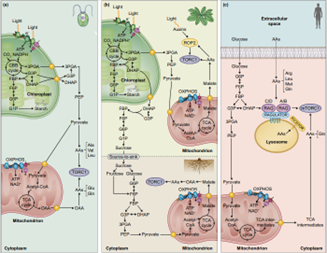
Tansley Insight: Analyzing the impact of autotrophic and heterotrophic metabolism on the nutrient regulation of TOR (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA protein kinase, target of rapamycin (TOR), controls cell growth and metabolism in all eukaryotes. The role of TOR in regulating synthesis and breakdown of organic compounds in response to nutrients, hormones and cellular energy to promote growth and development is universal in autotrophs and heterotrophs.…
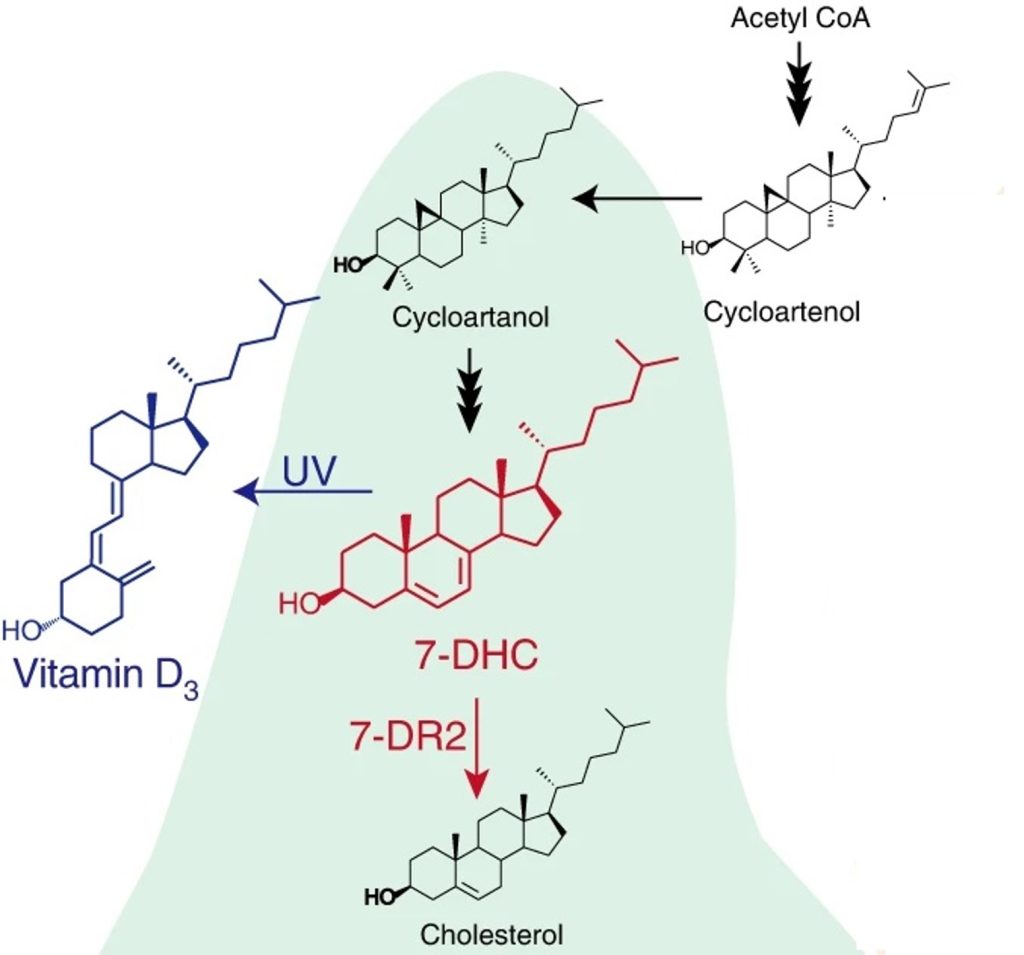
Biofortified tomatoes provide a new route to vitamin D sufficiency (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyVitamin D deficiency in humans is correlated with malfunction of the immune system and inflammation together with cancer, Parkinson disease, depression, neurocognitive decline, dementia, and severe COVID-19 infection. In humans, exposure of the skin to UV light promotes the production of Vitamin D from…
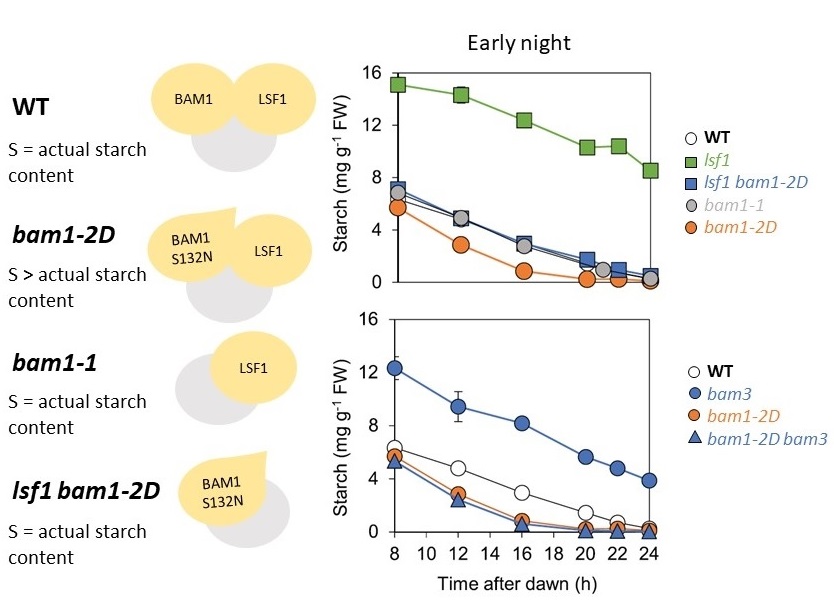
A dominant mutation in β-AMYLASE1 disrupts nighttime control of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants use starch in leaf chloroplasts to fuel their growth and metabolism during the night. In Arabidopsis, nighttime starch degradation is tightly regulated; the degradation rate is linear and adjusts to both the availability of starch and length of night, so that most but not all the starch is used…
