
The Real Yield Deal? Nitrate Transporter Expression Boosts Yield and Accelerates Maturation
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefApproaches to improve final grain production must consider yield stability, that is ways to prevent yield losses. For example, flowering time affects yield and yield stability-- if grains mature late, they may be literally caught out in the cold, as late-season weather turns. Indeed, the application…
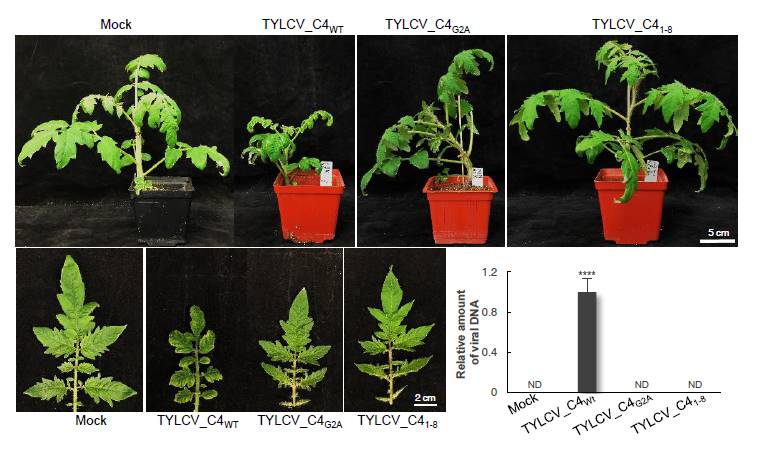
A virus-targeted plant receptor-like kinase promotes cell-to-cell spread of RNAi (PNAS) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogViruses can move from cell to cell through plasmodesmata. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are key components in the plant's arsenal against viruses. They function by harnessing the AGO system to target and cleave viral RNA, thus silencing the viruses. Like the viruses they target, siRNAs move from cell…
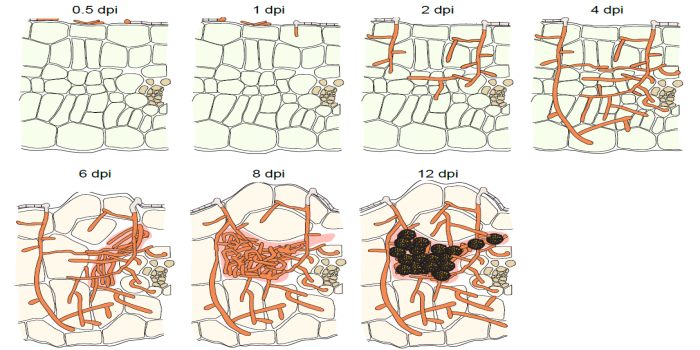
The biotrophic development of Ustilago maydis studied by RNAseq analysis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe corn smut fungus Ustilago maydis that causes tumorous symptoms on all aerial parts of maize has established itself as a model system to dissect host colonization strategies by biotrophic fungi. Transcriptional responses upon U. maydis colonization were previously demonstrated by several studies using…
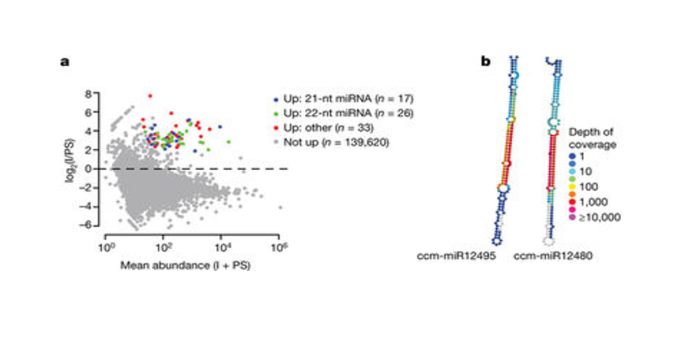
MicroRNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris target host messenger RNAs
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNature. Cuscuta sp. commonly known as dodder, is an obligate parasitic plant that colonizes a broad range of host plants and obtain water and nutrients by specialized feeding structure called haustorium. Literature suggests that this specialized structure is involved in bidirectional movement of viruses,…
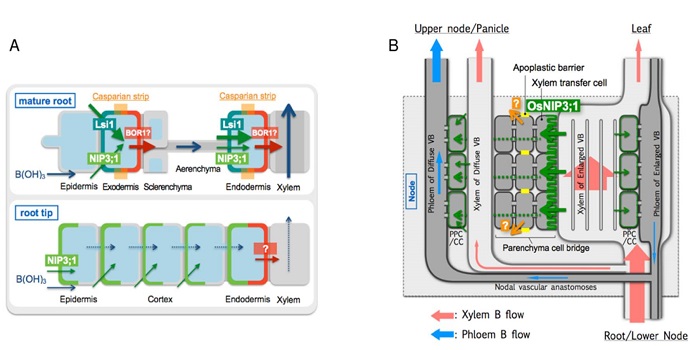
Boron Transport in Rice
