
New Teaching Tool: "Molecular Control of Plant Shoot Architecture"
BlogWe’re excited to announce the publication of The Plant Cell’s latest Teaching Tool, “Molecular Control of Plant Shoot Architecture,” by Agustin Zsögön and Lázaro E. P. Peres, available without subscription at Plantae.org.
Manipulation of plant form and height has been instrumental in…

Master MYCs: MYC2, the jasmonate signaling ‘master switch’
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTo optimize their fitness in the field, plants need to respond rapidly, specifically and dynamically to an ever-changing and often hostile environment. By integrating external environmental cues with endogenous developmental programs, phytohormones play a critical role in the cross-talk between signal…
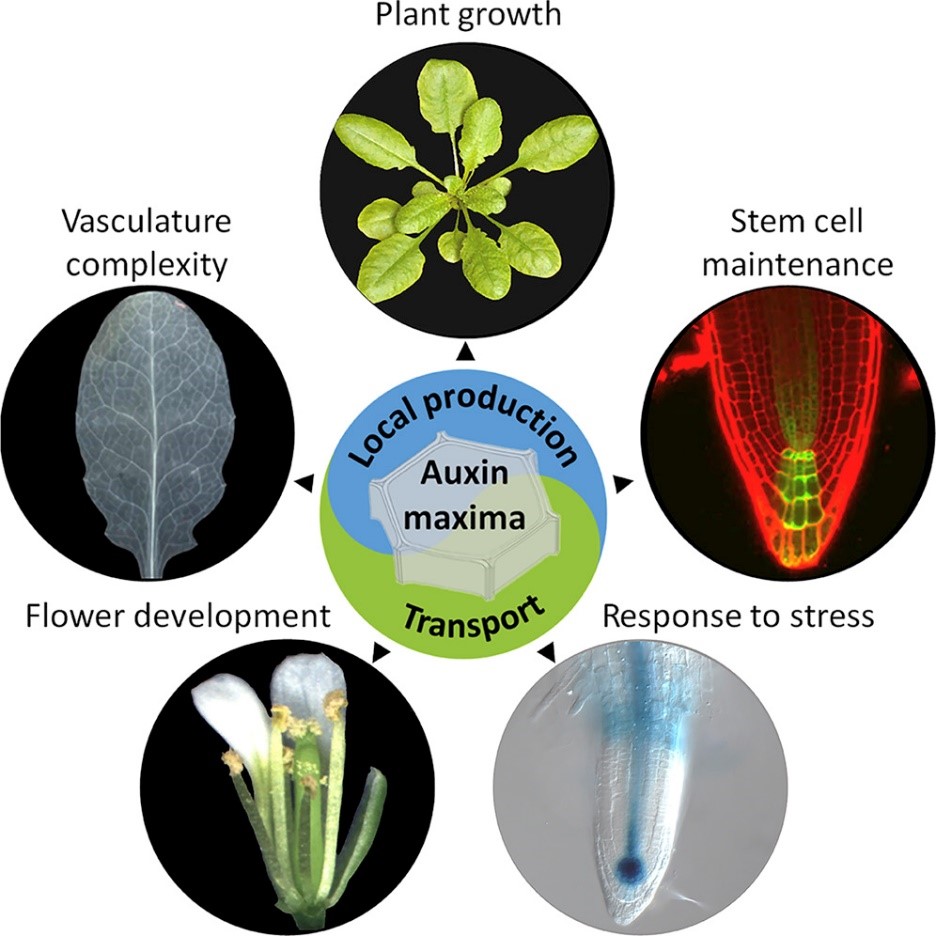
Local auxin biosynthesis is a key regulator of plant development ($) (Devel Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMorphogenic gradients of auxin are essential for plant phenotypic plasticity. Polar auxin transport plays a central role in auxin maxima generation. The exquisite spatiotemporal expression patterns of auxin biosynthesis genes suggested that local sources of auxin may contribute to the formation of auxin…
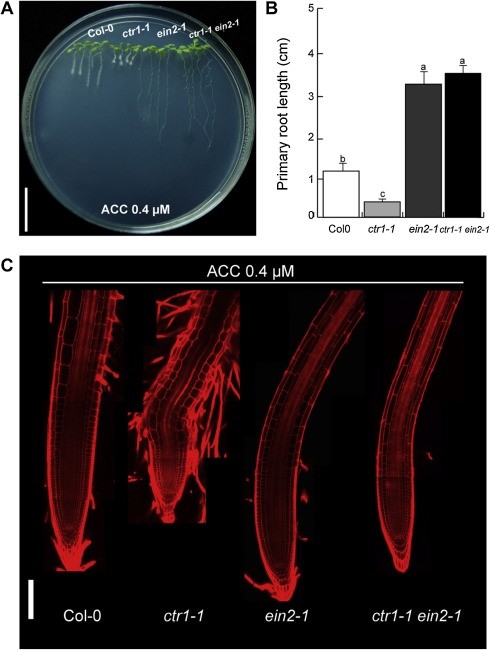
