
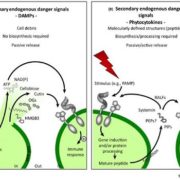
Review: Sensing danger – key to activating plant immunity
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe first step in defending yourself is recognizing that you need to defend yourself. Gust et al. review the mechanisms through which plants sense danger, drawing parallels to similar mechanisms in animals. They define three categories of danger signals. Exogenous signals are “non-self” signals,…
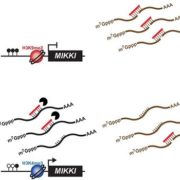
Regulation of rice root development by a retrotransposon acting as a microRNA sponge
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTransposable elements (TEs) compose a considerable portion of most plant genomes, and mounting evidence shows various roles of TEs in the regulation of gene expression. Some TE transcripts have been hypothesized to work as “sponges” to help fine-tune the levels of miRNAs through complementary binding.…

The G-box transcriptional regulatory code in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe G-box (CACGTG) is a DNA element widespread in plant genomes and recognized by two large families of transcription factors (TFs), the basic leucine zipper family (bZIP) and the basic-helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family. Members of these TF families contribute to growth, temperature and light signaling,…

Completing the whole puzzle of whole genome duplications in land plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogA hot topic in plant evolutionary biology is whole genome duplications (WGDs), in which an organism copies its entire genetic dataset. Having double the required DNA is often viewed as detrimental but can be useful in times of rapid environmental change. Recently, the role of WGDs during plant evolution…
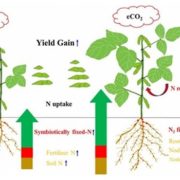
Elevated CO2 increases N2 fixation and contributes to various yield responses of soybean
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogClimate change is certain to affect our ability to produce food crops and feed a growing global population in the twenty-first century. Free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) experiments have shown that elevated CO2 (eCO2) levels, a major driver of climate change, have a consistently positive effect on the…
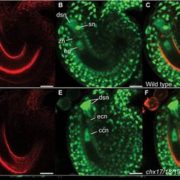
Cation/H+ exchangers affect pollen wall formation, male fertility, and embryo development
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCells have developed different mechanisms including control of ion and pH homeostasis to adapt to their constantly changing environment. Such adaption is accomplished by different ion transporters at the membranes. AtCHX17, AtCHX18 and AtCHX20 are members of the cation-H+ exchanger (CHX) family, which…

An acidophilic green algal genome provides insights into adaptation to an acidic environment ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHirooka et al. examined the genome of an acid-loving green alga, Chlamydomonas eustigma, to learn how it tolerates its low pH environment. Key differences between the acidophilic species and the neutrophilic species Chlamydomonas reinhardtii include: an increase in expression of genes encoding plasma…
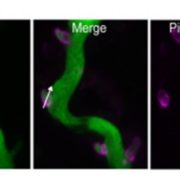
Tracking effector delivery in Irish famine potato pathogen
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPathogenic microbes interfere with the host cellular and physiological processes to promote infection. This interaction is monitored by pathogen molecules called effectors that either act in intercellular space or enter the host cells. Mechanisms underlying the uptake of these effectors are not fully…

