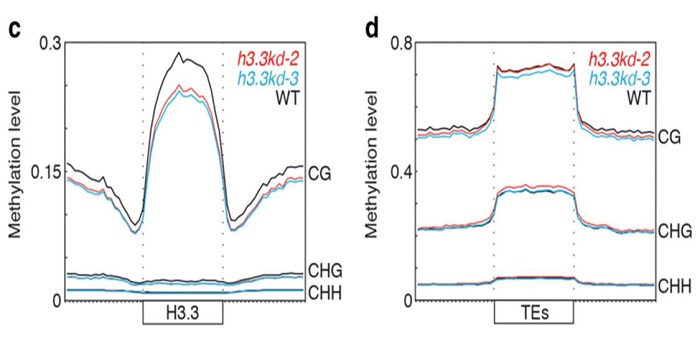
The histone H3 variant H3.3 regulates gene body DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe histone H3 variant H3.3 is distinguished by its expression throughout the cell cycle, while H3.1 is expressed predominantly during DNA replication. Genome-wide ChIP studies in plants have shown that H3.3 is associated with actively transcribed genes, and enriched near the transcriptional end sites.…

The chickpea Early Flowering 1 (Efl1) locus is an ortholog of Arabidopsis ELF3 ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogChickpea is a highly cultivated member of the legume family, mostly in India, Australia, Pakistan, Turkey, Burma, Iran, Canada and the US. The detrimental threat for chickpea is the invasion of Ascochyta blight, which is caused by the fungal pathogen Ascochyta rabiei (formerly known as Phoma rabiei). The…
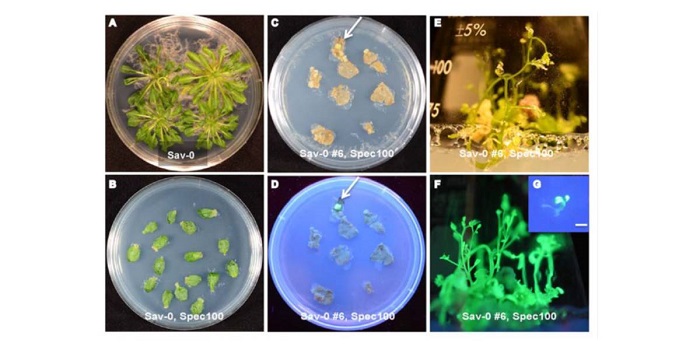
Efficient Plastid Transformation in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
The plastid genome of higher plants encodes about 100 genes, the products of which assemble with approximately 3,000 nucleus-encoded proteins to form the plastid transcription and translation machinery and carry out complex metabolic functions, including photosynthesis and fatty acid and amino acid biosynthesis.…
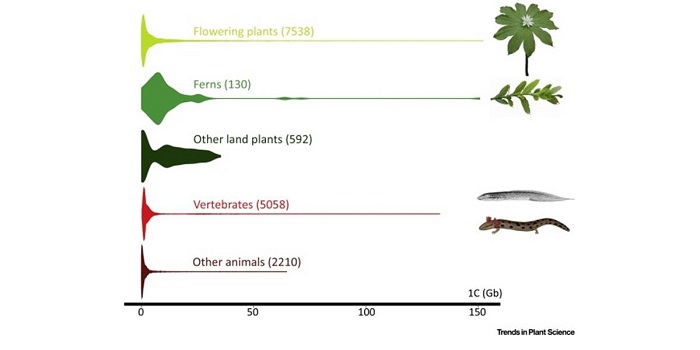
Opinion: Is there an upper limit to genome size? ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThere are only ten organisms known to have genomes larger than 100 Gb in size and six of those are plants. Both Numbers 1 and 2 on the list are plants with genomes that are nearly 50x the size of the human genome (which is 3 Gb), and over 1000x that of Arabidopsis: the 148.8 Gb-genome Paris japonica…
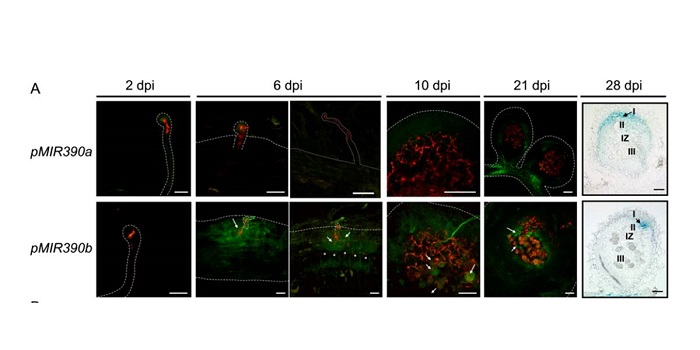
A MicroRNA Switch that Controls Lateral Root Growth and Nodulation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogLegume roots form two types of organs, lateral roots and symbiotic nodules, which participate, respectively, in the uptake of water and mineral nutrients and in nitrogen fixation. Since both organs have considerable impacts on plant growth, understanding the mechanisms underlying the development of lateral…

A Taste of CRISPR
GPC BlogThis week’s blog was written by Dr Craig Cormick, the Creative Director of ThinkOutsideThe. He is one of Australia’s leading science communicators, with over 30 years’ experience working with agencies such as CSIRO, Questacon and Federal Government Departments.
