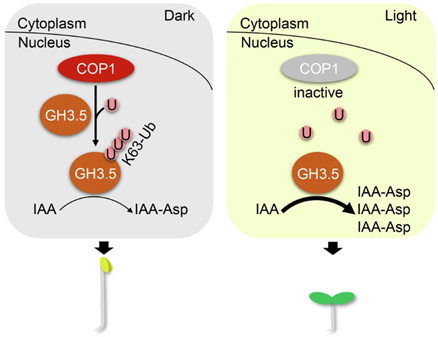
Beyond degradation: COP1 fine-tunes plant growth through non-destructive protein tagging
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the dark (e.g., under soil), hypocotyls elongate, but when exposed to light, they stop elongation. The biosynthesis of the plant hormone auxin is implicated in the elongation of hypocotyls in the dark. In the light, however, auxin action is inhibited, thereby limiting hypocotyl elongation. The E3…
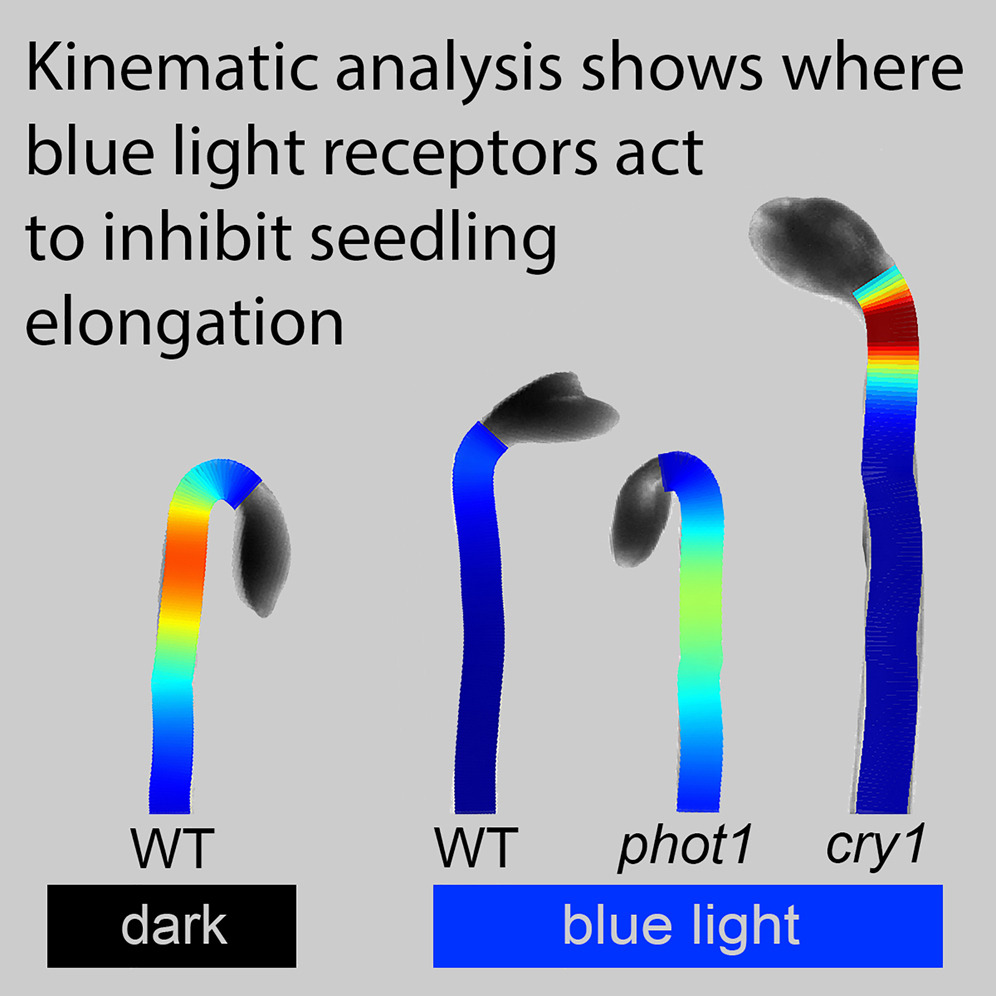
Two blue-light photoreceptors (cry1 and phot1) function differently in hypocotyl light responses
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have several types of light receptors that control various responses to light, such as leaf expansion, time-of-flowering, and hypocotyl elongation. When seeds are germinated in the dark, their hypocotyl elongates rapidly because darkness is perceived as being deep underground; the elongation is…

Plant eyes in the dark: How a blue-light photoreceptor senses and functions without light
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight is both a source of energy for photosynthesis and a key environmental signal that regulates plant growth. Seedlings grown in darkness exhibit elongated hypocotyls and shorter roots, while light promotes shorter hypocotyls and longer roots. Cryptochromes (CRYs), as blue-light receptors, mediate…
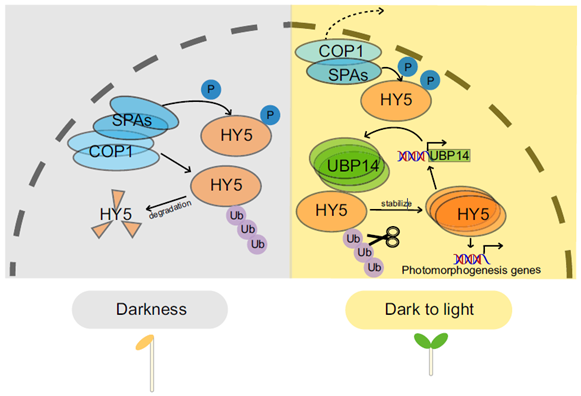
UBIQUITIN-SPECIFIC PROTEASE (UBP14) interacts with HY5 to promote photomorphogenesis under dark-to-light conditions
Plant Science Research WeeklyELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 (HY5) is a transcription factor that regulates about one-third of Arabidopsis genes, affecting growth and development of seedlings through light and hormone signaling. UBIQUITIN-SPECIFIC PROTEASE (UBP14) is a deubiquitinating enzyme that removes ubiquitin from substrate proteins.…
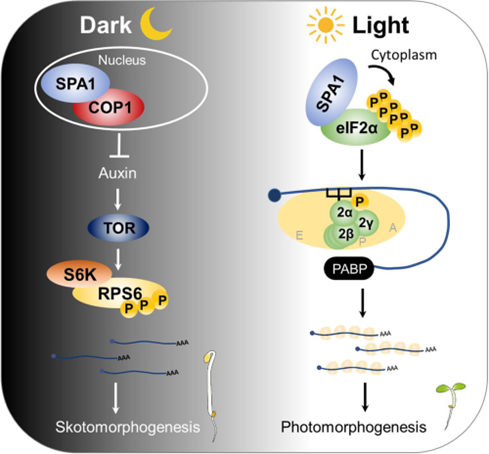
Flip the light switch for protein production
