
Commentary: The discovery of nickel hyperaccumulation in the New Caledonian tree Pycnandra acuminata 40 years on: an introduction to a Virtual Issue (OA)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA Commentary by Jaffé et al. introduces a New Phytologist Virtual Issue on the curious and fascinating plants that hyperaccumulate metals. These diverse species have shed light on metal transporter proteins and mechanisms of metal tolerance, on the ecological function of metal hyperaccumulation (possibly…
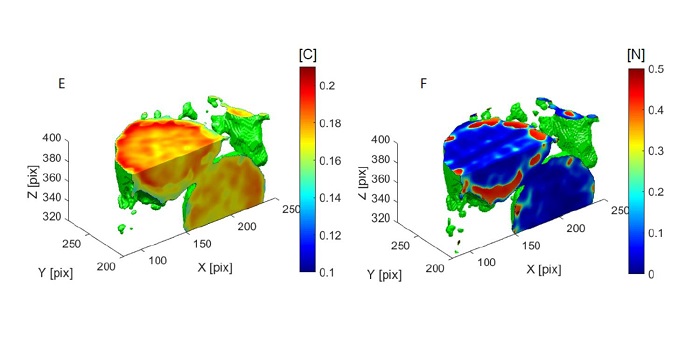
Breakthrough Technology: Soft X-ray imaging of cellular carbon and nitrogen distributions in cyanobacteria (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklySoft X-ray imaging is a promising new technology that can be used to measure elemental compositions of living cells. By adjusting the energy (wavelength) of the incident X-rays, it is possible to specifically measure C or N, which have different photo-absorption edges. Teramoto et al. demonstrate the…

Update: Phytochrome, Carbon Sensing, Metabolism, and Plant Growth Plasticity
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: UpdatesBy Johanna Krahmer, Ashwin Ganpudi, Ammad Abbas, Andrés Romanowski, and Karen J. Halliday
Plants continuously monitor fluctuations in their environment and actively adjust their metabolism to cope with variations in light and carbon resource availability. However, the links between photoreceptor signaling…
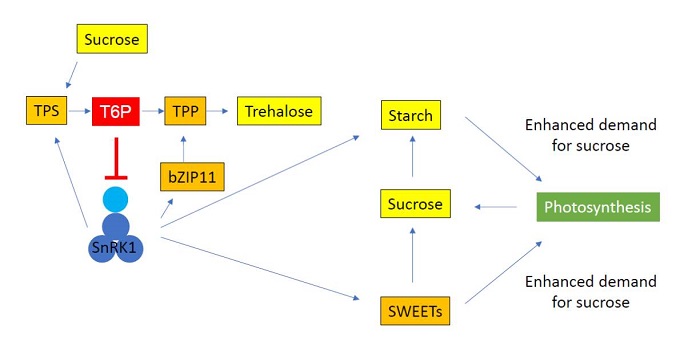
Update: The role of trehalose 6-phosphate in crop yield and resilience
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: UpdatesBy Matthew J. Paul, Asier Gonzalez-Uriarte, Cara A. Griffiths, and Keywan Hassani-Pak
Significant increases in global food security require improving crop yields in favourable and poor conditions alike. However, it is challenging to increase both the crop yield potential and yield resilience simultaneously,…

Darkened leaves use different metabolic strategies for senescence and survival (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPut a plant into full darkness and it will gradually senesce, whereas as individually darkened leaf (IDL) will undergo radid senescence. Law et al. used transcriptomic and metabolomic methods to identify the metabolic responses of plants to these two conditions. In fully darkened plants, metabolism is…

Update: Ethylene exerts species-specific and age-dependent control of photosynthesis
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: UpdatesBy Johan Ceuster and Bram Van de Poel
Abstract
The volatile plant hormone ethylene plays a regulatory role in many developmental processes and in biotic and abiotic stress responses. One of the under-explored actions of ethylene is its regulation of photosynthesis and associated components such…

Sweet route to greater yields
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Editorials, ResearchThree years ago, biotechnologists demonstrated in field trials that they could increase the productivity of maize by introducing a rice gene into the plant that regulated the accumulation of sucrose in kernels and led to more kernels per maize plant.
They knew that the rice gene affected the performance…
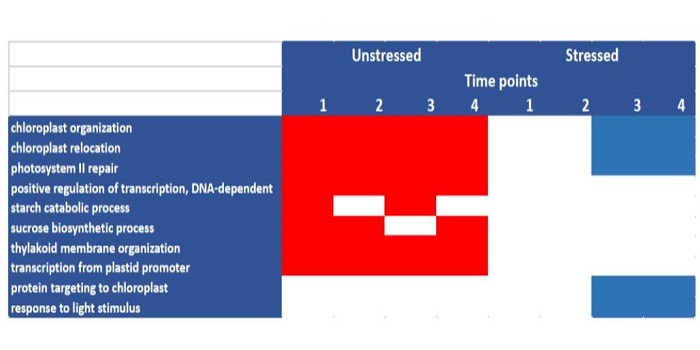
Trehalose-6-Phosphate and Reproductive Resource Allocation in Maize
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideFlowering is a developmental stage that is particularly sensitive to drought; restriction of water at this time can decrease seed set, final seed number, and harvested seed yield. Kernel abortion during drought at flowering can be alleviated by supplying Suc to reproductive tissue. Consequently, Suc…
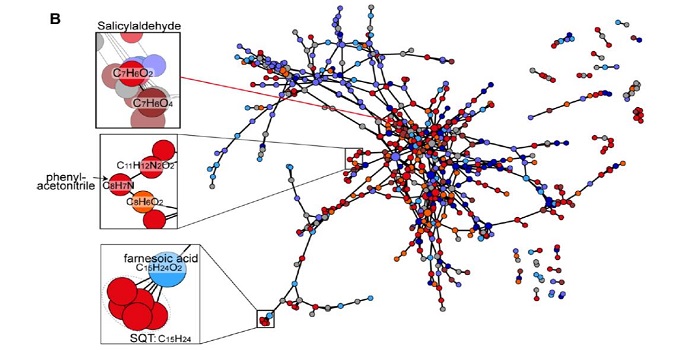
Mycorrhiza-Triggered Networks in Leaves
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideOne effect of mycorrhizal fungi is to stimulate the plant immune system, leading to induced systemic resistance (ISR). Thus, mycorrhizal fungi influence the interactions between plants and aboveground herbivores. The molecular mechanisms underlying these types of beneficial microbe-plant interactions…

