
Production of low-Cs+ rice plants by inactivation of the K+ transporter OsHAK1 with the CRISPR-Cas system
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNuclear accidents in recent years such as the Fukushima incident during the tsunami in 2011 revealed the detrimental effects of leaked radioactive cesium (Cs) in environmental soil and water. Due to Cs's chemical similarity with potassium, an essential macronutrient for plants, cesium is taken up by…

Temporal and spatial transcriptomic and miRNA dynamics of CAM photosynthesis in pineapple ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) is the form of photosynthesis in which carbon assimilation occurs at night. CAM allows plants, especially those growing in arid regions, to avoid excessive water loss. With the long-term goal of eventually engineering this water-conserving trait into crop plants, Wai…

Phloem loading through plasmodesmata: a biophysical analysis
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSugars produced in photosynthetically active mesophyll cells move into the phloem through a process known as phloem loading, but not all plants phloem load the same way. Some use a passive process in which sugars move down a concentration gradient into the phloem, but others use active transport processes.…

A Regulator of Calcium Signatures Revealed
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogCalcium (Ca2+) is an important cellular second messenger for diverse developmental processes and environmental responses in both plants and animals. Transient increases in cytosolic Ca2+ are activated in plants during a host of environmental and developmental processes, including root growth, stomatal…
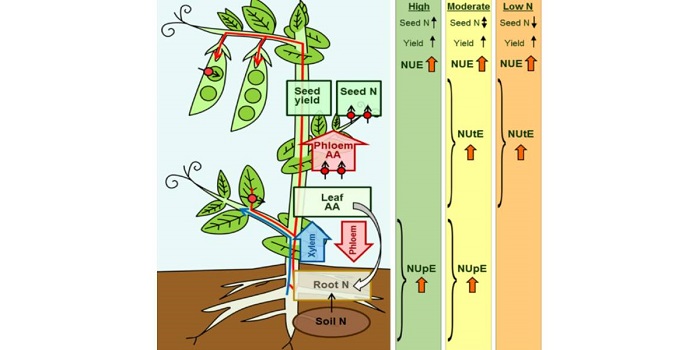
Transporter Function and N Use Efficiency
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogNitrogen (N) is an essential nutrient that plants require in large amounts for growth and development. In industrial countries, high N fertilization enables maximum crop yields, and in the last 50 years, the use of synthetic N fertilizers has increased dramatically to meet food demands. Improving the…
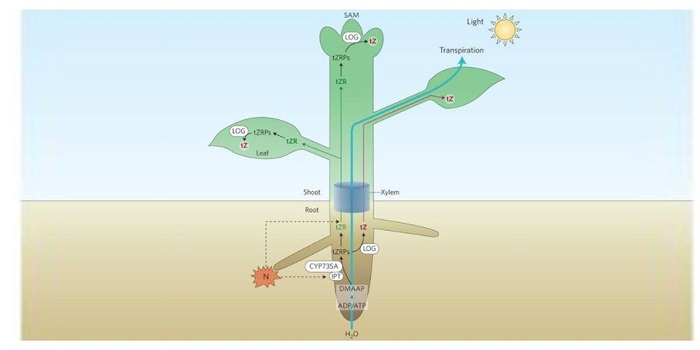
Systemic transport of trans-zeatin and its precursor have differing roles in Arabidopsis sho
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant hormones are made in one tissue and usually transported to act in another. One example of this is the transport of cytokinin. In the root, the precursor trans-zeatin riboside (tZR) is synthesized, then xylem loaded and transported to the shoot. Once at a site of action like the leaf or shoot…
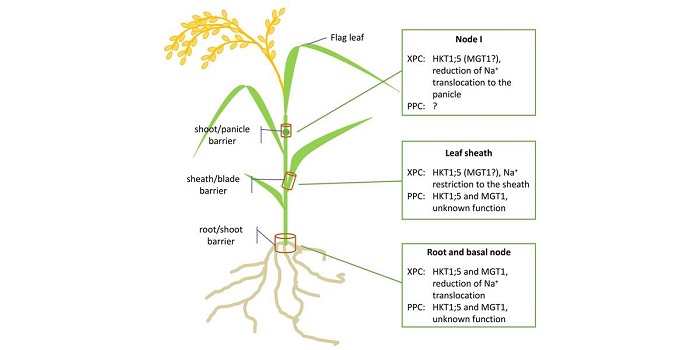
Commentary: Salt Tolerance in Crops: Not Only a Matter of Gene Regulation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Research, Research BlogBy Elide Formentin
Rice (Oryza sativa), the primary source of calories for more than 2 billion people, is the most sensitive of all cereal crops to soil salinity, which affects more than 20% of irrigated arable land (FAO and ITPS, 2015). Rice paddies are mainly located at the delta of rivers, where…

Emission of volatile organic compounds from petunia flowers is facilitated by an ABC transporter
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants can emit up to 10% of the carbon they fix as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which function in abiotic stress tolerance, pollinator attraction, signalling between plants, and defending against pathogens and herbivores. It has been an open question whether these small molecules pass directly…
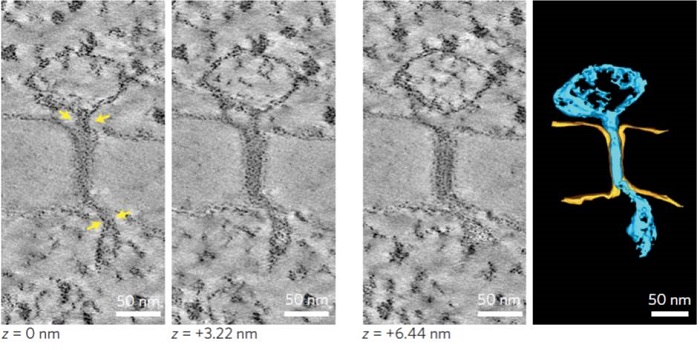
Architecture and permeability of post-cytokinesis plasmodesmata lacking cytoplasmic sleeves ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlasmodesmata are pores between cells through which viruses, proteins, small RNAs and other molecules can pass. The pores are usually described as being lined with a layer of plasma membrane with a tube of endoplasmic-reticulum membrane through the center. These membranes and associated proteins are…

