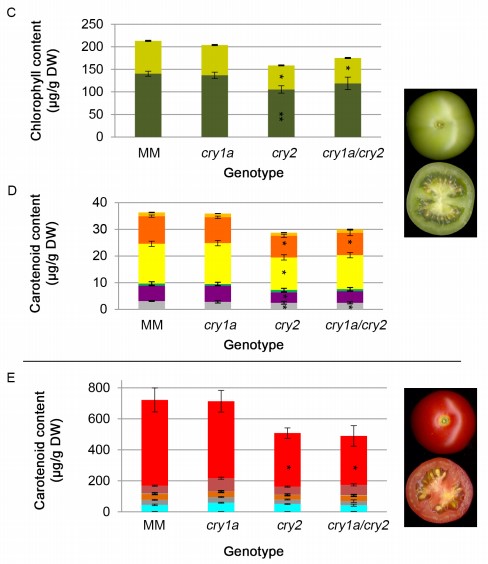
Pivotal roles of cryptochromes 1a and 2 in tomato development and physiology (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCryptochromes are a class of flavoproteins found in plants and animals that are sensitive to blue light. In Arabidopsis, cryptochromes are involved in many important physiological processes including de-etiolation, flowering, circadian rhythms, cotyledon opening and expansion, anthocyanin accumulation,…
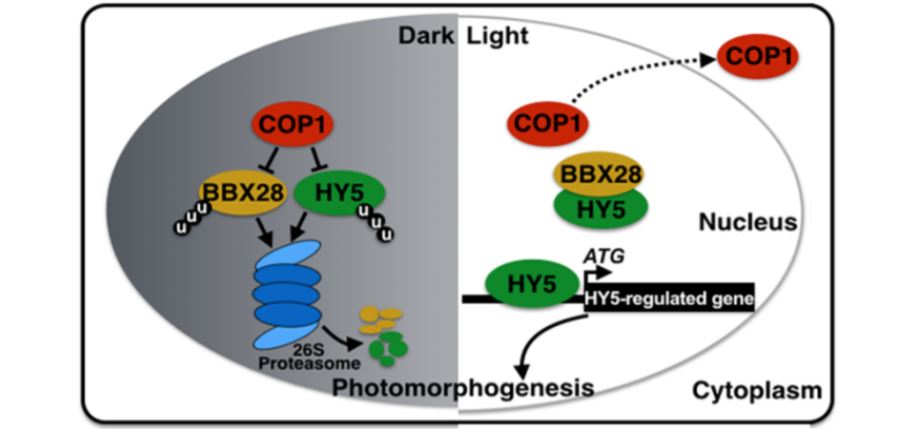
BBX28 Negatively Regulates Photomorphogenesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLin et al. show that B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN28 plays a role in regulating plant development in response to light signals. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00226.
By Dongqing Xu and Xing Wang Deng
Background: Sunlight is one of the key environmental cues influencing plant growth and development.…
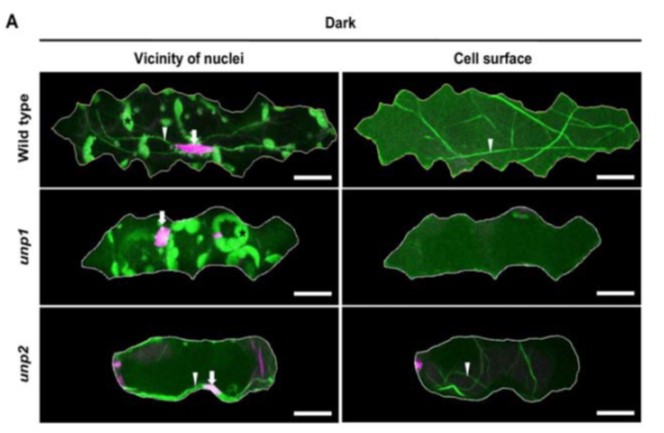
Dark-Induced Nuclear Positioning in Leaf Cells
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe appropriate spatial arrangement of nuclei is essential for various cellular activities during cell division, growth, migration, and differentiation in eukaryotes. In plants, nuclear positioning is also required for proper responses to environmental stimuli, including pathogen infection, touch, temperature,…
