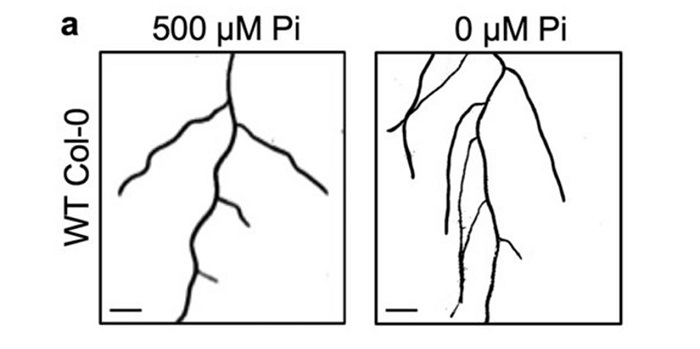
Regulation of gravitropic set point angle
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
One parameter that defines a plant’s architecture is the angle at which its branches and lateral roots lie with respect to gravity, known as the gravitropic set point angle (GSA). Like all aspects of plant architecture, GSA is a highly plastic trait that is sensitive to light and nutrient availability.…
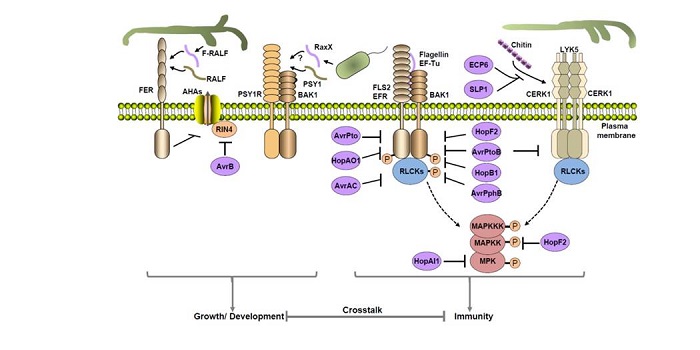
Review: Receptor kinases in plant pathogen interactions: More than pattern recognition
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchZhou et al. review the contributions of Receptor-Like Kinases (RLKs) and Receptor-Like Proteins (RLPs) as Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) that contribute to the recognition of pathogens, as well as the contributions of receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCKs). The authors summarize recent studies…
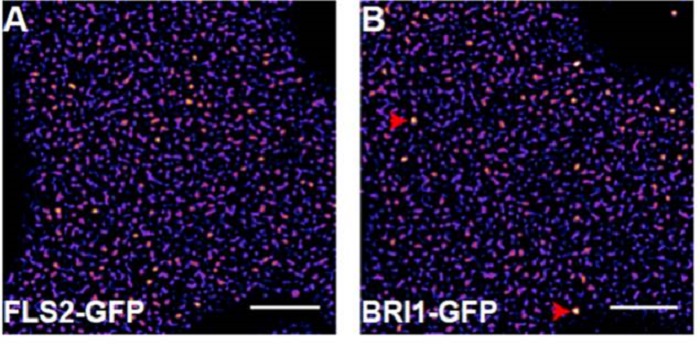
Plant immune and growth receptors share common signaling components but localize to distinct plasma membrane nanodomains
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSignal transduction in plant and animal cells is often initiated at the plasma membrane (PM) and involves common signaling components, raising the question of how receptor complexes elicit distinct signaling outputs. To address this question, Bücherl et al. investigated physical characteristics of the…

Review: Methods of cell-specific hormone analysis ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlant hormones are active at very small quantities and often act differently in different cell types. Various methods, primarily involving mass spectrometry and sensors, have been developed to identify and quantify hormones with cellular-level precision. Novák et al. review these methods and discuss…
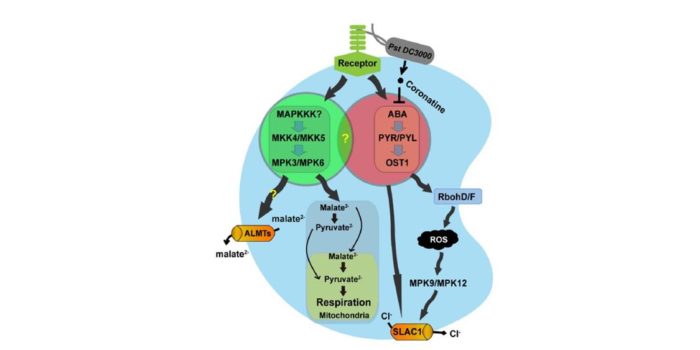
Stomatal immunity: Roles of MAP kinases and cytokinin
