
MYB30 negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by interacting with PIFs and phytochromes in Arabidopsis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotomorphogenesis is the growth and development of plants in response to light. The phytochrome family of photoreceptors absorbs red and far-red light, and in Arabidopsis the most abundant phytochromes are phyA and phyB. PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) repress photomorphogenesis, and under red…
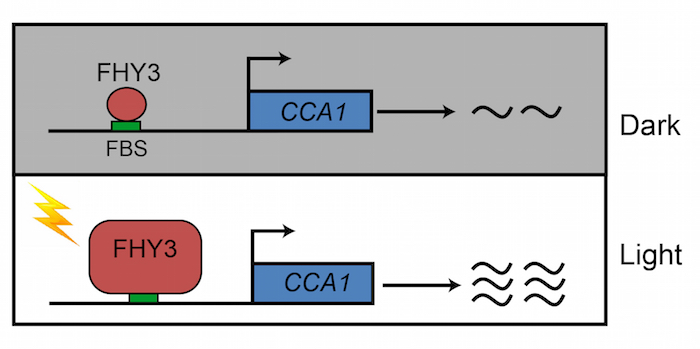
How Light Activates the Plant Circadian Clock
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLiu et al. discover how members of the photosensory-signaling pathway orchestrate circadian clock gene expression to regulate plant responses to daily changes in the light environment. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00981
Background: Plants use an endogenous time-keeping mechanism known…
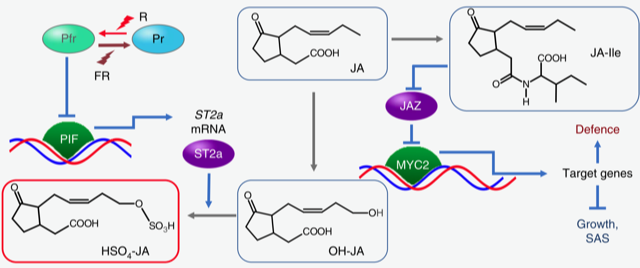
A molecular link between photoreceptors and jasmonates (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants balance their efforts on growth and defense depending on the situation. Competitive conditions signaled by the low ratios of red (R) to far-red (FR) light suppress defense responses mediated by the plant hormone jasmonate (JA), presumably for allocating more resources to promote plant growth.…
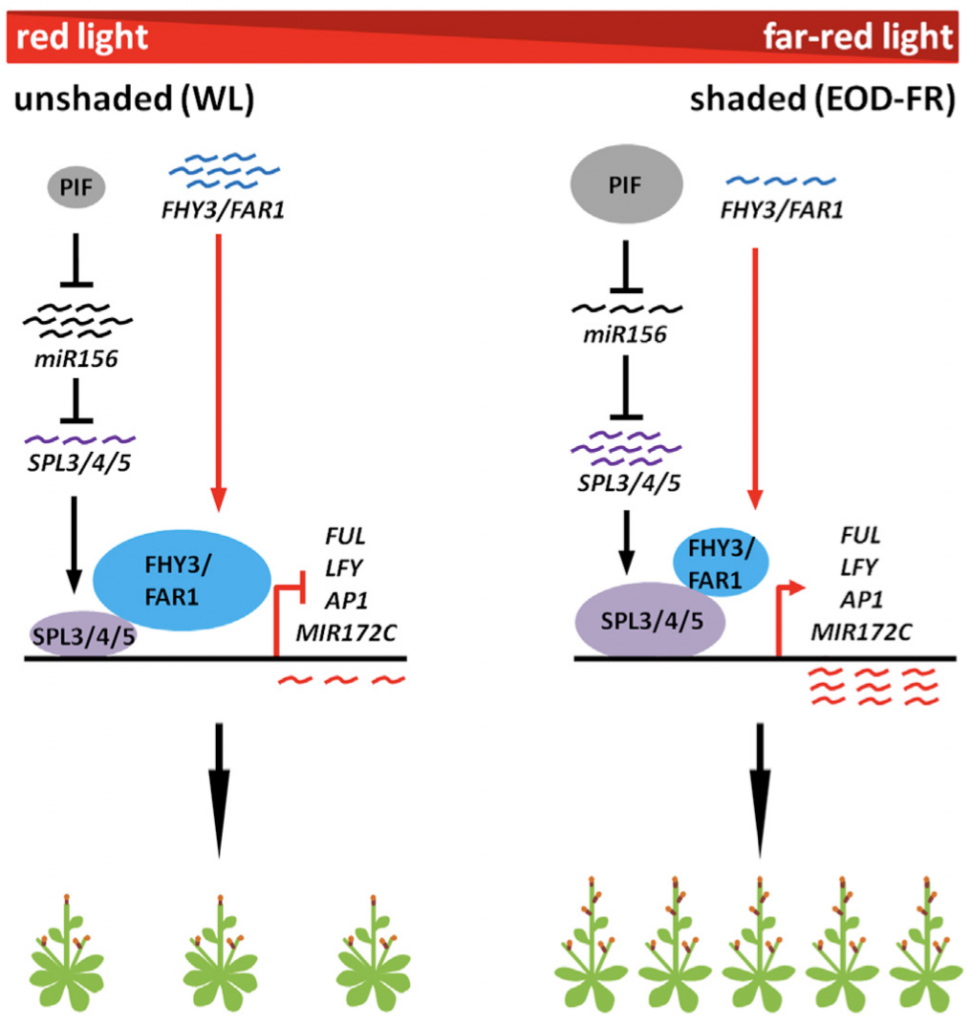