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogBoron (B) is an essential micronutrient for plant growth and development. Its major physiological function is to maintain the structure of the cell wall by crosslinking pectic polysaccharides through borate-diol bonding of two rhamnogalacturonan II molecules. B is immobile in most plant species. Therefore,…

Arabidopsis pollen tube integrity and sperm release are regulated by RALF-mediated signaling
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSuccessful fertilization in plants requires sperm cells (SCs) to be carried along the growing pollen tube (PT) until reaching the female gametophyte where the PT then bursts to release the SCs. One challenge PTs must overcome in order to achieve fertilization is deciding to rupture or not to rupture.…
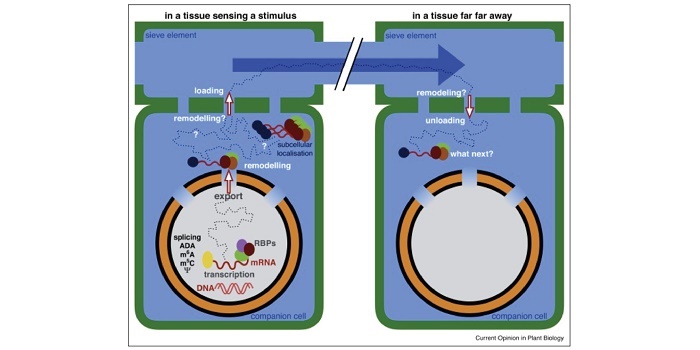
Review: On the selectivity, specificity and signaling potential of long-distance movement of messenger RNA
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRegulation of transcription occurs at the cell-type specific level, but transcribed messenger RNA is mobile and can move between tissues through plant vasculature, serving as a long distance messenger. Many mRNA molecules have been identified in the phloem sap, suggesting that mRNA transport goes through…
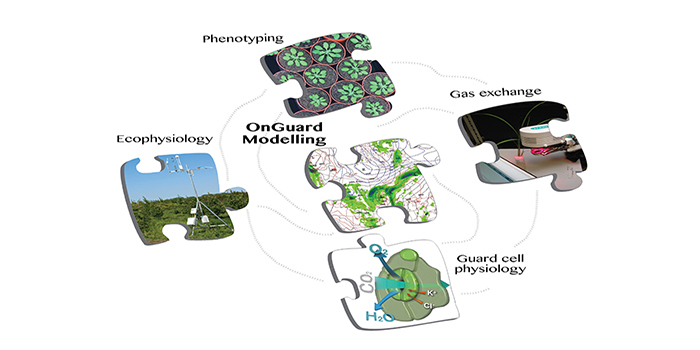
OnGuard2 Computational Platform Tracks Guard Cell Processes
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. discover unexpected connections between humidity and ion transport using a model that bridges guard cell-to-leaf scales https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00694
By Maria Papanatsiou
Background: Plants rely on stomata on the leaf epidermis for their survival. Stomata are small pores formed…
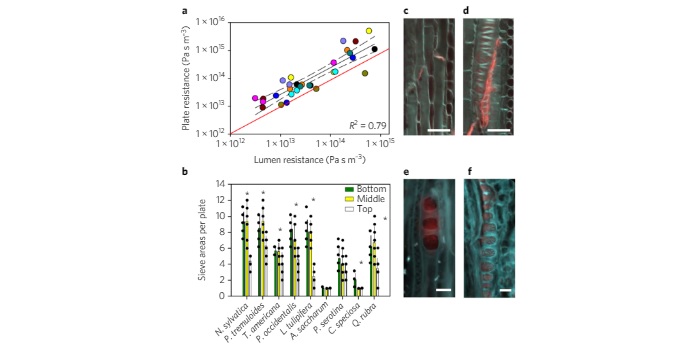
How do trees transport carbohydrates?
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogAs a tree grows in height, increasing the length of the transport pathway, the hydraulic resistance of the vascular tissues should increase. It is not clear if trees only rely on passive transport mechanisms (no active loading of sugars) to move carbohydrates from shoots to roots. To answer this question,…

