
A prion-like domain in ELF3 functions as a thermosensor in Arabidopsis (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs sessile organisms, sensing the external conditions is critical for plants to complete their life cycle and temperature is one of the major factors. In Arabidopsis, the evening complex senses the temperature and it consists of EARLY FLOWERING3 (ELF3), a scaffolding protein; ELF4, helical protein; LUX…
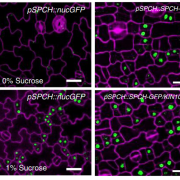
KIN10 promotes stomatal development through stabilization of the SPEECHLESS transcription factor (Nat. Commun.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plants communicate with the environment through stomata (i.e., pores found on leaf surfaces) and regulate gas exchange depending on internal and external cues by optimizing stomata density. Still, how plants integrate metabolic and environmental signals remain to be determined. Here, Han and colleagues…
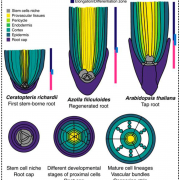
Development and cell cycle dynamics of the root apical meristem in the fern Ceratopteris richardii (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Roots are essential organs for nutrient and water uptake and have been extensively investigated in angiosperms. Many studies suggest that roots originated through convergent evolution in vascular plants, a clade that includes seed plants and ferns. Besides Arabidopsis and crops, little is known about…
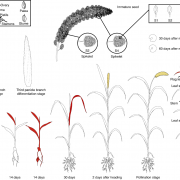
Mini foxtail millet as a new C4 model species (Nat. Plants) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The three most widely adopted plant models all use C3 photosynthesis, but discoveries made in these plants are not always applicable to C4 plants. Foxtail millet (Setaria italica) has been emerging as a potential C4 model species, but its use for genomics research is challenging due to long generation…

Cuscuta australis (dodder) parasite eavesdrops on the host plants’ FT signals to flower (PNAS)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plants sense environmental cues, such as day length, to induce flowering and successfully reproduce. An important mobile regulator of flowering is FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT). Upon floral induction, FT is transported from the leaves to the shoot apical meristem where it triggers flower development. Dodders…

Plant Science Research Weekly: 18 September 2020
WWR Full PostGuest Edited by Michela Osnato.
I completed my studies at the University of Milan (ITALY), with a M.S. in Plant Biotechnology and a PhD in Plant Biology and crop productivity. The plasticity of plant development has always fascinated me. For this reason, I decided to investigate regulatory genes…

Peripheral? Not Really! The Extracellular Arabinogalactan Proteins Function in Calcium Signaling
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefArabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) are a family of extracellular proteoglycans that existed in land plants and algae (Johnson et al., 2017). AGPs are part of the hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein (HRGP) superfamily that also includes extensins and proline-rich proteins. Based on the protein sequence, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol…
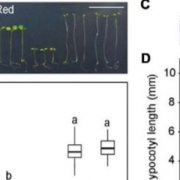
A Chloroplast-derived Signal Attenuates Growth in Red Light by Acting on the phyB-PIF Pathway
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAuthor: David S. Favero1 (ORCID: 0000-0002-6879-0323)
[email protected]
Affiliation:
1RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science, Yokohama, Kanagawa, 230-0045 Japan
Plant growth and development are regulated by a complex network of signals, many of which converge at the nucleus and…

Chemical labeling of proteins in live plant cells
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellIwatate et al. demonstrate that SNAP-tag technology can be used to label plant cell proteins.
Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00439
By Ryu J. Iwatatea,b, Akira Yoshinaria, Noriyoshi Yagia, Wolf B. Frommera,c, and Masayoshi Nakamuraa
a Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM),…

