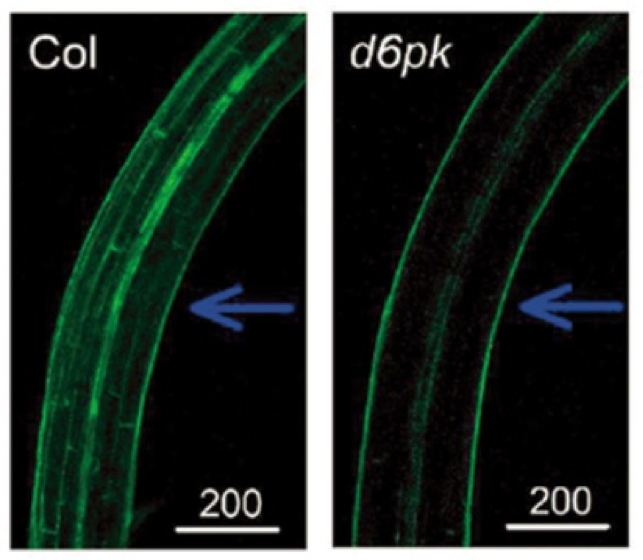
Roles of AGCVIII kinases in the hypocotyl phototropism of Arabidopsis seedlings (Plant Cell Physiol.)
Phosphorylation and de-phosphorylation are fundamental events for signal transduction. Phytohormone and light signaling are no exception in this case. Plants face towards light by creating lateral auxin gradient between exposed and shaded sides. This asymmetric auxin distribution is mediated through…

Phytochrome B mutants discern distinct roles of PIF degradation and sequestration (Plant Cell)
The interaction between phytochromes and phytochrome-interacting factors (PIFs) is key to light signaling. Both sequestration and degradation of PIFs occurs, and Park et al. have explored the relative contributions of these two PIF fates to the light response. They studied two mutants, one with a point…
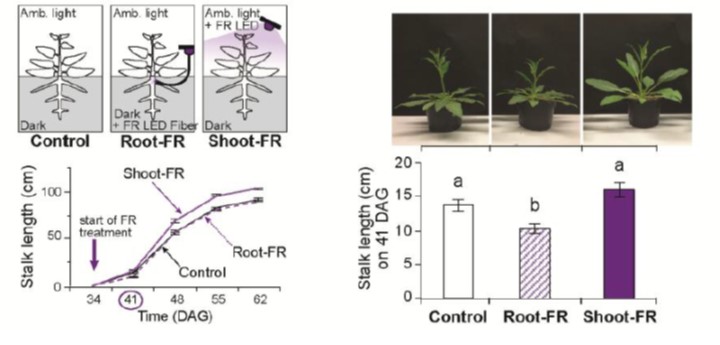
Root-expressed phytochrome B1 and B2 regulate shoot growth in nature (Plant Cell Environ.)
Light is not only a driving force of photosynthesis, but also an important environmental signal. Oh et al. report that a number of light sensing phytochromes are expressed in roots of native tobacco (N. attenuata) at higher levels than in the shoots. The authors investigated the roles of those root phytochromes…
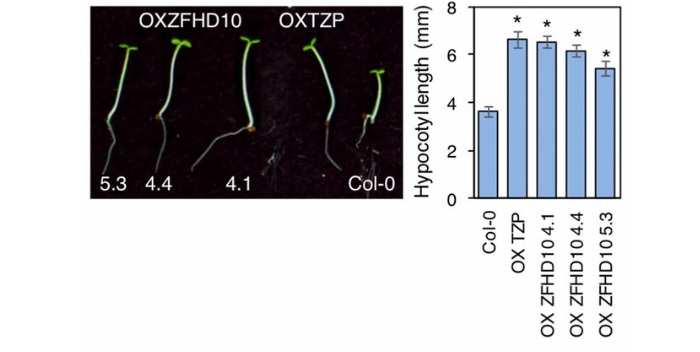
Regulation of Arabidopsis hypocotyl growth by transcriptional regulators (PNAS)
The integration of light-based environmental signals with photoreceptors and transcriptional regulators is essential for coordinating plant growth, development and energy production. One such integrator of light and signaling components is the Arabidopsis thaliana TANDEM ZINC-FINGER PLUS3 (TZP). TZP…
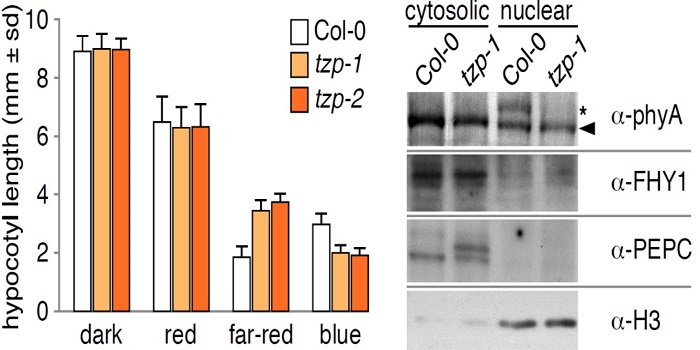
Developmental Timing is Everything: TZP and Phytochrome Signaling
Although they lack eyes, plants can differentiate between colors with a full complement of photoreceptors. Phytochromes (phys) are such photoreceptors dedicated to the visible light spectrum ranging from red light (600-700 nm) to far-red light (700-750 nm). phys are some of the most studied genes and…

Update: Phytochrome, Carbon Sensing, Metabolism, and Plant Growth Plasticity
By Johanna Krahmer, Ashwin Ganpudi, Ammad Abbas, Andrés Romanowski, and Karen J. Halliday
Plants continuously monitor fluctuations in their environment and actively adjust their metabolism to cope with variations in light and carbon resource availability. However, the links between photoreceptor signaling…
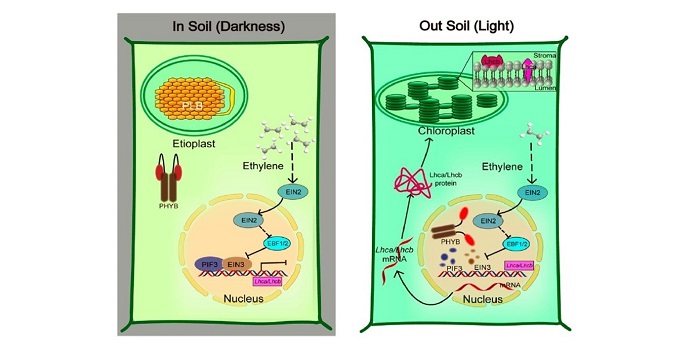
EIN3 and PIF3 form an interdependent module that represses chloroplast development in buried seedlings ($) (Plant Cell)
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process for plants to produce food. Beneath the soil there is an impairment of chloroplast development. In this article, Liu et al. identified that mechanical pressure works through the ethylene-responsive transcription factor EIN3, while light signaling is mediated…

Supression of phyB dark reversion by PCH1 and PCHL (Nature Comms.)
Nature Comms. Phytochromes can exist in two states: an inactive state Pr and an active state Pfr. They convert into each other by light absorption. They can also revert to the inactive state by a light-independent thermal relaxation process called dark reversion. Phytochrome B is the primary receptor…

Phytochrome, metabolism and growth plasticity
Phytochromes are plant photoreceptors that can sense red and far-red light, as-well-as the ratio of these light qualities. This review examines the relationship between phytochrome signalling and carbon metabolism. Krahmer et al. assess the influence of phytochrome signalling on the synthesis of…

