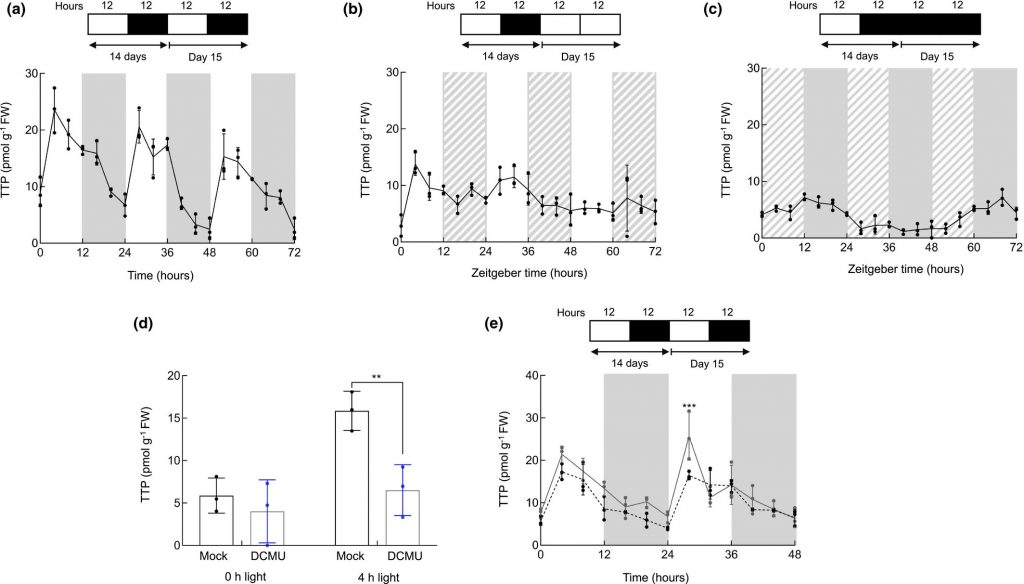
The vitamin B1 family grows: detection and roles of thiamine triphosphate in plants (Plant Direct)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe term “vitamin B1” indicates a family of molecules that includes thiamine, thiamine monophosphate and thiamine diphosphate (TDP). The latter is the most famous family member and plays a pivotal role in carbon metabolism. Thanks to an optimized detection protocol, Hofmann and colleagues have demonstrated…
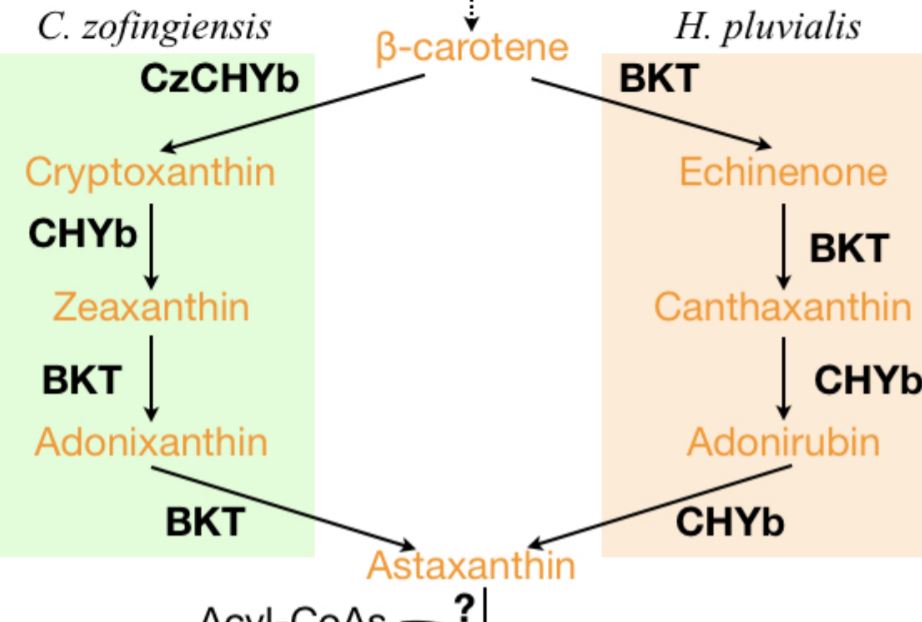
An Alternative Route for Astaxanthin Biosynthesis in Green Algae
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchTianhu Sun
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-2513-1387
Plant Breeding and Genetics Section, School of Integrative Plant Science, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853
[email protected]
Astaxanthin is the reddish carotenoid pigment that gives color to shrimp, salmon, and flamingo. However, these animals…
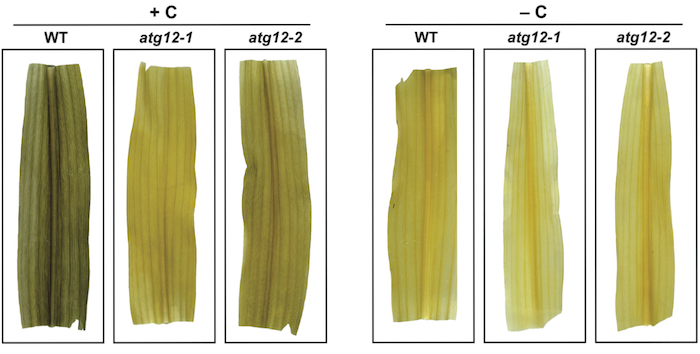
The Multifaceted Roles of Autophagy in Fixed-carbon Starvation