CONSTITUTIVE TRIPLE RESPONSE 1 and PIN2 coordinately regulate indeterminate root growth (Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMéndez-Bravo et al. explored the mechanism for the dramatic phenotype of the ctr1 mutant (CONSTITUTIVE TRIPLE RESPONSE 1), which inhibits both cell division and elongation. In the ctr1-1 mutant background, auxin response is induced at the root tip and an increase in expression of the auxin transporter…
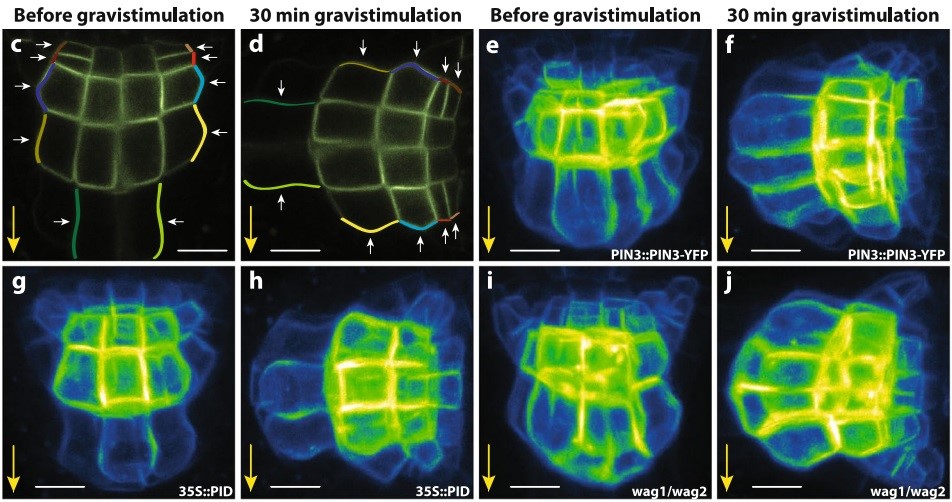
PID/WAG-mediated phosphorylation of PIN3 mediates polarity switches during gravitropism (Sci Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin distribution depends on the polar localization of PIN-FORMED or PIN proteins. Based on different development and environmental stimuli, PIN proteins switch polarity to redirect the auxin flux. Additionally, phosphorylation of PIN is required for its function. For instance, PIN3 phosphorylation…
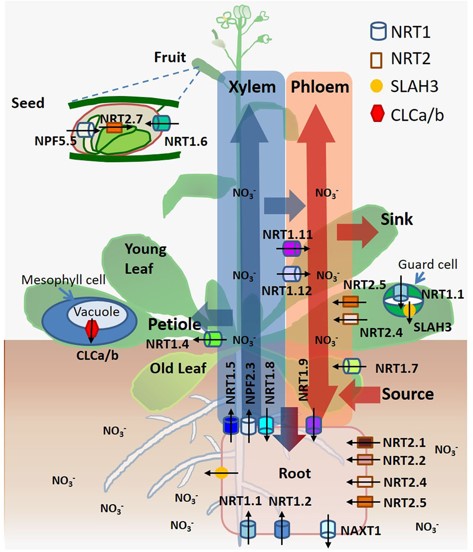
Dancing with hormones: A current perspective of nitrate signaling and regulation in Arabidopsis (Frontiers in Plant Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen (N) is a main constituent of amino acids and nucleotides and therefore plays a central role in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plants are able to take up nitrogen from the soil in two forms, nitrate and ammonium. Nitrate is the predominant form of nitrogen found in most crop…
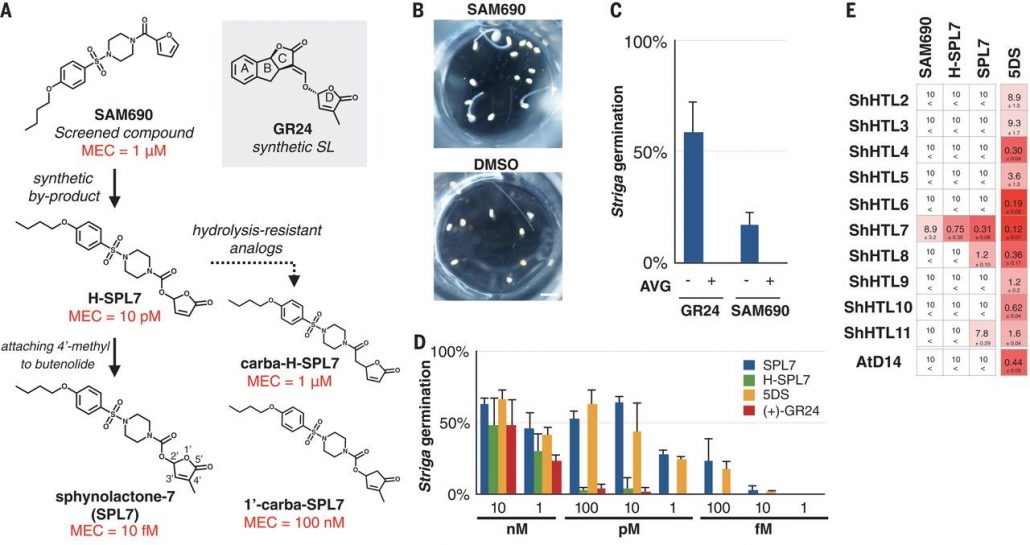
