
Synthetic biogenesis of chromoplasts from leaf chloroplasts (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChromoplasts are a type of plastid, usually found in fruits and flowers, that can accumulate large amounts of carotenoids including beta-carotene (pro-vitamin A). It has been proposed that increasing chromoplast formation could be a way to enhance human consumption of vitamin A. In a new report, Llorente…
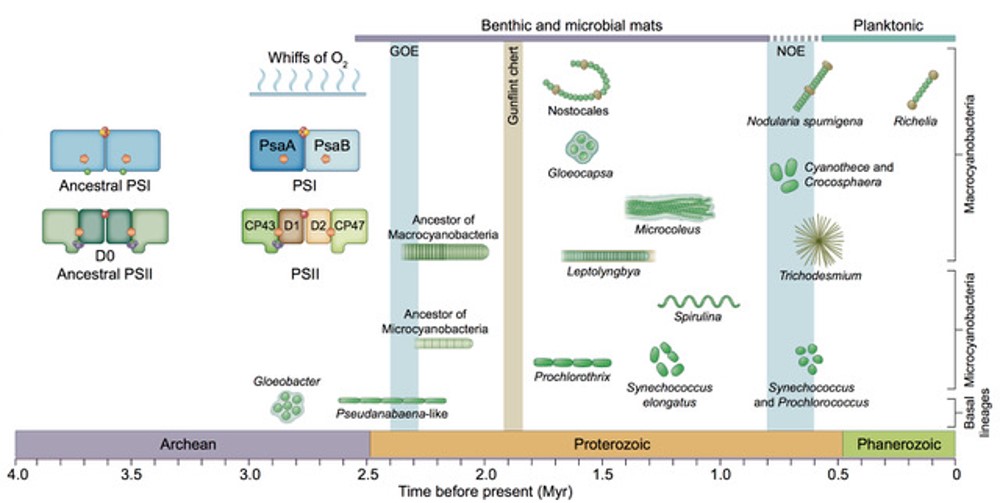
On the origin of oxygenic photosynthesis and cyanobacteria (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis occurs in several ways, only one of which releases oxygen as a product. As oxygen-breathing organisms, we are totally dependent on oxygenic photosynthesis, which is restricted to cyanobacteria and green plant plastids. In this review, Sánchez‐Baracaldo and Cardona examine how recent…
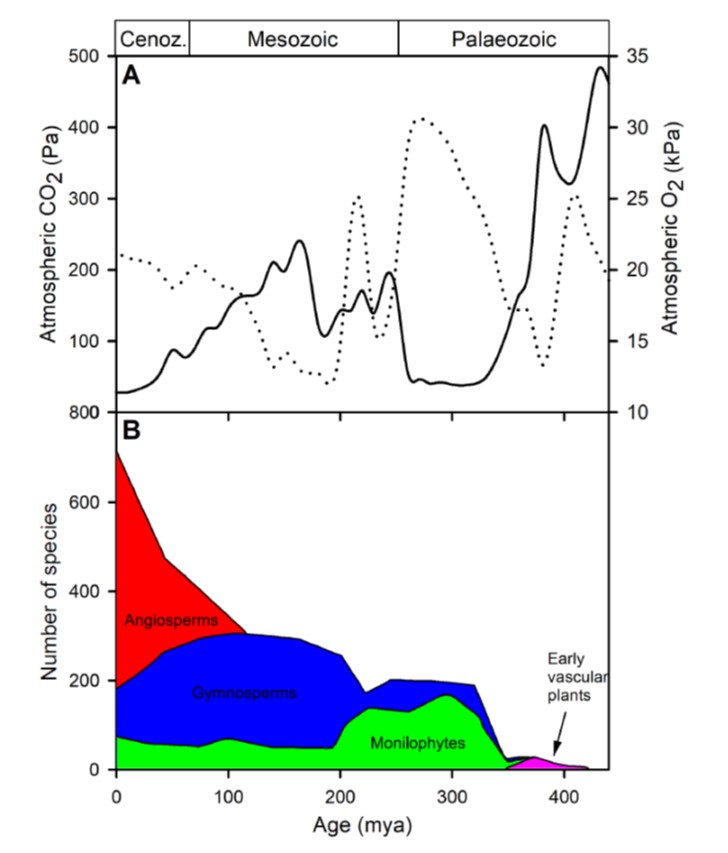
A novel hypothesis for the role of photosynthetic physiology in shaping macroevolutionary patterns (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the 450 million(ish) years since plants acquired the ability to live on land, they have caused dramatic changes in the concentrations of atmospheric CO2 and O2 levels. As an example, due to tremendous increases in photosynthesis, CO2 levels dropped and O2 levels rose dramatically in the late Paleozoic…
