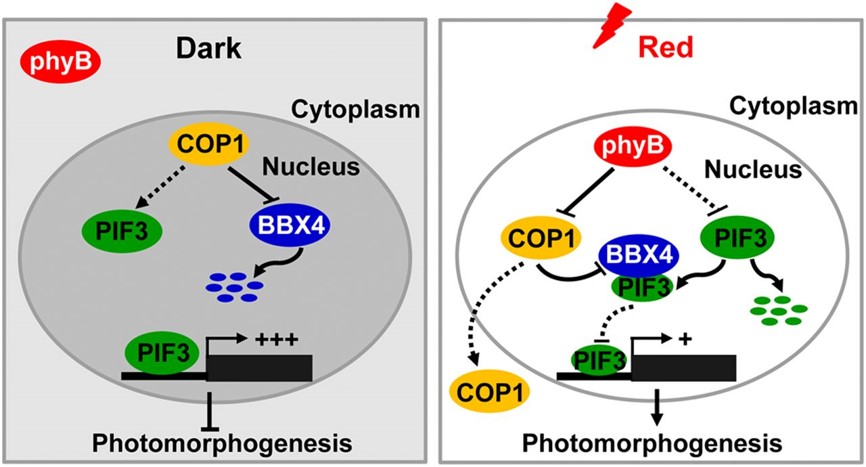
A new B-BOX containing protein regulates red light photomorphogenesis ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs the primary red light photoreceptor in Arabidopsis, phyB affects various developmental processes, such as seed germination, shade avoidance, etc. PIF3 is a key repressor of phyB-mediated photomorphogenesis that is degraded in red light. Recently Heng et al. identified a positive regulator of red light…
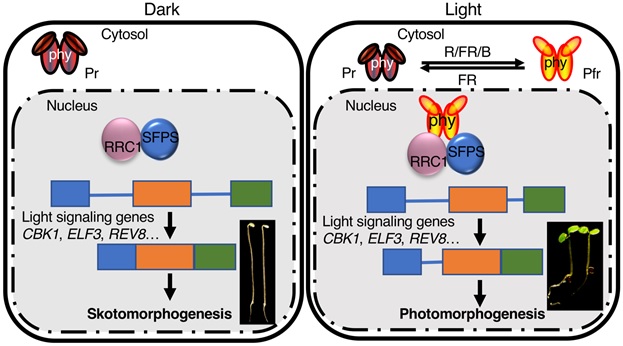
Coordinated regulation of pre-mRNA splicing by the SFPS-RRC1 complex to promote photomorphogenesis ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytochromes are a family of red/far-red light photoreceptors, which positively regulate photomorphogenesis upon red-light perception. Photomorphogenesis is driven by light-induced global transcriptional reprogramming, of which phytochromes are one of the most important regulators. In addition to transcriptional…

A phyB-PIF1-SPA1 kinase regulatory complex promotes photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis (OA) (Nature Communications)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1 (COP1) is one of the best characterized E3 ubiquitin ligases with broad roles as a central repressor of light signaling in plants to cancer biology in mammals. In plants, COP1 interacts with SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA-105 1 family members (SPA1-SPA4) and forms a stable COP1/SPA…

Arabidopsis PP6 phosphatases dephosphorylate PIF proteins to repress photomorphogenesis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the absence of light, plants undergo skotomorphogenesis, characterized by longer hypocotyls, closed and yellowish cotyledons, and apical hooks. in the presence of light, they undergo photomorphogenesis, with inhibited hypocotyl elongation, and open and expanded green cotyledons. Light also modulates…