Integration of light signaling with endogenous developmental pathway to regulate flowering (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResponse to changing environmental conditions is key for plant reproductive success. Previous studies have implicated FAR-RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL3 (FHY3) and FAR-RED IMPAIRED RESPONSE1 (FAR1) as inhibitors of flowering in phytochrome A signaling pathway. miR156-targeted SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN…
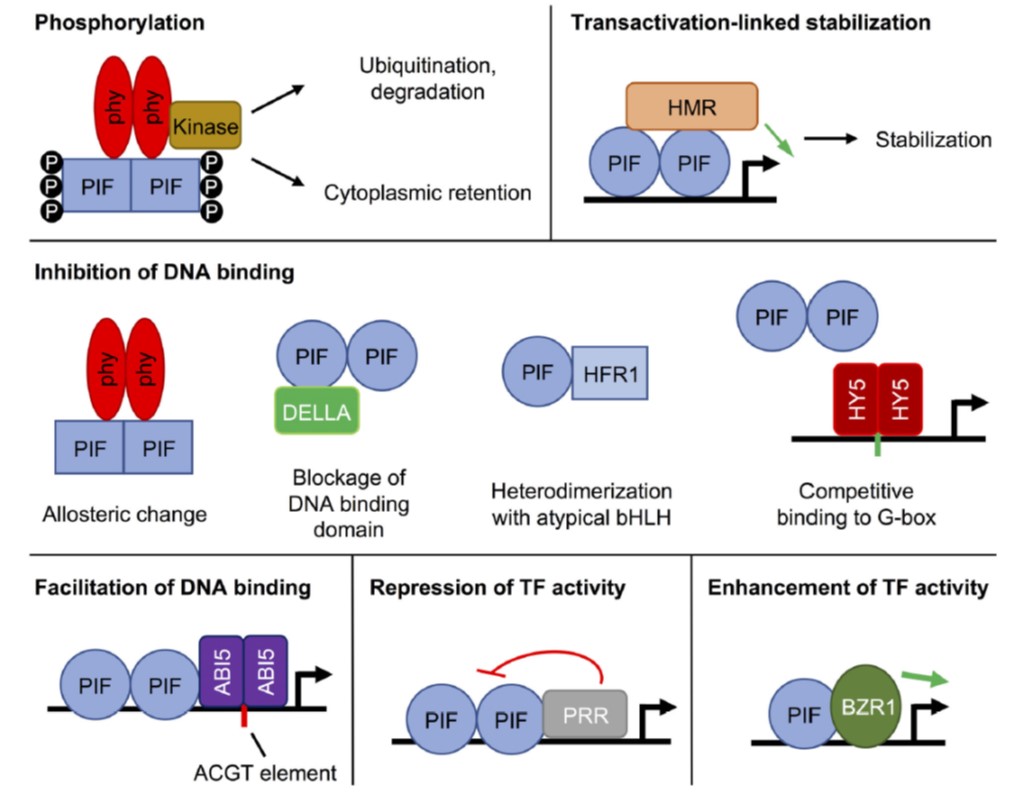
Review: Mechanisms regulating PIF transcription factor activity at the protein level ($) (Physiol. Plant.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbsorption of red and far-red light by phytochromes dramatically affects plant development, and many of these effects are mediated by the PIF (PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR) family of transcription factors. Favero reviews the many ways that PIF activity is regulated beyond through their interactions…

Central clock components modulate plant shade avoidance by directly repressing transcriptional activation activity of PIF proteins ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORs (PIFs) are transcriptional factors that relay light signals from the phytochrome photoreceptors to regulate the expression of light-sensitive genes, but there is not a direct correlation between PIF binding and expression of the target genes. In this paper, Zhang Y et…