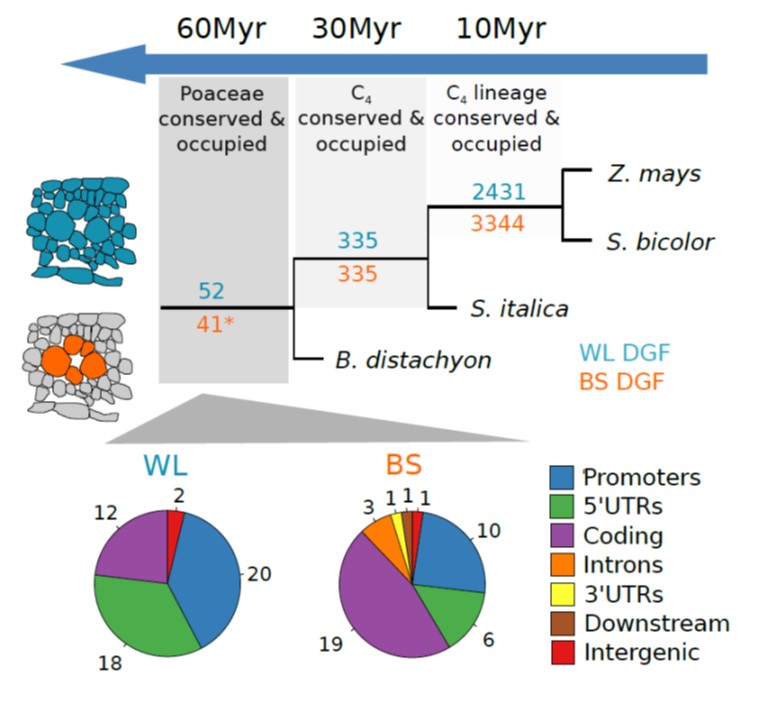
Mapping the landscape of C4 gene regulation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBurgess et al characterize genome-wide patterns of transcription factor binding to provide insight into the architecture associated with C4 photosynthesis gene expression. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00078
By Steven James Burgess (University of Cambridge, UK) and Ivan A. Reyna-Llorens…
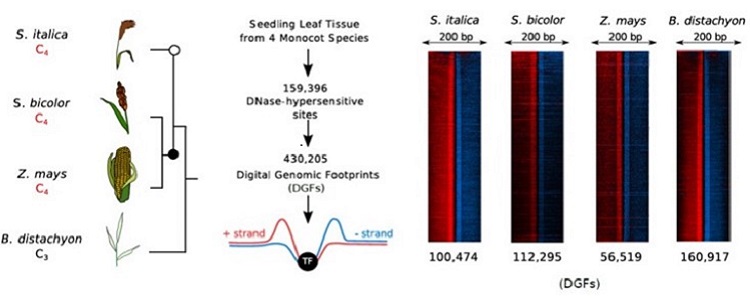
Genome-wide transcription factor binding in leaves from C3 and C4 grasses (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost plants use the C3 photosynthesis pathway, however many have evolved strategies like C4 photosynthesis that accumulate CO2 around RuBisCO. Burgess et al. performed DNAseI-SEQ in three C4 plants: S. bicolor, Z. mays and S. italica, and one C3: B. dystachion, to offer an insight into the cis-element…

A Rubisco-binding protein is required for normal pyrenoid number and starch sheath morphology in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn most eukaryotic algae, carbon fixation takes place in an organelle within an organelle, the pyrenoid inside of the chloroplast. Besides being functionally very important, pyrenoids are interesting because they are what is called a phase-separated structure, that is they are not membrane enclosed;…
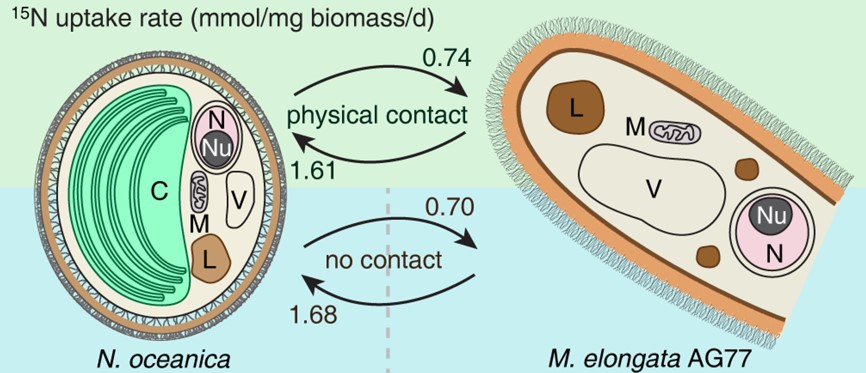
