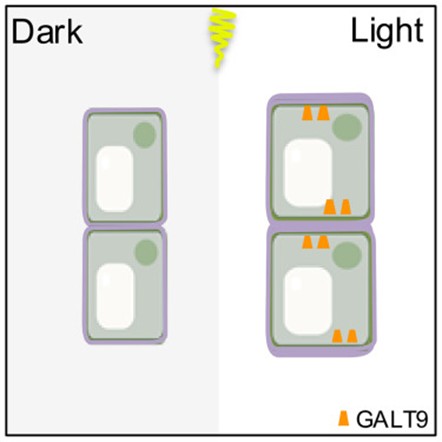
Lights, camera, pectin: Bringing hypocotyl elongation out of the dark
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight is a powerful signal, shaping plant development and growth. However, the cellular mechanisms that translate light signals into precise developmental responses are still being unravelled. The Arabidopsis hypocotyl (the embryonic stem, situated underneath the cotyledons in seedlings) rapidly restricts…
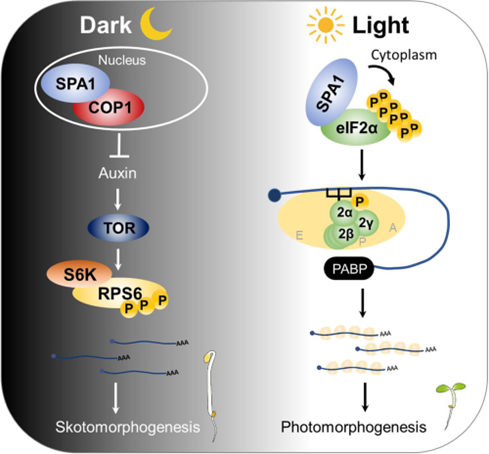
Flip the light switch for protein production
Plant Science Research WeeklyProtein synthesis, modification, and degradation are not only crucial for responding to environmental change, but they also represent significant energy costs for a plant. Energy homeostasis is highly affected by the presence of light. In young seedlings, light enhances translation during the dark-to-light…
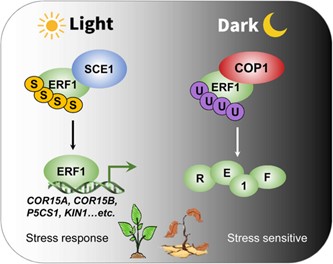
Tailored protein stability for stress resilience in light and dark
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight influences essentially all aspects of plant growth and development. Furthermore, plants are likely to adjust their stress responses based on fluctuations in energy availability during the dark-light cycle. Lin et al investigated a hormone downstream component, ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 1 (ERF1),…