Plant Science Research WeeklyProtein synthesis, modification, and degradation are not only crucial for responding to environmental change, but they also represent significant energy costs for a plant. Energy homeostasis is highly affected by the presence of light. In young seedlings, light enhances translation during the dark-to-light…
SnRK1 and TOR—in a different light
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSaile et al. explore the role of SnRK1 and TOR in light-dependent seedling development and splicing.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad168
Jennifer Saile and Andreas Wachter
Institute for Molecular Physiology (imP), University of Mainz
Background: Plants adjust their development to light…
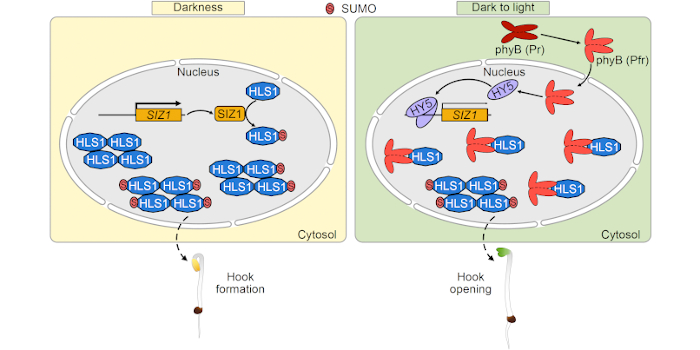
Inhibition of SIZ1-mediated HLS1 SUMOylation promotes light-induced apical hook opening
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellXiong and Yang et al. explore how plants regulate rapid opening of the apical hook in the light.
By Jiawei Xiong and Dawei Zhang, Ministry of Education Key Laboratory for Bio-Resource and Eco-Environment, College of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Hydraulics and Mountain River Engineering, Sichuan…
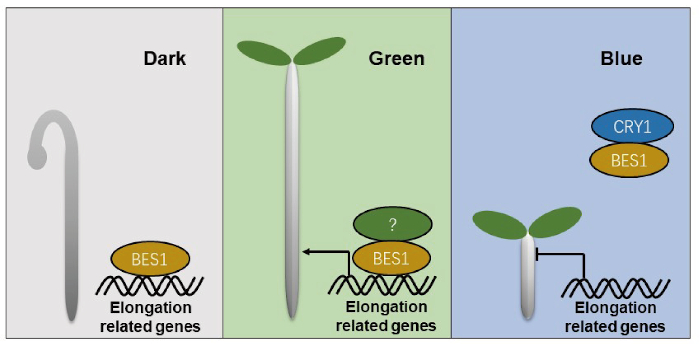
Green means go: Green light and hypocotyl elongation
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHao et al. explore the role of green light in plant growth and development.
By Yuhan Hao, Hongtao Liu
National Key Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 200031 Shanghai,…

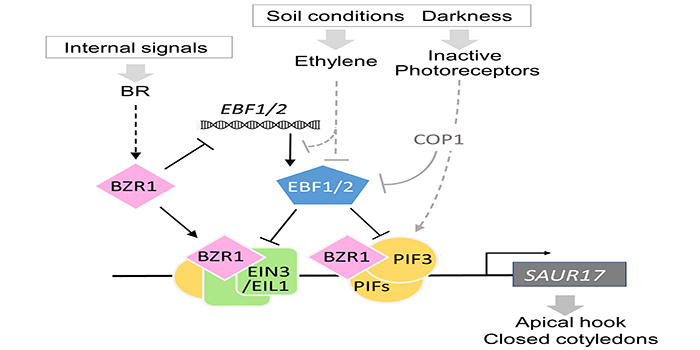
How do brassinosteroids promote etiolation of apical organs in Arabidopsis?
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. explore how plants maintain apical etiolation.
By Jiajun Wang (Southwest University, China), Haodong Chen (Tsinghua University, China), Xing Wang Deng (Peking University, China), Ning Wei (Southwest University, China)
Background: Seeds germinate underneath the soil; to help the shoot…

