
Leaf angle control across the sorghum canopy (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn a rosette-forming plant like Arabidopsis, leaf radial angle is optimized to prevent self-shielding. By contrast, in a plant such as sorghum, leaf vertical angle affects self-shading. A “smart canopy” model has been proposed in which upper leaves have a more upright orientation to allow more light…
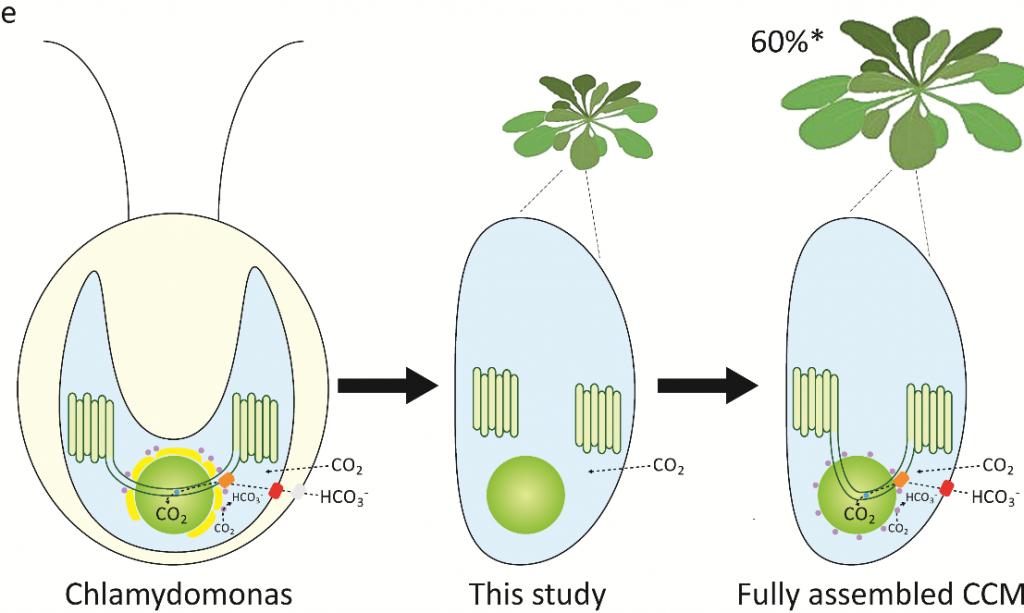
Condensation of Rubisco into a proto-pyrenoid in higher plant chloroplasts (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Rubisco is a major enzyme in assimilating CO2 during photosynthesis. The efficiency of CO2 assimilation is compromised by a low ratio of CO2/O2, especially in C3 plants like rice, wheat and soybean. Algae sequester Rubisco as a condensate in a microcompartment called a pyrenoid within the chloroplast…

How circadian changes in metabolism affect hybrid vigor
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhi Li, Andan Zhu, et al. compare inbred and hybrid lines to explore how daily changes in metabolic pathways affect hybrid vigor. The Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00320
Background: Heterosis or hybrid vigor refers to the superior growth or fitness in the hybrid progeny compared to one…

The structure of a triple complex of plant photosystem I with ferredoxin and plastocyanin (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosystem I (PSI) is a membrane-bound protein complex that plays a central role in the conversion of solar energy to chemical energy to drive assimilate production. Photosystem I is an enzyme complex that transfers electrons from plastocyanin (Pc) to ferredoxin (Fd). Here Caspy et al. have characterized…

Gains in Grain Yield: A Pair of Spikelets Makes All the Difference, Even When One is Sterile
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMother Nature has a way of keeping seemingly useless structures around millions of years. Such structures are likely to have a use that is not obvious, although they could also be remnants of the evolutionary past without extant function, or non-functional but harmless byproducts of a different adaptive…
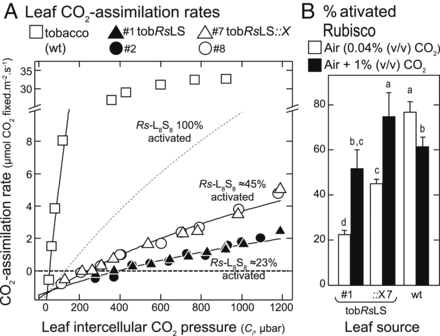
The dependency of red Rubisco on its cognate activase for enhancing plant photosynthesis and growth (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rate of carboxylation by Rubisco versus the rate of the competing oxygenation reaction limits photosynthesis in some conditions, so many researchers are investigating ways to enhance Rubisco. Rubisco is not limited to green plants but can be found in other lineages including red algae and photosynthetic…
Useless no more: infertile spikelets contribute to grain yield in a major food crop and its relatives
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellAuBuchon-Elder and Coneva et al. reveal an important function for apparently non-functional floral structures.
Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.004242
By Taylor AuBuchon-Elder1,*, Viktoriya Coneva1,2*, Doug K. Allen1,3†, and Elizabeth A. Kellogg1†
1Donald Danforth Plant Science…
The photobiology paradox resolved: photoreceptors drive photosynthesis and vice-versa
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchCharlotte Gommers, Assistant Features Editor
[email protected]
For a long time, the study of light fueled two independent fields of plant sciences. On the one hand, light energy is absorbed in the chloroplasts, to drive sugar production via photosynthesis. On the other hand, light is an…

Small subunits can determine enzyme kinetics of tobacco Rubisco expressed in Escherichia coli (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Rubisco is the enzyme responsible for the fixation of CO2 to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) during photosynthetic reactions. However, this enzyme has some functional issues, such as a slow catalytic turnover rate and sensitivity to temperature and CO2, and it catalyzes a competing oxygenation process…

