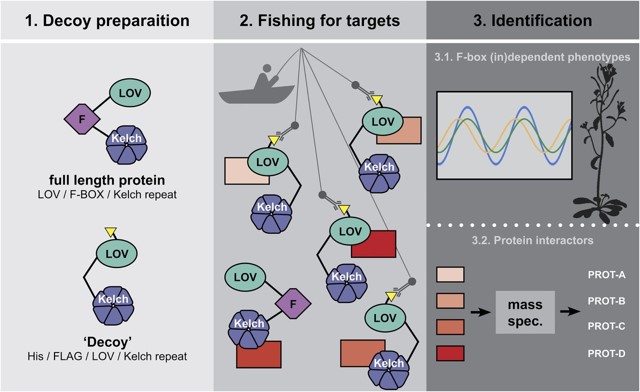
Save Time and Fish for the Clock
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsPlants live by the clock. It helps them to predict day and night as well as upcoming seasons, and to decide when it’s time for reproduction. These predictions depend on oscillating processes that involve gene transcription and protein stability, cycling in a period of, for example, 24 h. Environmental…
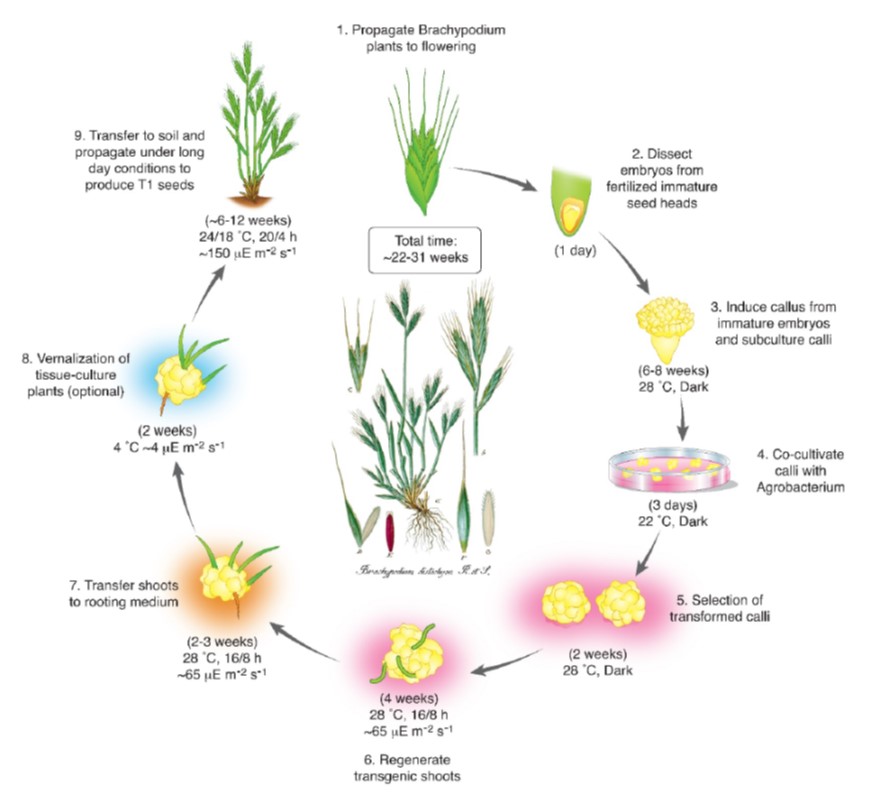
Review. Brachypodium: A monocot grass model system for plant biology (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBrachypodium distachyon is an annual C3 grass that has become an important model species. Scholthof et al. review the genetic tools and resources (sequences and mutants) as well as robust protocols for transformation that have been developed for it. The presence of wild and perennial species within the…

Review. Genetically encoded biosensors in plants: Pathways to discovery (Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenetically-encoded biosensors are produced from genes, and provide a specific readout (usually fluorescence or luminescence) of the amount and distribution of a compund of interest (the analyte). We’ve all see data obtained from genetically encoded biosensors, such as the widely-used cameleon family…
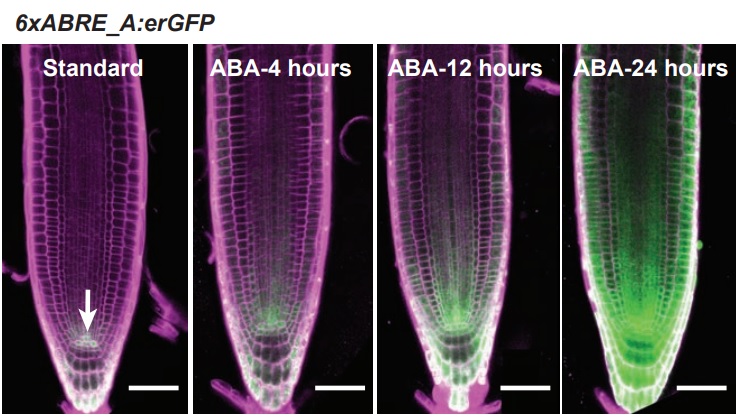
The 6xABRE synthetic promoter enables the spatiotemporal analysis of ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbscisic acid (ABA) is known as stress hormone. Apart from its role in plant growth and development, it is widely studied due to its involvement in biotic and abiotic stresses. Although it had been studied for such a long time, a sensitive spatiotemporal marker for ABA is still elusive. Wu et al. developed…
Live-Cell Imaging of Mobile RNAs in Plants
