
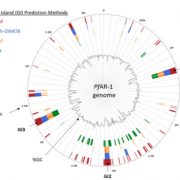
Effector gene reshuffling involves dispensable mini chromosomes in wheat blast fungus (PLOS Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe emerging disease wheat blast is devastating and has the capacity to cause 100% yield loss. Wheat blast is caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype Triticum (MoT). This pathotype is distinct from most of the pathotypes that causes disease in other plants such as M. oryzae Oryza (MoO) in rice.…
Plant microbe co-evolution: Allicin resistance in Pseudomonas fluorescens (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGarlic (Allium sativum L.) produces allicin (diallylthiosulfinate), which is an antibiotic defense substance. It can oxidize thiols in celular targets such as cysteines and glutathione. Because allicin has multiple sites and mechanisms of action, it is difficult for an organism to become resistant.…

Exploring the hydraulic failure hypothesis of esca leaf symptom formation (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEsca is a leaf scorch (necrosis) disease of grapevine that causes tremendous yield losses. Bortolami et al. have investigated the etiology of this condition, which is known to be a consequence of fungal pathogen infection. But how exactly does the fungal infection contribute to the observed symptoms?…

Carbon nanotube-mediated DNA delivery in intact plants (Nature Protocols)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne promising use of nanomaterials is the delivery of biomolecules into cells. Demirer et al. report a detailed protocol for Carbon Nano Tube-mediated DNA delivery into intact plants, allowing transformation without transgene integration, that can be used in both model and crop species. In brief, carboxylated…

Plant Science Research Weekly: September 27th
Blog, WWR Full PostEvolutionary flexibility in flooding response circuitry in angiosperms ($)
Flooding is unpredictable and can lead to plant death due to insufficient oxygen (hypoxia). Some plant species and varieties are better able to survive periods of submergence. Here, Reynoso et al. looked at gene networks…
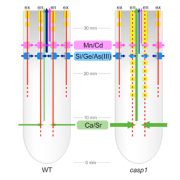
Casparian Strip Formation in Rice
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. identify a protein that mediates Casparian strip formation at the endodermis in rice roots. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.000296
By Jian Feng Maa and Jixing Xiab
aInstitute of Plant Science and Resource, Okayama University, Japan
bCollege of Life Science and Technology,…

Promoting production: UPL3 promoter variation modulates seed size and crop yields
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIdentifying natural genetic variation, understanding how it influences traits, and utilizing it for crop improvement is a major objective in plant science. Miller et al. (2019) have identified genetic variation in the promoter region of BnaUPL3.C03 from a panel of Brassica napus accessions that can influence…

A novel specialized immune player: BSK5 is required for restricting pathogen progression
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAmna Mhamdi, Ghent University, Department of Plant Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, and VIB Center for Plant Systems Biology, 9052 Ghent, Belgium
Defense reactions are the fascinating result of a complex network between signals, receptors and effectors, where any missed nodes may spell disaster.…

The genome history of camelina emerges from the shadows
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMandáková et. al. explore the origin of an ancient oilseed crop. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00366
Background: Camelina (Camelina sativa; gold of pleasure or false flax) is an ancient oilseed crop grown in Europe as early as 4000 BC. Gold of pleasure was largely forgotten as a crop, being replaced…