COP1 can be hijacked by photoreceptors via their VP motifs (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant development is characterized by a high degree of plasticity in response to light. Light‐activated plant photoreceptors bind and inhibit the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1, thus protecting downstream transcription factors from degradation. However, the detailed mechanisms of how COP1 can function between…
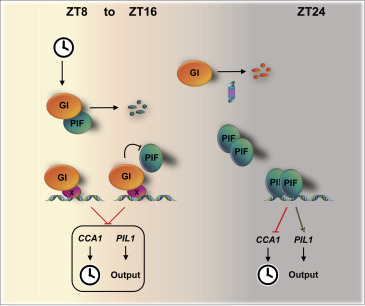
Multi-level modulation of light signaling by GIGANTEA regulates both the output and pace of the circadian clock ($) (Devel Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe daily cycle of light and dark controls many facets of plant growth and development, but these cycles depend on and are most efficient when integrated with the rhythms of the circadian clock. Nohales et al. have identified a key mechanism that directly links the regulation of light-responsive genes…
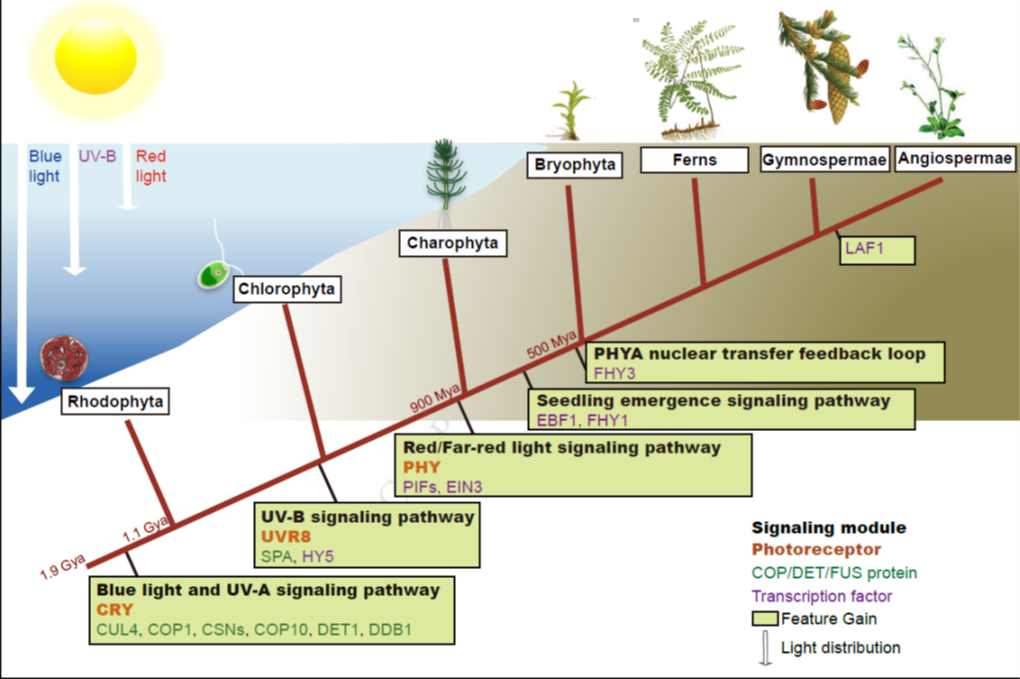
The macroevolutionary history of light signaling ($) (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability to sense and respond to light is a fundamental feature of photosynthetic organisms like plants. Much has been learned about the molecular genetic mechanisms controlling light perception and downstream signaling processes in evolutionarily young land plant lineages like angiosperms, with comparatively…
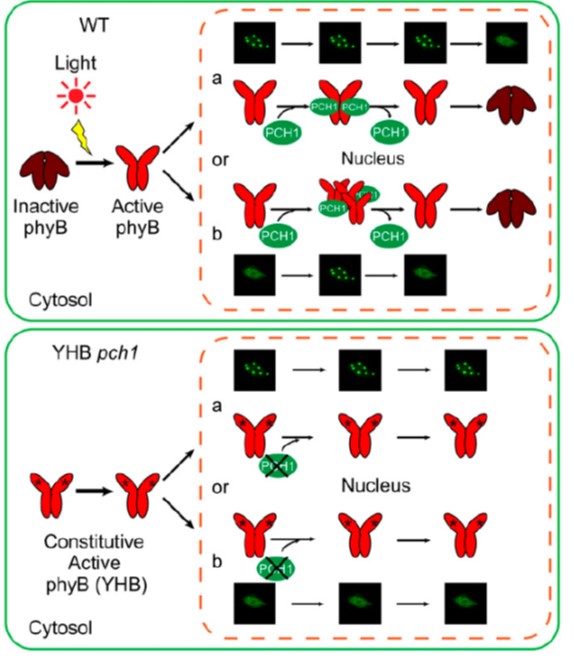
PCH1 regulates light, temperature, and circadian signaling as a structural component of phytochrome B-photobodies in Arabidopsis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytochrome is one of the key photoreceptors in plants, and famous for switching between active and inactive (Pfr and Pr) forms by absorption of far-red and red light; additionally, Pfr converts slowly to Pr independently of light. Furthermore, in the nucleus, the Pfr form can aggregate into photobodies.…
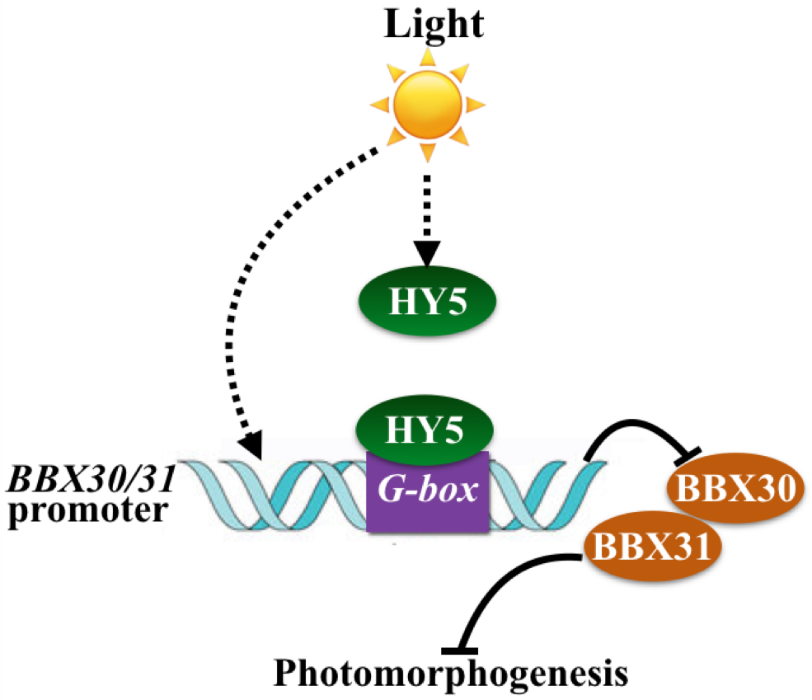
Two novel repressors of photomorphogenesis act downstream of HY5 in Arabidopsis (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHigher plants rely on a sophisticated photo-sensory system to cope with the vast variety of environmental stimuli. Under light conditions, young seedlings display photomorphogenic development to maxize the usage of light. Recently, YQ Heng et al. discovered two B-box containing proteins, BBX30 and BBX31,…