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWhen a pathogen is perceived, plants have the ability to induce stomatal closure to prohibit the pathogens from passing into the inner tissues; this response is known as stomatal immunity. Two new papers in The Plant Cell investigate mechanisms by which pathogen perception is transduced into stomatal…
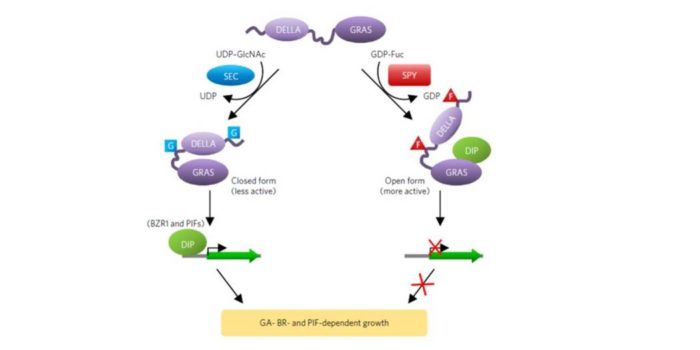
Arabidopsis O-fucosyltransferase SPINDLY activates growth repressor DELLA ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe SPINDLY (SPY) gene was identified through a genetic screen; spy mutants are abnormally tall and thin, suggesting that they are overly sensitive to gibberellins. Later, the SPY gene was shown to act downstream of GIBBEERLLIN INSENSITIVE (GAI), which is a DELLA-domain containing protein. SPY was previously…
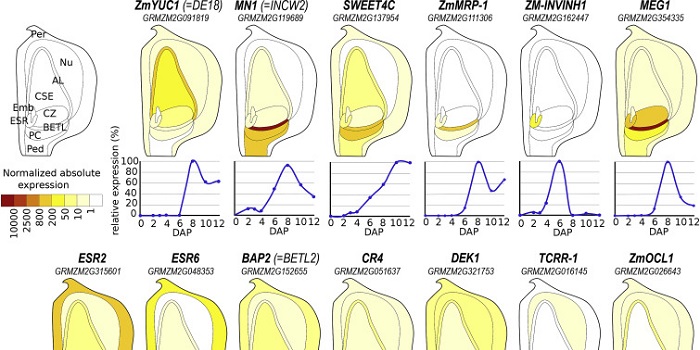
Review: Signaling in early maize kernel development
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe formation of a maize kernel requires growth coordination between embryo, endosperm, and surrounding maternal tissues. Key molecular actors in this coordination are hormones, sugars, peptides and transcription factors. Doll et al. review recent advances in our understanding of maize kernel development,…
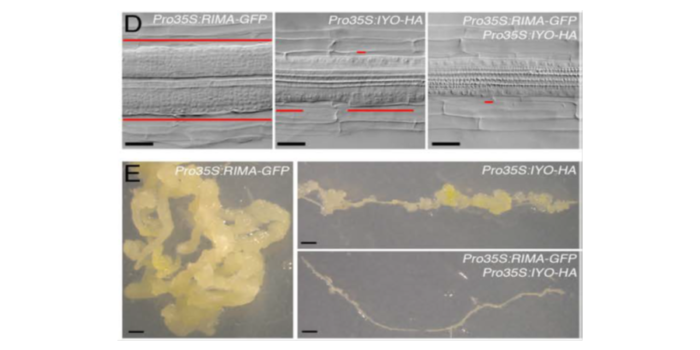
Molecular signals for regeneration ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchEvery gardener knows that pulling off a shoot is not sufficient to kill a plant. Plants are able to reprogram cells in order to regenerate missing tissues. Pulling off a shoot removes photosynthetic tissues, but the root responds by activating chloroplasts to take over this role. Kobayashi et al. (Plant…
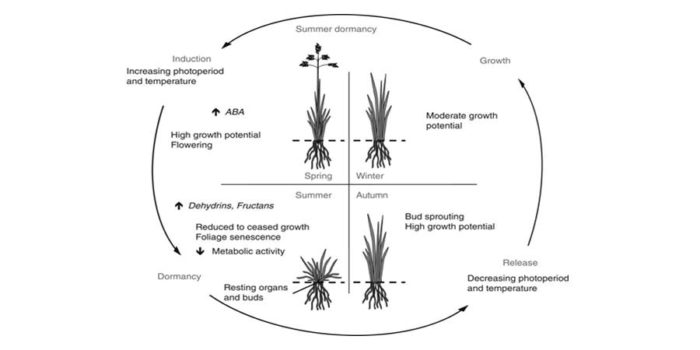
Review: Winter and summer dormancy: similar adaptive strategies?
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchDormancy (growth arrest) is a state by which seeds and plants can survive harsh conditions. Seasonal dormancy is a strategy to survive seasonally unfavorable conditions. Plants can display winter and summer dormancy. Although woody species are the main study systems for winter dormancy, herbaceous species…