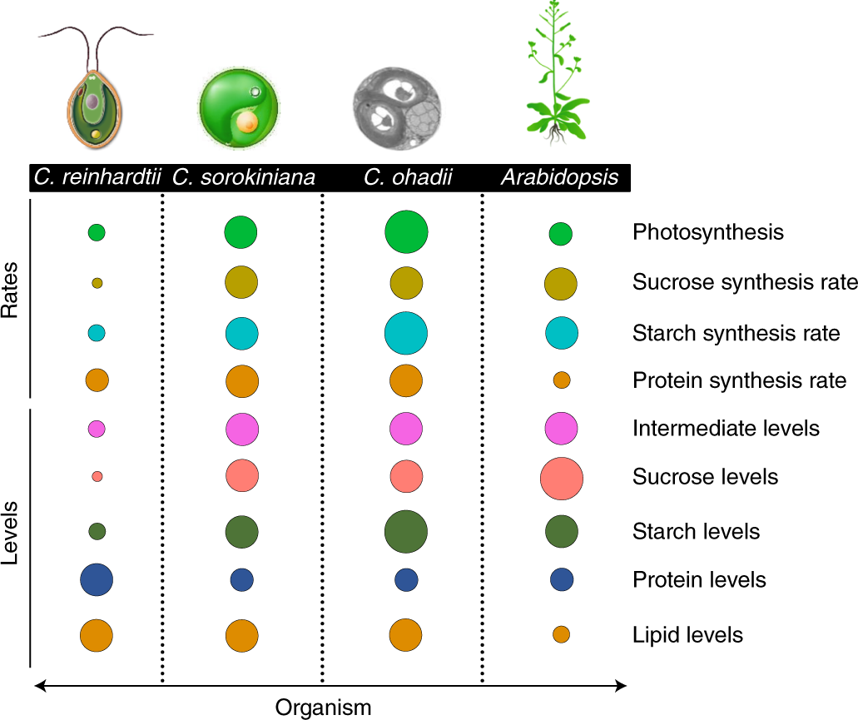
Carbon flux through photosynthesis and central carbon metabolism show distinct patterns between algae, C3, and C4 plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is an attractive target for improving crop yields, and tailoring downstream photosynthesis-associated metabolism is a relatively unexplored path for achieving this. Chlorella ohadii is the fastest growing photosynthetic organism identified, has high photosynthetic rates, and can survive…
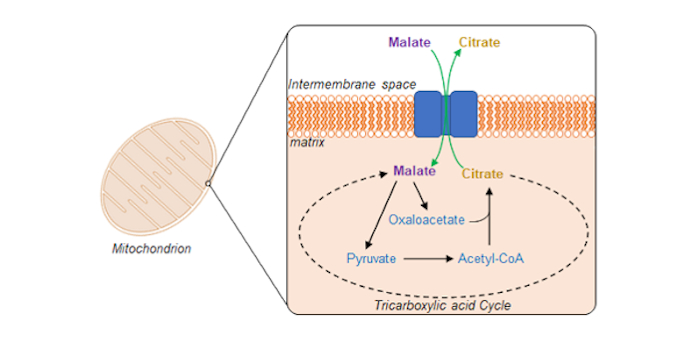
Swapping citrate for malate by plant mitochondria
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLee et al. unravel a mitochondrial transporter responsible for selectively exporting citrate in exchange for malate. Plant Cell (2021)
By Chun Pong Leea, Marlene Elsässerb, Philippe Fuchsb,c, Ricarda Fenskea, Markus Schwarzländerb, A. Harvey Millara
aARC Centre of Excellence in Plant Energy Biology,…

Redox regulation of NADP-malate dehydrogenase is vital under fluctuating light environment (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRedox switches regulate photosynthetic reactions and are mediated by conserved cysteine pairs, activated by reduction under light and deactivated by oxidation in the dark. Those reactions are mediated by thioredoxins (Trx). Usually, only plastidic and not cytosolic isozymes show these redox switches.…

