
Interesting autophagy review articles
Blog0 Comments
/
A curated list of some interesting plant autophagy-related review articles
1. Special Issue: Plant Autophagy: Mechanisms and Functions, Journal of Experimental Botany
https://academic.oup.com/jxb/issue/69/6;
2. Autophagy in Plants – What's New on the Menu?
https://www.cell.com/trends/plant-science/fulltext/S1360-1385(15)00256-3
3.…
Keeping an Eye on Lutein Stability
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCarotenoid pigments not only produce the vibrant yellows and oranges of flowers, fruits, and autumn leaves, but they also are important in both plant and human health. They act both as accessory pigments in photosynthetic light harvesting and as photoprotectants that absorb excess energy during photosynthesis. …

Enhancing wheat Rubisco activase thermostability by mutagenesis of conserved residues from heat-adapted species
Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMaria Grazia Annunziata
Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, 14476 Potsdam-Golm, Germany.
[email protected]
ORCID ID: 0000-0001-8593-1741
Rubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the central enzyme of photosynthetic carbon assimilation in the…

How Autophagy Is Activated under Extended Dark Conditions
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHuang et al. uncover how SnRK1 kinase complex promotes the autophagy activity by phosphorylating ATG6 under prolonged dark conditions. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00066
By Huang Xiao and Faqiang Li, College of Life Sciences, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
Background:…

Comparing genes that govern flower development in Petunia and Arabidopsis: Evolution made a mess!
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMorel et al. investigate AP1/SEP/AGL6 MADS-box transcription factor functions in Petunia. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00162
By Michiel Vandenbussche
Background: The ABCE model is a simple genetic model that explains how the different floral organs in the flower (sepals, petals, stamens…
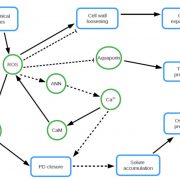
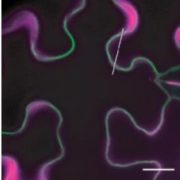
Review: Interplay between turgor pressure and plasmodesmata during development (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata, small cytoplasmic channels connecting adjacent cells, allow small molecules to move and redistribute information and resources. Plasmodesmatal aperture is highly regulated, which is crucial to development and defense. Hernández-Hernández et al. review the contribution of turgor pressure…
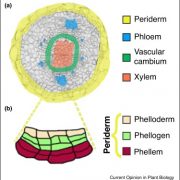
Review. The development of the periderm: the final frontier between a plant and its environment (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCampilho et al. have written an interesting review about the molecular basis of periderm development. During secondary growth (increase in girth) of most gymnosperms and dicots, the outer epidermal layer is gradually replaced by the periderm, which facilitates gas exchange and defense. Periderm is composed…
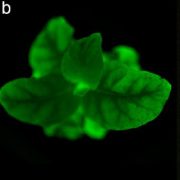
Plants with self-sustained luminescence (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNothing beats being able see gene expression in real time and space. In recent years, plant biologists have made great strides in understanding plants by using the visual reporters GUS, green fluorescent protein (and other fluorescent proteins) and luciferase. Each of these requires either a substrate…
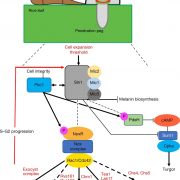
A sensor kinase controls turgor-driven plant infection by the rice blast fungus ($) (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMagnaporthe oryzae, the causal organism of blast disease in rice and wheat, is the most devasting pathogen in rice production. During infection, it develops a germ tube that forms an infection structure called the appressorium. Through septin-mediated reorganization of the cytoskeleton, a high amount…