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsOne of the most exciting findings in the past few decades is the discovery that individual mRNAs and noncoding RNAs can act as long-distance signaling messengers traveling cell to cell to distant sites in the plant. Numerous examples unveiled the involvement of endogenous RNAs as non-cell-autonomous…
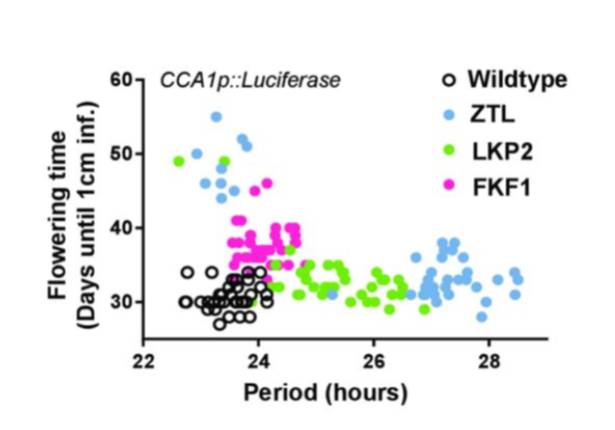
New Insights into the Molecular Biology of Plant Circadian Rhythms
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe circadian clock is an endogenous timekeeper that synchronizes essential biological processes with the outside world. Eukaryotic clocks rely on the ubiquitin proteasome system to target core clock factors for degradation. Altering clock protein degradation can change the period length of the clock.…

RecQ Proteins: Masters of Genome Surveillance
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWiedemann et al. show that RecQ6 in Physcomitrella enhances homologous recombination and gene targeting https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00632.
Background: All living cells have mechanisms to protect their DNA against breaks during duplication and against damage by UV-light or chemicals. RecQ helicases…
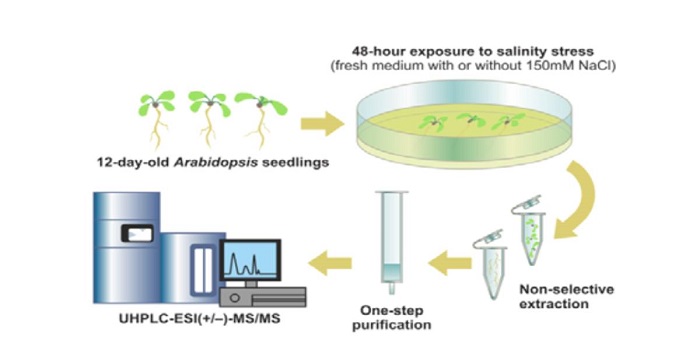
Multiple Phytohormone Screening Method
Plant Physiology: On The InsidePhytohormones are naturally occurring signaling molecules that play key roles in the regulation of plant physiology, development, and adaptation to environmental stimuli. Generally, their concentrations in plant tissues are extremely low (fmol-pmol/g fresh weight, FW). Although certain phytohormones…
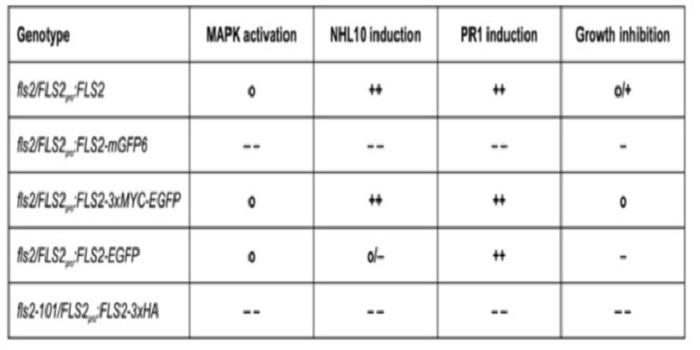
Variable effects of C-terminal fusions on FLS2 function – not all epitope tags are created equal (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA protein’s function and localization are often studied by fusing to it a small “tag” to enhance visualization (through the tag’s fluorescence or antibodies that recognize the tag). These tags are often assumed to have little effect on the protein of interest, but as Hurst et al. show using several…

