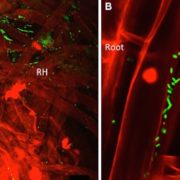
A root hair-seeking endophytic microbe from an unusual volcanic swamp corn enhances phosphate uptake
In plants the location of microbes to specific cell types, including endophytes, is still scarcely described in contrast with the situation in the animal kingdom. Shehata et al. describe a bacterial endophyte (Strain 3F11, possibly Enterobacter asburiae) from Zea nicaraguensis, a wild corn growing at…

The role of botanical gardens in species conservation
Botanical gardens are sanctuaries where plant diversity is celebrated, conserved, studied, and shared. As more species are put under pressure from anthropogenic activities, the importance of botanical gardens in preserving and protecting threatened species is increasing. A recent study on the role of…
What We're Reading: October 27th
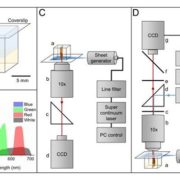
Review: Outer, inner and planar polarity in the Arabidopsis root
Despite vast differences across all living organisms, most eukaryotes display some form of cellular polarity which enables them to carry out specialized functions. The coordination of cell polarity within a single tissue layer is known…
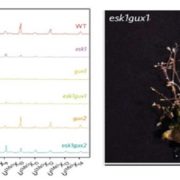
An even pattern of xylan substitution is critical for interaction with cellulose in plant cell walls
Plant cell wall architecture is a very complex specific design and the interaction between xylan and cellulose is believed to be that way too. Grantham et al. reveal the details of the association between xylan and cellulose using mass spectrometry and NMR in Arabidopsis. ESKIMO1 (ESK1) is a xylan-specific…
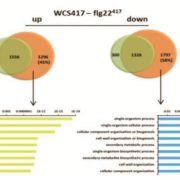
Signatures of adaptation to mutualists revealed by root transcriptional dynamics
A plant's rhizosphere consists of a huge array of pathogenic microbes many of which can trigger defense responses, leading to decreased growth. On the other hand, beneficial microbes such as rhizobacteria promote growth and can induce systemic resistance while suppressing local immune responses. A recent…
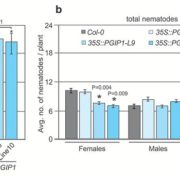
Damage-associated signals differentially impact nematode parasitism
Roots must protect themselves from a diverse range of microbial and animal pests. To accomplish this, plants have evolved sophisticated signalling machinery to detect the presence of these pests or to quickly react to the damage that they cause. In a recent study, Shah et al. identified host receptor…

Tomato Genome Goes Nano
Schmidt et al. demonstrate that nanopore technology can be applied to plant genomes https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00521
By Schmidt, M. H.-W., Vogel, A., Denton, A. K., Bolger, A. M., Bolger, M. E., and Usadel, B.
Background: An organism’s genome contains all the necessary information for its…

Images for Impact – How-to tips. Created for the Plantae Seminar Series
Earlier this year I gave a Plantae seminar on "Images for Impact" - simple, free tips about how to source and create images to use in your science writing and communicating.
Here is the text of the handout I created to accompany the seminar. You can get this as a PDF here. You can download the…
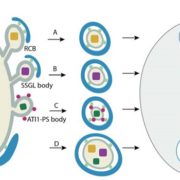
Update on autophagy: Dynamics of autophagosome formation
By Junmarie Soto-Burgos, Xiao-Hong Zhuang, Liwen Jiang, and Diane C. Bassham
Autophagy, literally defined as “self-eating”, functions as a degradation process by recycling cytoplasmic contents under stress conditions or during development. Upon activation of autophagy, a membrane structure known…