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMcLoughlin et al. uncover the critical roles of autophagy in recycling amino acids and nitrogen-rich nucleotides, adjusting respiratory substrates, and the retention of assimilated nitrogen in maize during fixed-carbon starvation. The Plant Cell (2020) https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00226
Background:…

Secret Talents: STARCH SYNTHASE 5—Not an Enzyme, but Very Active!
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellAbt et al. found that Arabidopsis SS5, a protein homologous to typical starch-synthesizing enzymes, is itself enzymatically inactive, but rather has an important role in the starch granule initiation process. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00946
By Melanie R. Abt and Samuel C. Zeeman, Institute…
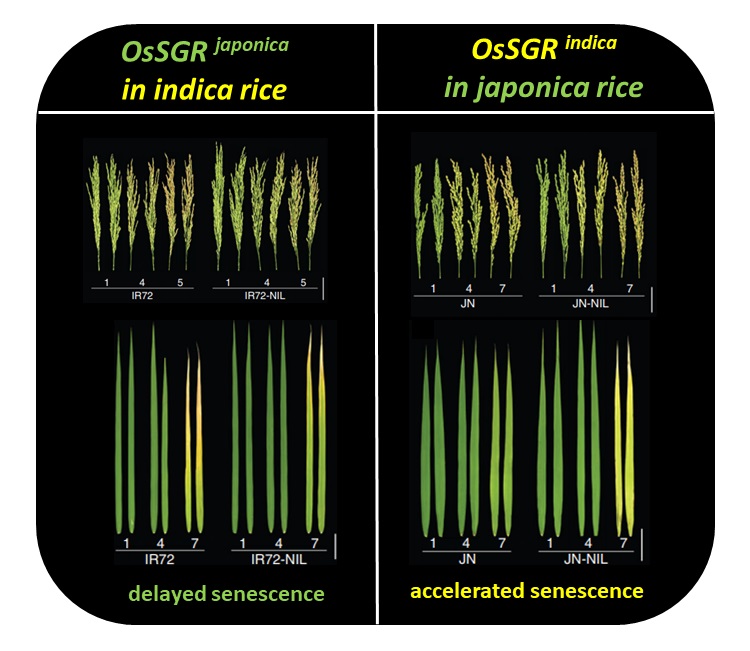
Natural variations at the Stay-Green gene promoter control lifespan and yield in rice cultivars (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrop production is greatly influenced by the