
KAI2 regulates seedling development by mediating light-induced remodeling of auxin transport (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed germination is can be described as having two phases depending on light availability, skoto- and photomorphogenesis. Skotomorphogenesis, which occurs while the seed is still buried, is characterized by the elongation of the coleoptile and the inhibition of the root system. When the seed reaches…

NF-YCs mediate plant growth during the dark-to-light transition
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. uncover the roles of NF-YC transcription factors in repressing brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling to mediate photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis.
Background: Seedlings, which germinate in the soil, generally undergo rapid hypocotyl elongation to seek light for growth and development.…

SAURs protein antagonistically regulate a phosphatase activity during apical hook development and cotyledon opening (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Upon germination in dark, plants adopt a strategy known as skotomorphogenesis, or etiolation, to protect the shoot apical meristem and cotyledon from damage while the seedling moves through the soil. The seedlings de-etiolate when they perceive light and the apical hook and cotyledon open. Wang et…

True Blue: How Cry1 Inhibits Phototropism in Green Seedlings
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchKasper van Gelderen
Plant Ecophysiology, Dept. of Biology, Utrecht University, Padualaan 8 3584CH, Utrecht, The Netherlands.
The study of plant movement towards light, also called phototropism, has a venerable history with giants such as Charles Darwin and Frits Went involved in its study, which…

How COR27 and COR28 Promote Hypocotyl Growth: Bind to COP1 And Suppress HY5 Activity
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSeedling growth and development rely on the successful integration of information from external signals, such as light and temperature, and endogenous processes, such as the rhythmic ticking of the circadian clock. Together, these signaling pathways tune hypocotyl elongation to allow seedlings to escape…
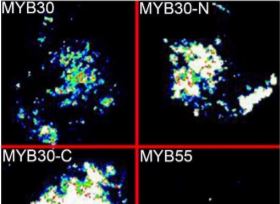
MYB30 Regulates Photomorphogenesis via Interactions with Active Phytochromes and PIFs
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefMYB proteins are a group of transcription factors that are highly conserved in all vertebrates and were first implicated in avian myeloblastosis (leukemia). Subsequently, they were shown to be cellular proto-oncogenes that regulate production of blood cells in animals. MYB proteins contain a DNA-binding…

MYB30 negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by interacting with PIFs and phytochromes in Arabidopsis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotomorphogenesis is the growth and development of plants in response to light. The phytochrome family of photoreceptors absorbs red and far-red light, and in Arabidopsis the most abundant phytochromes are phyA and phyB. PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) repress photomorphogenesis, and under red…
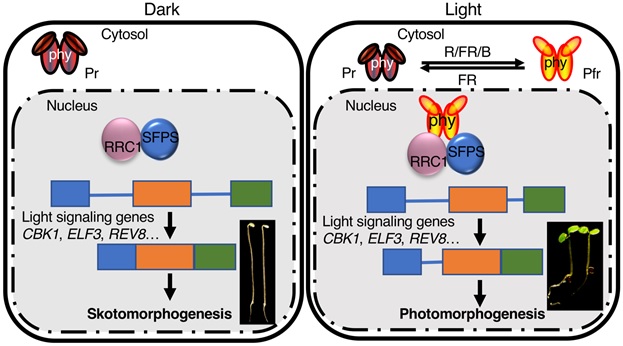
Coordinated regulation of pre-mRNA splicing by the SFPS-RRC1 complex to promote photomorphogenesis ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytochromes are a family of red/far-red light photoreceptors, which positively regulate photomorphogenesis upon red-light perception. Photomorphogenesis is driven by light-induced global transcriptional reprogramming, of which phytochromes are one of the most important regulators. In addition to transcriptional…

A phyB-PIF1-SPA1 kinase regulatory complex promotes photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis (OA) (Nature Communications)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1 (COP1) is one of the best characterized E3 ubiquitin ligases with broad roles as a central repressor of light signaling in plants to cancer biology in mammals. In plants, COP1 interacts with SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA-105 1 family members (SPA1-SPA4) and forms a stable COP1/SPA…