Algal-fungal symbiosis may account for the origin of basal land plant species (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight serves as the source of energy as well as an information signal for photosynthetic plants. During evolution, plants have acquired the ability to monitor environmental light radiation and adjust their developmental patterns to optimally utilize light energy for photosynthesis. However how the early-diverging…
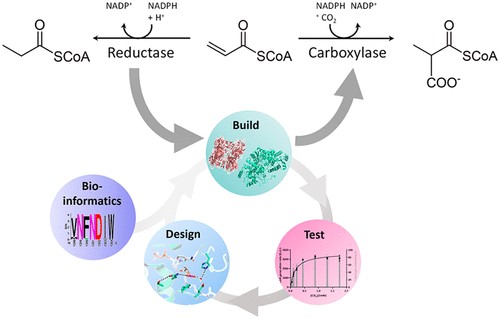
Awaking the sleeping carboxylase ($) (JACS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the things I like most about synthetic biology is the “why not” attitude. This article by Bernhardsgrütter et al. is intriguing because rather than taking the standard “let’s fix Rubisco approach,” the authors started with a non-CO2 fixing enzyme and engineered it towards having carboxylase…
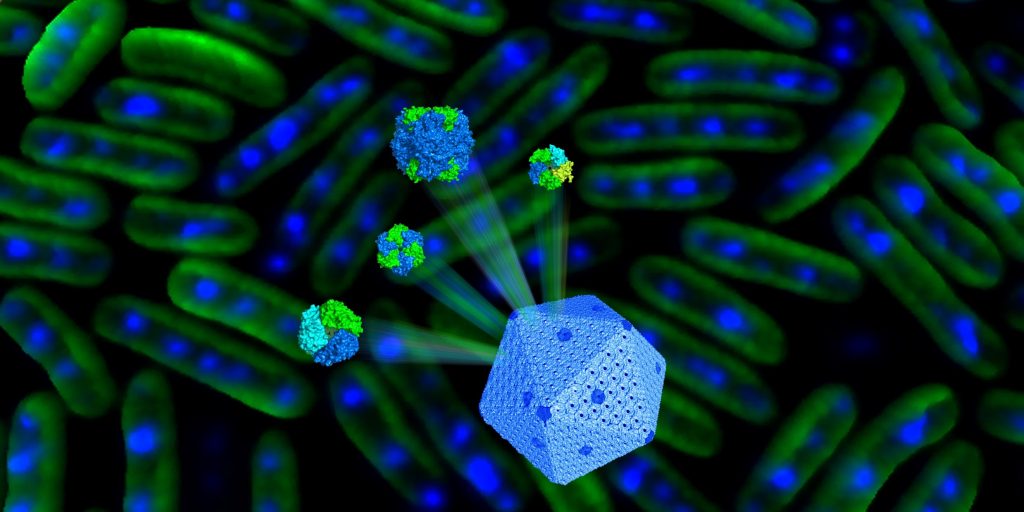
Self-assembling organelles for CO2 fixation: stoichiometry and structural plasticity
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSun et al. investigate how carboxysomes are constructed and regulated in cyanobacteria. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00787
By Luning Liu
Background: All cells are composed of well-defined compartments to encase enzymes and reactions to increase the efficiency of biological processes.…