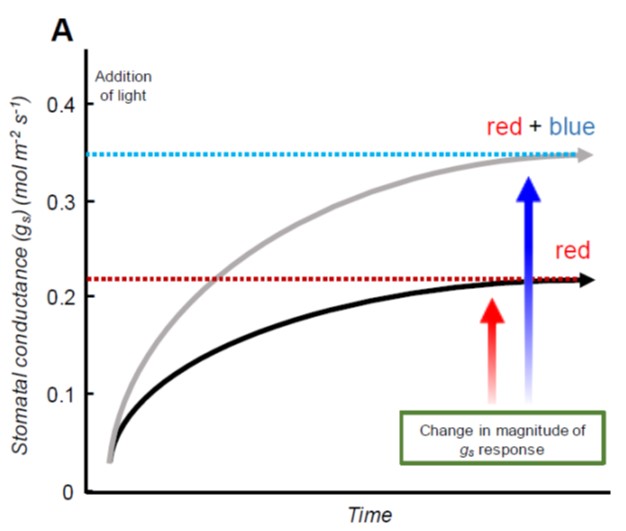
Review: Role of blue and red light in stomatal dynamic behaviour (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGuard cells are extremely sensitive and dynamic, and their behaviour controls rates of gas exchange and transpiration, which affect evaporative cooling and transport in the xylem. Matthews et al. review the roles of light signalling pathways in guard cell responses. Cues that control guard cell ion channels…

Subdivision of light signaling networks contributes to partitioning of C4 photosynthesis (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySome plants such as Zea mays partition different components of the photosynthetic pathway in mesophyll cells (MC) and bundle sheath cells (BSC) in a process known as two-cell C4 photosynthesis. For example, light-harvesting reactions carried out by photosystem I and II (PSI and PSII) occur only in the…
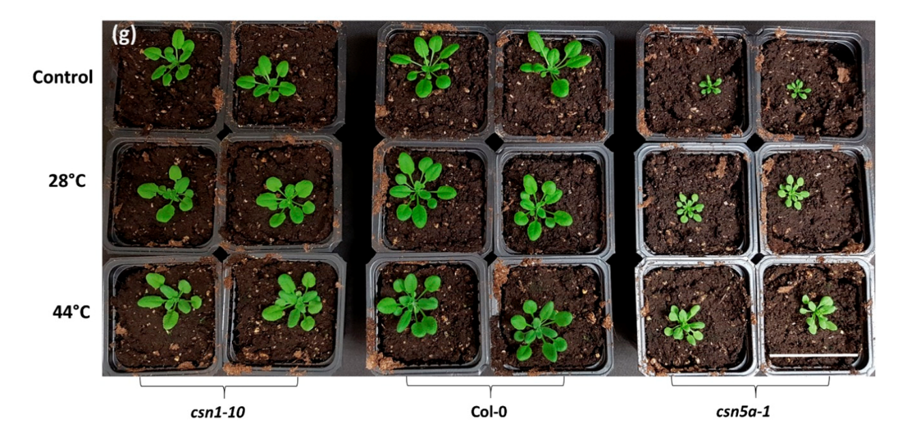

CSN5 of COP9 signalosome modulates heat-response of Arabidopsis (biomolecules)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCOP9 signalosome (CSN) is a conserved multi-subunit complex in higher eukaryotes that was originally identified as a regulator of plant photomorphogenesis. It functions by regulating ubiquitin-mediated protein stability, through the deneddylase enzymatic acitivity of the CSN5 subunit. CSN5 is encoded…