A femtomolar-range suicide germination stimulant for the parasitic plant Striga hermonthica (Science)($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStriga hermonthica (Striga) parasitizes a wide range of crops including sorghum and rice, mainly in sub-Saharan Africa. This parasite decreases crop yields and results in billions of dollars in economic damage. Striga seeds are numerous and remain dormant in the soil until prompted to germinate by…
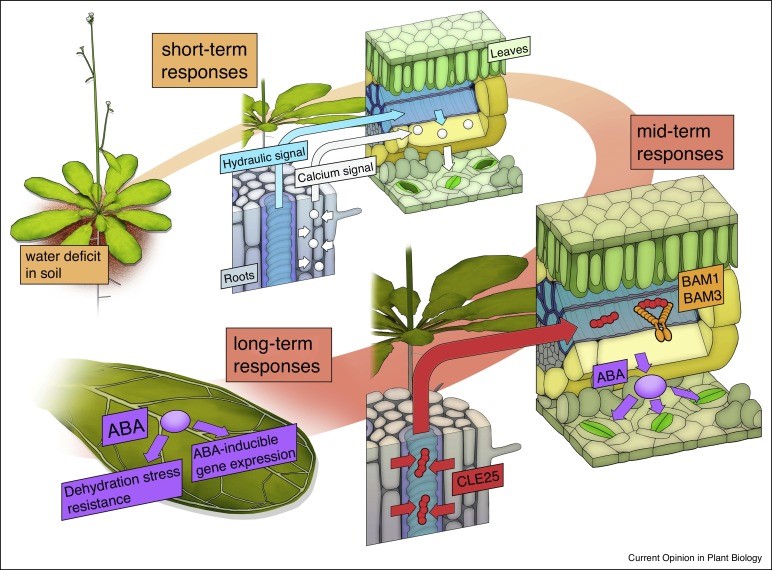
Review: Long distance signlaing in plant stress response (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo compensate for their lack of a nervous system, vascular plants have developed complex mechanisms to connect their organs and coordinate stress. Many different types of molecules are involved in long-distance signaling and must be integrated to maintain homeostasis. In this review, Takahashi and Shinozaki…
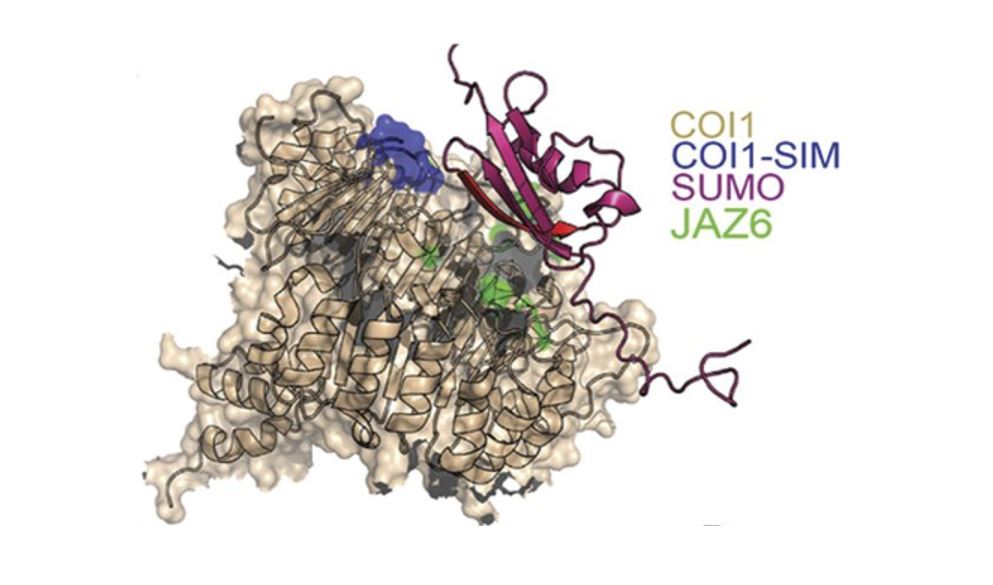
SUMO Aids Rapid Regulation of Hormone Responses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSrivastava et al. identify a mechanism for rapid regulation of jasmonic acid signaling. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00036
Background: The sessile nature of plants dictates that growth must be integrated with changes in the natural environment. Modulation of hormone signalling pathways…

