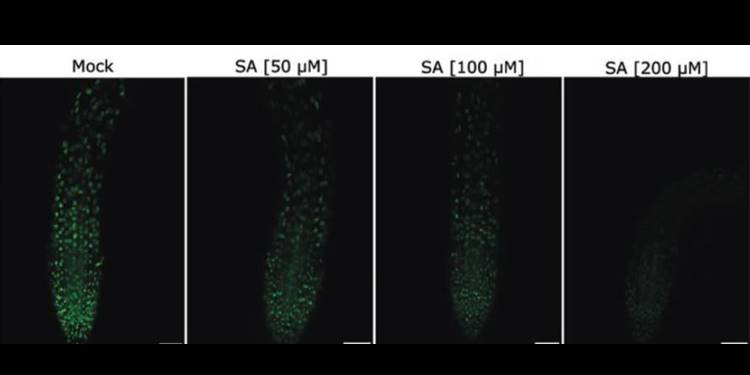
Salicylic acid interferes with GFP fluorescence in vivo
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) is a widely-used reporter with which to analyze protein localization and expression levels. De Jonge et al. report that GFP fluorescence is greatly diminished in the presence of the hormone salicylic acid (SA), as is the fluorescence of the reporters RFP and VENUS. The…
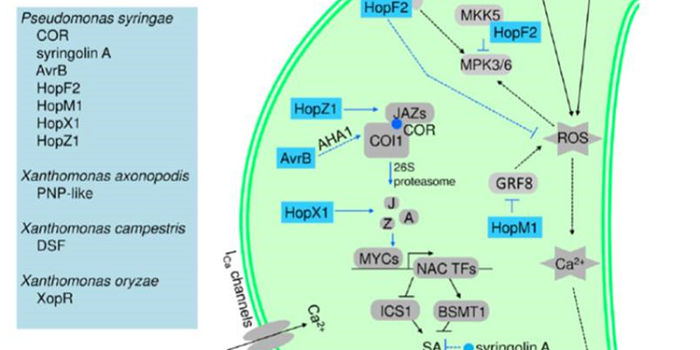
Update: Stomatal defense a decade later
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchStomatal defense, recognition of pathogens at the stomatal pore accompanied by stomatal closure to prevent their entry, was discovered ten years ago. Melotto et al. review what we’ve learned in the past decade about this key defense strategy. They discuss pathogen recognition, in which microbe-associated…
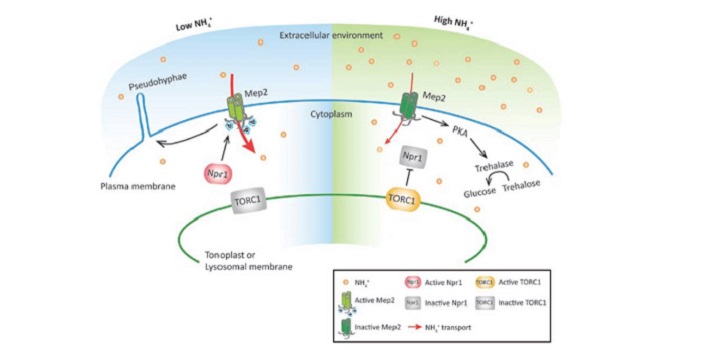
Review: Ammonium as a signal for physiological and morphological responses ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAmmonium is one of the major forms in which nitrogen is assimilated. Besides being a nutrient, it also acts as signal that affects gene expression and root system architecture. Some ammonium-induced genes are also induced by low pH (ammonium acidifies the apoplast), whereas others are specifically induced…
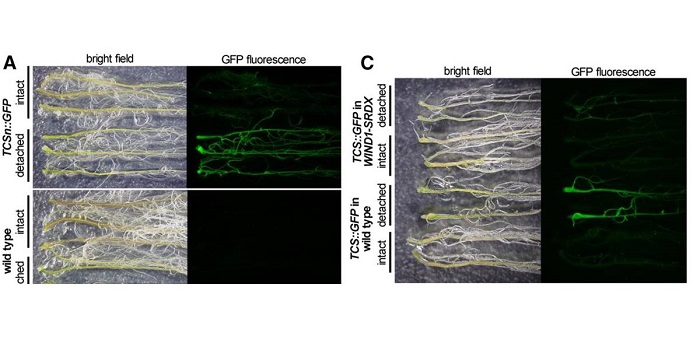
The Root Greening Response in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogBased on various developmental, environmental, and hormonal cues, proplastids can be converted into different types of plastids within cells. In Arabidopsis, chloroplast development is repressed in roots via auxin signaling. When roots are detached from the shoot, and its supply of auxin, roots develop…
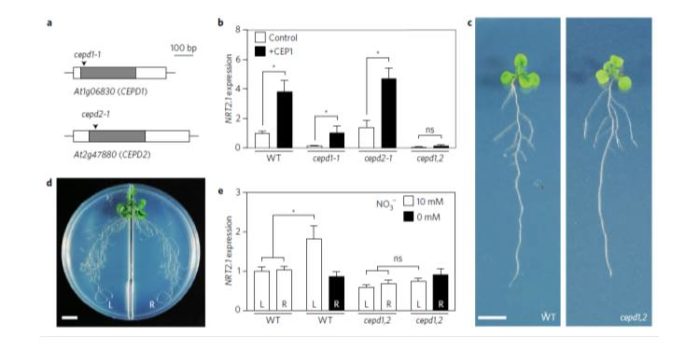
Shoot-to-root mobile polypeptides involved in systemic regulation of nitrogen acquisition ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchTo balance nutrient uptake (usually from heterogeneous sources) with nutrient demand, plants use a root-shoot-root signaling pathway. Previously, a root-to-shoot mobile peptide C-TERMINALLY ENCODED PEPTIDE (CEP) was shown to translocate from N-starved roots to the shoot, where it interacts with a leucine-rich…