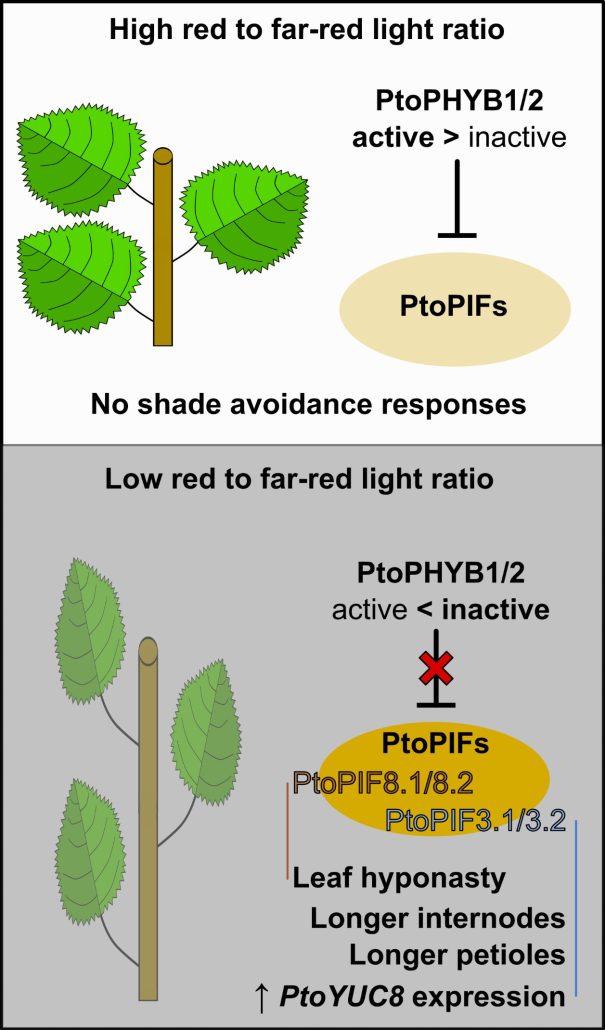
Shade avoidance responses in Chinese white poplar rely on shared and unique roles of phytochrome-interacting factors
Plant Science Research WeeklyShade avoidance syndrome (SAS) is a set of adaptive growth responses to low red to far-red light ratios. SAS includes petiole and internode lengthening and upward bending of leaves (hyponasty). In Arabidopsis, PHYTOCHROME B (PHYB) and PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) are implicated in these responses.…
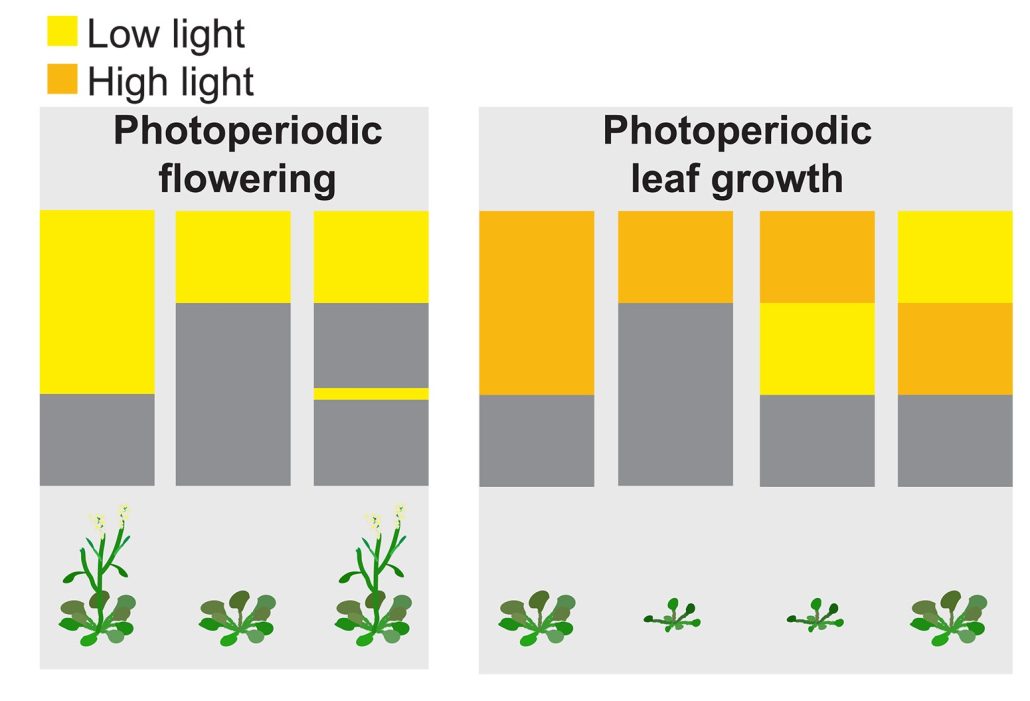
Seasonal flowering and seasonal growth measure light duration differently
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the first lessons a plant biologist learns is that many plants coordinate their seasonal flowering through measuring daylength, and that this process involves both photoreceptors and the biological clock that functions inside of cells. Of course, daylength also affects plant metabolism, in part…

Interconnected: Hydrotropism and phototropism in Arabidopsis root growth
Plant Science Research WeeklyTropisms enable plants to shift their growth direction in response to environmental changes. The roots of Arabidopsis plants respond to gravity by growing in the direction of gravity, a phenomenon known as gravitropism, while in response to unilateral blue light they bend away, demonstrating phototropism.…