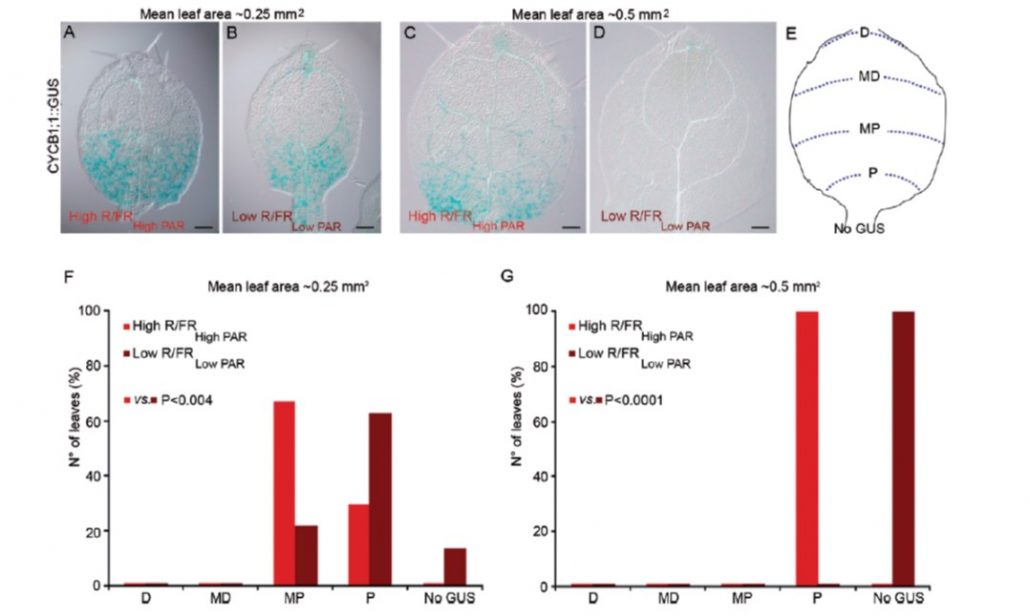
Leaf development in canopy shade (J. Exp. Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyVegetative shade affects the ratio of red (R) and far-red (FR) light; relative to sunlight, the R/FR ratio is decreased due to absorbance of photosynthetically-active R light by other leaves. Low R/FR ratios cause increased elongation of shaded plant stems and petioles, as the plants strive to raise…

Integrated regulation of apical hook development by EIN3/EIL1 and PIFs ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe apical hook helps to protect the fragile cotyledons and shoot apical meristem while pushing through the soil, and hook angle determines the success of emergence from soil. Multiple hormones and light signals have contrasting roles in the regulation of hook formation; e.g., auxin, ethylene and gibberellic…
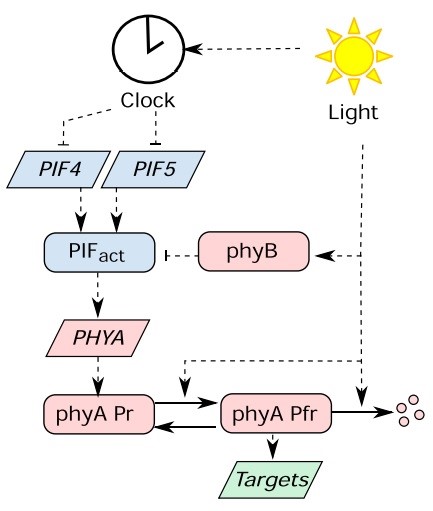
Dawn and photoperiod sensing by phytochrome A ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants perceive the change of seasons based on measuring the duration of daylight. Flowering is a major seasonal response that depends on photoperiod. In this study, Seaton et al. looked at the role of phytochrome A (phyA) in photoperiod sensing. PHYA is the direct target of PIF4 and PIF5 transcription…
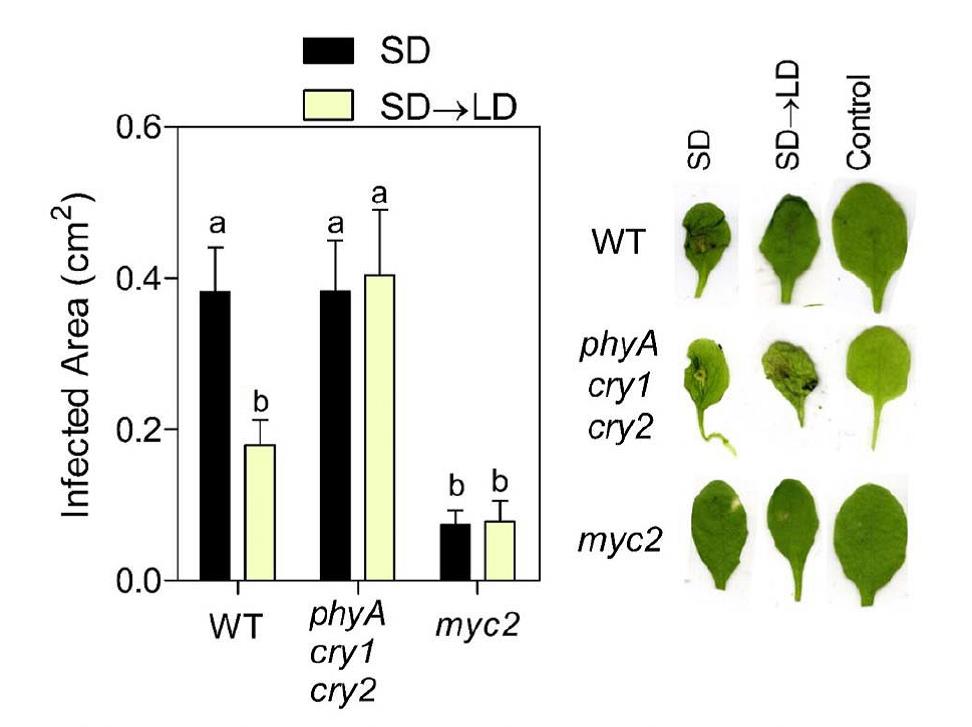