duration of the last stage of plant life cycle, senescence, through degradation of resources in leaves and remobilization of nutrients to developing seeds. Indeed, higher grain yield of important cereals such as maize and sorghum can be achieved by using stay-green…
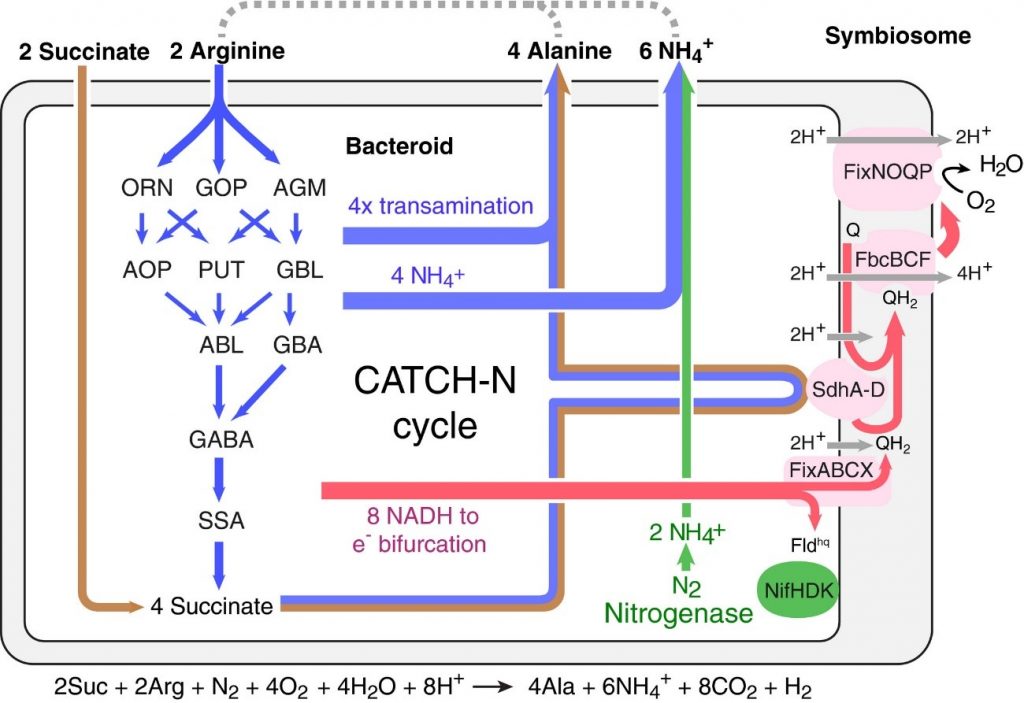
Co‐catabolism of arginine and succinate drives symbiotic nitrogen fixation (Mol Sys Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiotic nitrogen fixation is a mutualistic relationship between plants and microbes in which plants supply fixed carbon to bacteria in exchange for nitrogen. During this process, the microbes use nitrogenase enzyme to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a plant-usable form, but the metabolic interaction…
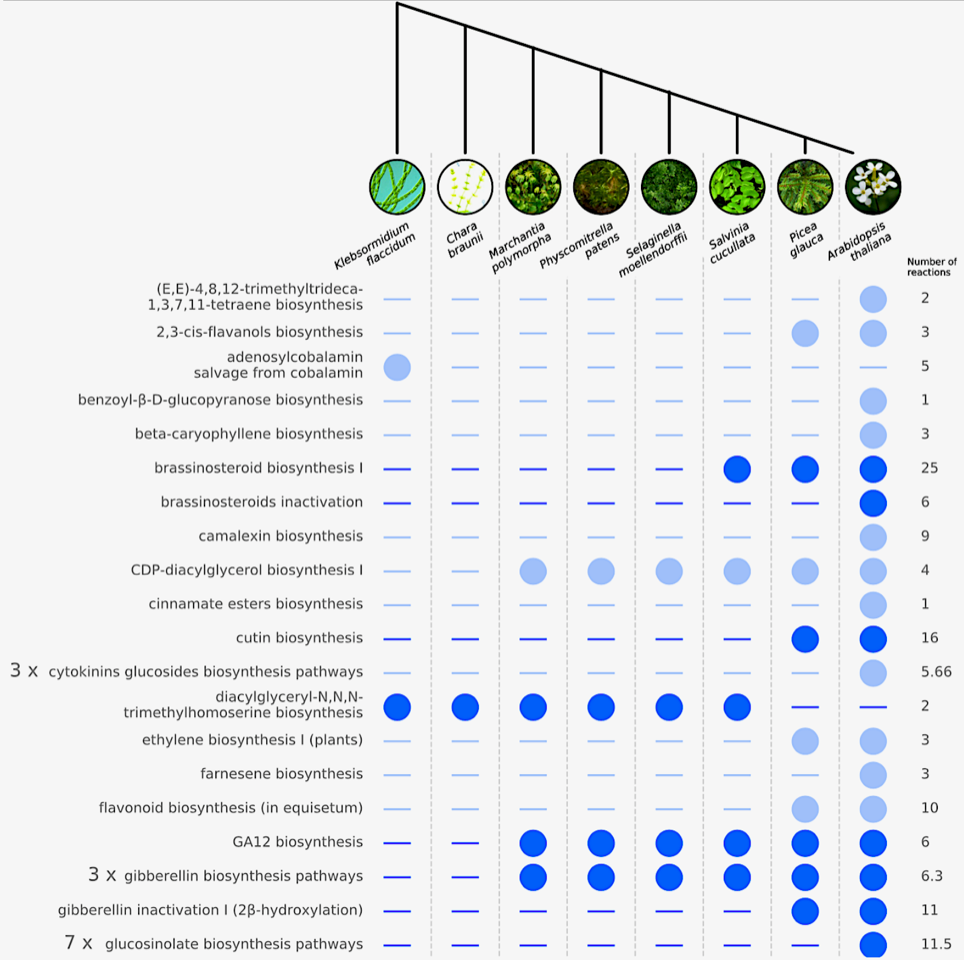
Multiple metabolic innovations and losses are associated with major transitions in land plant evolution (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe colonization of land by a single streptophyte algae lineage around 450 million years ago culminated in the evolution and