How circadian changes in metabolism affect hybrid vigor
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhi Li, Andan Zhu, et al. compare inbred and hybrid lines to explore how daily changes in metabolic pathways affect hybrid vigor. The Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00320
Background: Heterosis or hybrid vigor refers to the superior growth or fitness in the hybrid progeny compared to one…

Unexpected Role of a TCP Transcription Factor in Seed Oil Biosynthesis
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchTianhu Sun
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-2513-1387
Plant Breeding and Genetics Section, School of Integrative Plant Science, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853
[email protected]
Plant seed oils (such as canola oil, sunflower oil, and soybean oil) are important for the human diet and store energy…
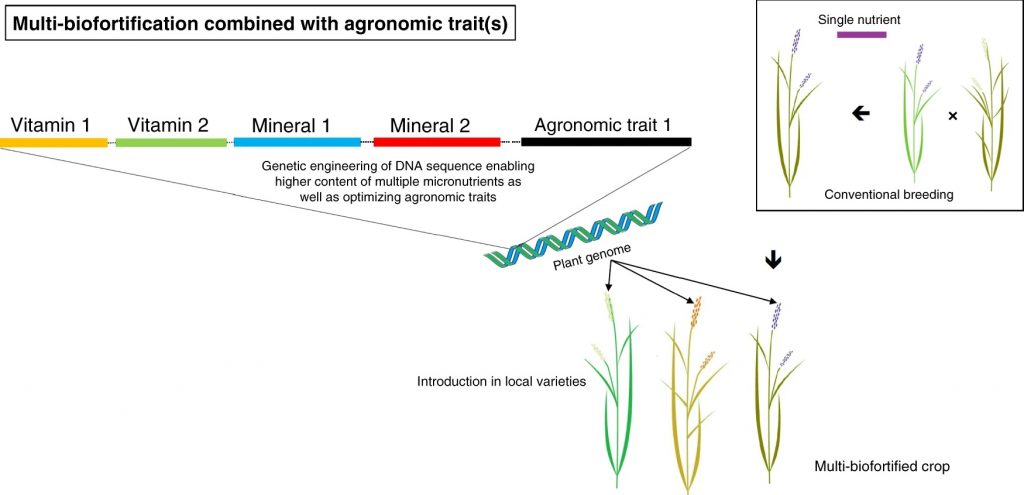
Perspective: Multiplying the efficiency and impact of biofortification through metabolic engineering (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
As heterotrophs, we are what we eat. One of the UN Sustainable Development Goals is to end all forms of hunger, including the “hidden hunger” that results from nutrient deficiencies. Van Der Straeten et al. provide an overview of biofortification strategies. They review current successes from…