Suns out, guns out: Plant defense responses are enhanced under long-day photoperiods ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs sessile organisms, plants must constantly sense and respond to a dynamic range of stimuli in their environment, which includes both the duration of light (photoperiod) and the presence of microbial invaders. In a recent article published in Plant Physiology, Cagnola et al. (2018) investigate how plant…
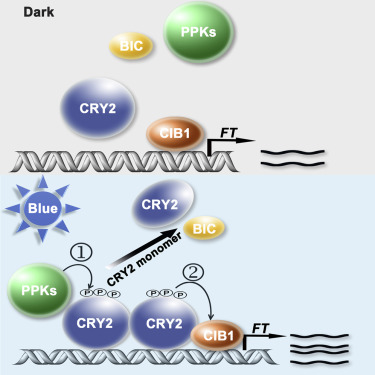
Reconstituting Arabidopsis CRY2 signaling pathway in mammalian cells reveals regulation of transcription by direct binding of CRY2 to DNA (Cell Rep)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCryptochromes (CRYs) are blue-light receptors that were first identified in plants more than 20 years ago, but with modes of action that have remained obscure. Yang, Mo, and Yu, et al. reassembled this blue-light signaling module in mammalian cells in order to better understand CRY function. Previously,…
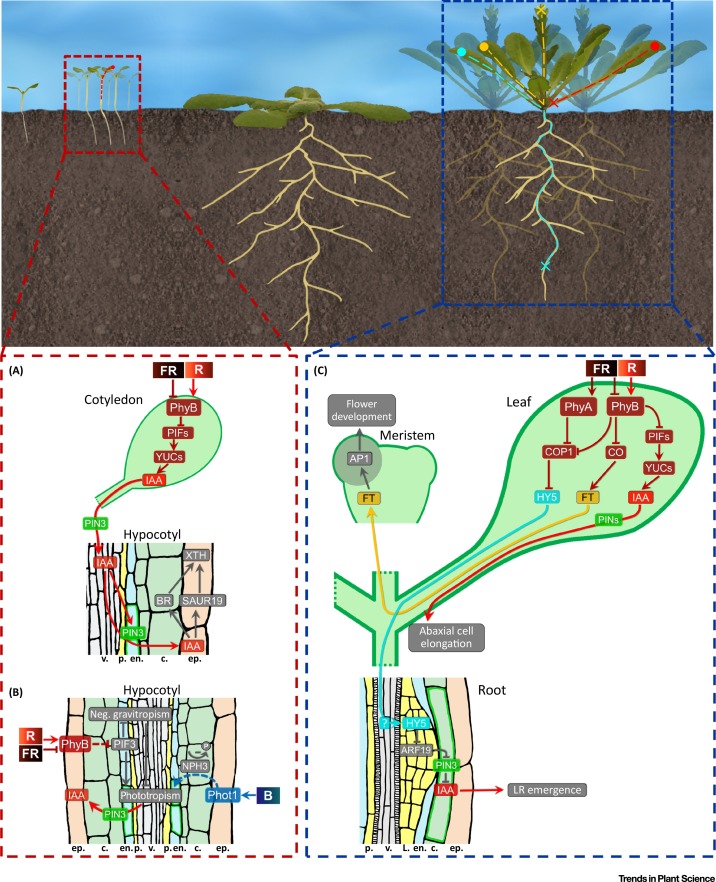
Opinion. Location matters: Canopy light responses over spatial scales ($) (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight is arguably one of the most important signals recognized by plants. Not surprisingly, plants exhibit a wide range of light responses, ranging from cell-specific to large-scale. Küpers et al. review these responses, with an emphasis on their spatial scales. For example, the production of extrafloral…