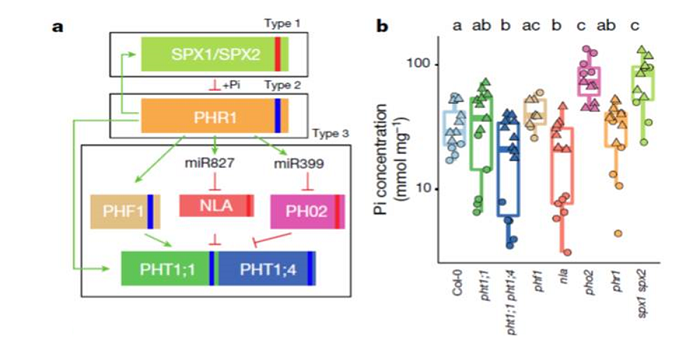
Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMany of the genes involved in the phosphate-stress response (PSR) have been identified from plants growing on sterile medium. Castrillo et al. examined how the root microbiota affectthe phosphate stress response, and how phosphate affects the association between roots and microbes. Plants deficient…
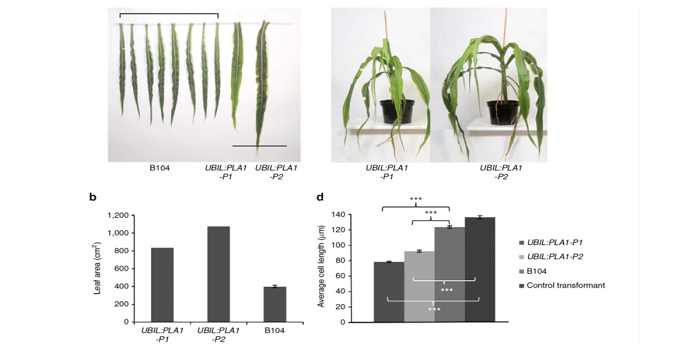
Altered expression of Maize PLASTOCHRON1 (CYP78A) increases auxin levels, extends cell division duration and increases biomass and seed yield
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPreviously, the rice PLA1 gene encoding a CYTOCHROME P450 (CYP78A) was shown to increase vegetative growth. Sun et al. enhanced expressed maize PLA1 specifically in the leaf growth zone under the control of the GA2ox promoter. Transgenic plants produced larger leaves and larger seed yields than control…
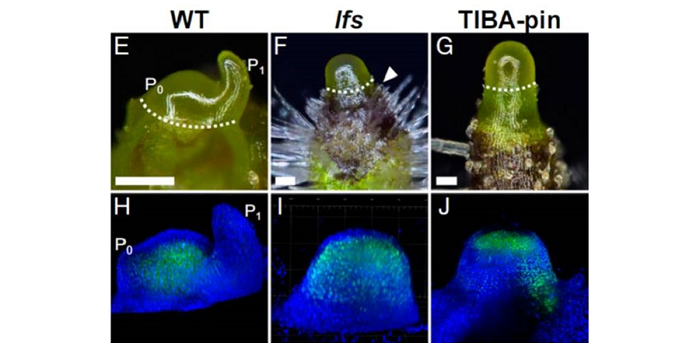
Coordination of auxin-triggered leaf initiation by tomato LEAFLESS ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCapua and Eshed explored the link between auxin and leaf initiation at the shoot apical meristem, using the tomato mutant leafless (lfs), which is an ortholog of the Arabidopsis DORNRONSCHEN (DRN) and DRN-like (DRNL) genes that encode AP2-type transcription factors. The lfs mutant and the drn/drnl double…
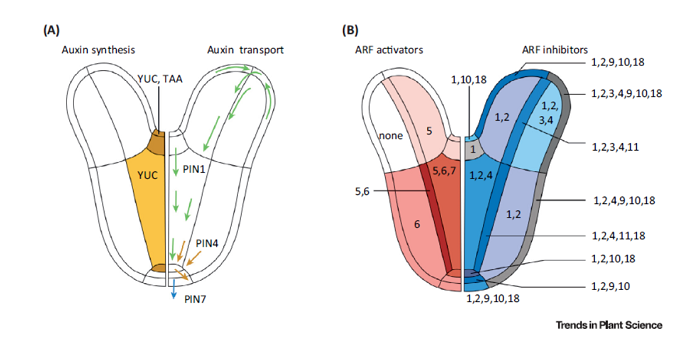
Review: The systems biology of auxin in developing embryos ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe transcriptional response to auxin depends in large part on the interactions between ARF transcription factors and the Aux/IAA transcription inhibitors that interact with them. The crucial role of auxin in embryo patterning is revealed by the embryo patterning defects observed in mutants of ARF and…