radiation of all terrestrial flora, the embryophytes. Adapting and thriving in the land environment required many morphological and physiological innovations, as well as the acquisition…
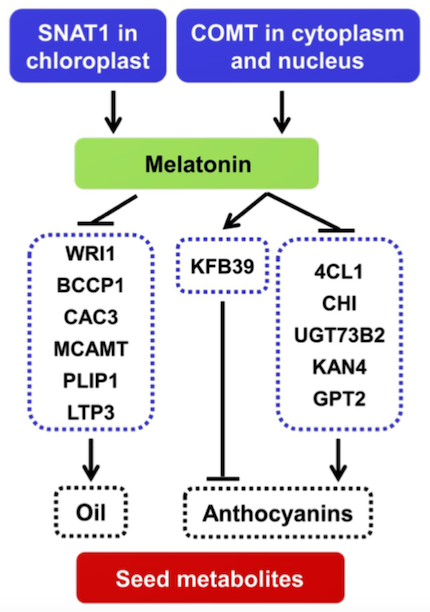
Melatonin represses oil and anthocyanin accumulation in seeds (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed oils and anthocyanins play several roles in plant physiology and are promising substances for crop engineering given their benefits for human health. Recent studies proposed that melatonin –a potent antioxidant present in all plant species– regulates the deposition of these metabolites in seeds,…
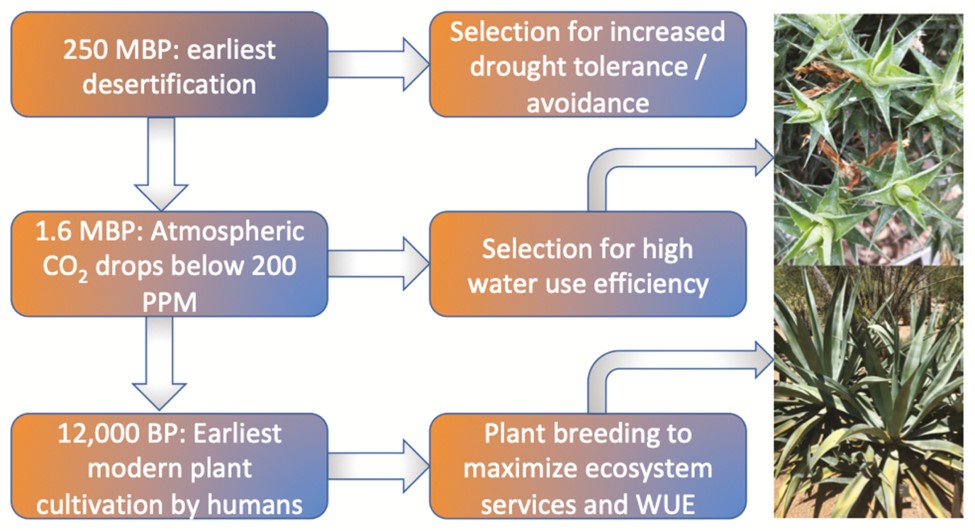
Special Issue: New perspectives on crassulacean acid metabolism biology
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) is a water-conserving strategy in which stomata open at night and carbon is stored until daytime photosynthesis provides the energy to fix it. This special issue of the Journal of Experimental Botany, edited by Hultine, Cushman, and Williams, brings together a set of…