So what do you think…
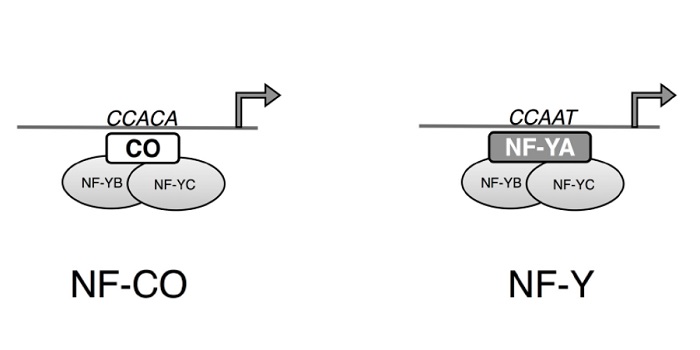
CONSTANS Companion: CO Binds the NF-YB/NF-YC Dimer and Confers Sequence-Specific DNA Binding
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefOne of the central players in the complex regulation of flowering, CONSTANS (CO) functions as a center for integration of the various signals that determine the timing of flowering. As output, CO regulates the expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and other genes (reviewed by Shim et al., 2017). CO contains…
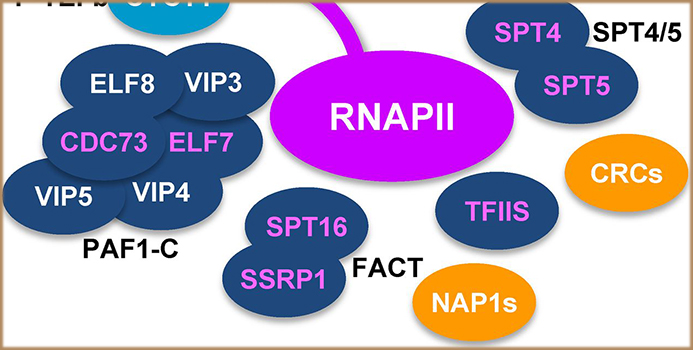
The composition of the Arabidopsis RNA Polymerase II Transcript Elongation Complex reveals the interplay between elongation and mRNA processing factors
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchGene expression is regulated at multiple levels such as genome, transcription, RNA processing and nuclear export, translation, and post-translation. Functional mRNA levels are regulated at transcription stage where RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) controls initiation and elongation of mRNA. In particular,…
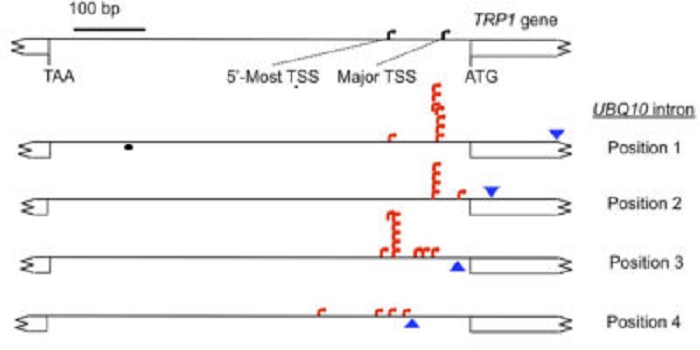
A Surprising Function for Gene Introns
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellGallegos and Rose investigate how introns affect transcript initiation http://www.plantcell.org/content/29/4/843.abstract.
For the information stored in the DNA of genes to be converted into functional protein products, first a molecular copy of the information called messenger RNA is made, using…