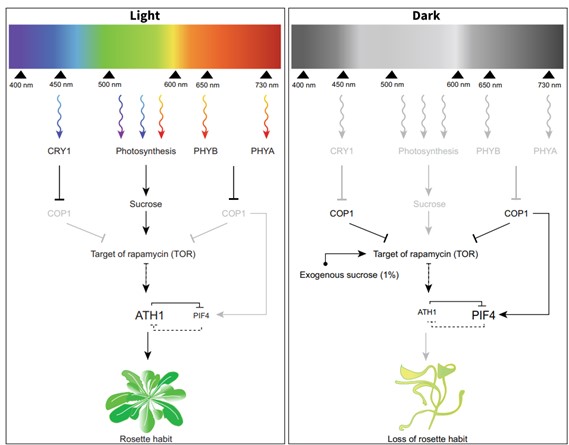
Light and sucrose signaling converge at TOR kinase to control plant development
Plant Science Research WeeklyDifferent photoreceptors (mainly phytochromes and cryptochromes) perceive light, which acts as a signal for controlling plant growth and development. Similarly, light is absorbed by chlorophylls (and carotenoids) for generating energy via photosynthesis. In search of a link between these two light-mediated…
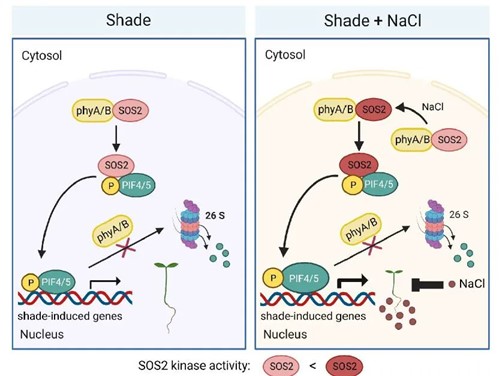
Shade finds a salty connection
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight acts as a crucial signal for plant growth and development and is perceived by several types of photoreceptors including phytochromes (phys). Sun-loving plants often exhibit shade avoidance syndrome (SAS), like longer hypocotyl, lesser branching, and earlier flowering to outcompete their neighbors…
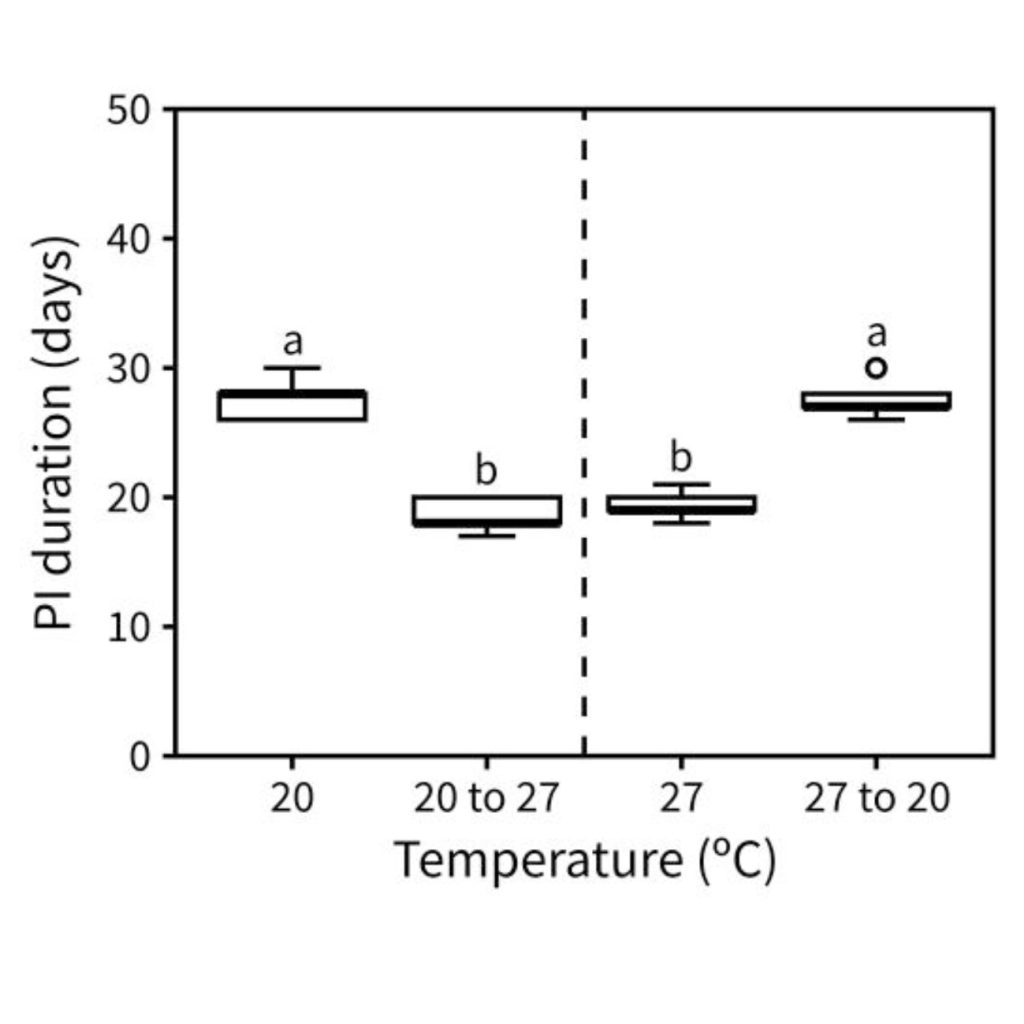
Photo-thermally controlled transcriptional regulation of FT drives the arrest of flowering time in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight and temperature are important external signals required by plants for flower initiation. These external signals along with some internal cues (plant age, gibberellins, etc.) are established factors for floral initiation, but the factors required for end-of-flowering time are not yet established.…

