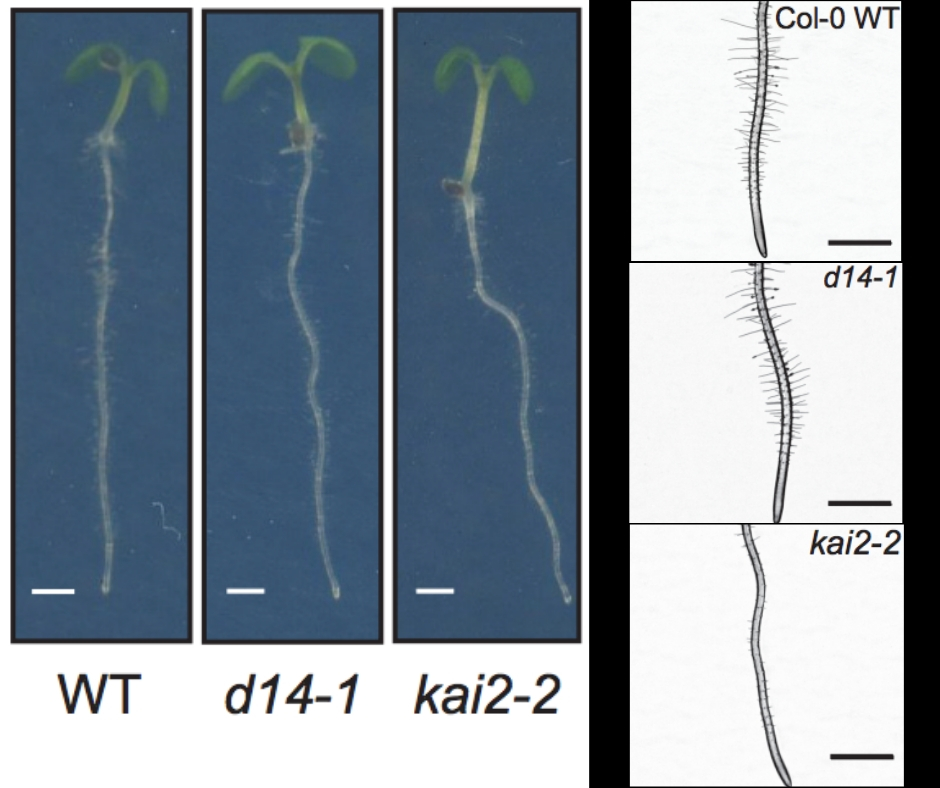
KAI2 regulates root and root hair development by modulating auxin distribution (bioRxiv)
To optimize growth, plant development is regulated by environmental information. Root morphology is adaptable to stimuli due to a network of phytohormone signalling pathways. Here Villaecija et al. studied the roles of strigolactones (SL) and karrikins (KL) signalling in controlling root and root hair…
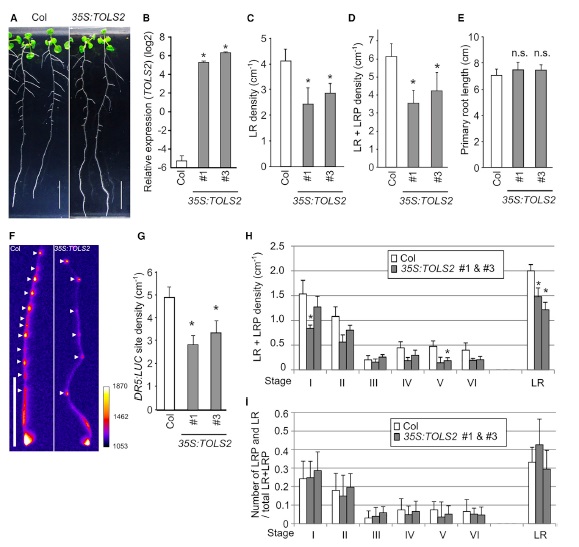
Lateral inhibition by a peptide hormone-receptor cascade during Arabidopsis lateral root founder cell formation (Devel. Cell)
The plant hormone auxin acts as a general coordinator of growth and development, transferring information over both long and short ranges. Among other roles, it promotes the formation of the founder cells in roots and it triggers the position of the lateral roots (LR). LR founder cells are determined…

Auxin efflux carrier ZmPGP1 mediates root growth inhibition under aluminum stress (Plant Physiology)
Acid soils (pH < 5.5) mobilize aluminum (Al) in the rhizosphere, which damages the root meristem and hinders exploration for nutrients and water. Zhang et al. demonstrate that a mutation in ZmPGP1, an auxin transport protein, imparts enhanced root growth under toxic Al conditions. The enhanced root…
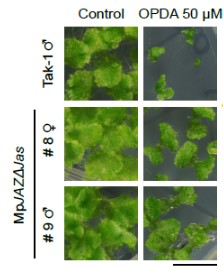
A single JAZ repressor controls the jasmonate pathway in Marchantia polymorpha (Molecular Plant) ($)
Previously, Monte et al. showed that the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha perceives the jasmonate pathway precursor dn-OPDA instead of the well known JA-Ile phytohormone of vascular plants. Now, Monte and colleagues focus on the MpJAZ, downstream of the signal transduction pathway. MpJAZ is the sole…
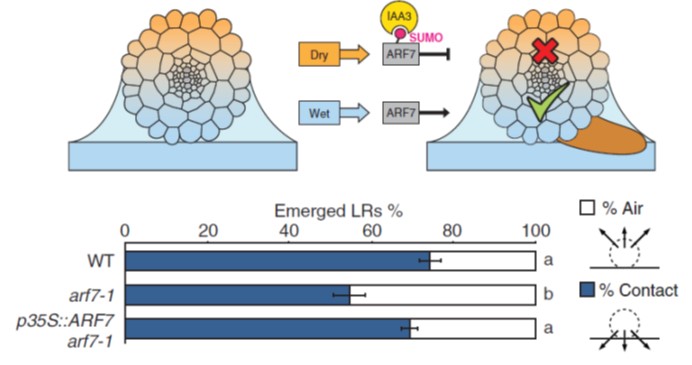
Root branching toward water involves posttranslational modification of transcription factor ARF7 ($) (Science)
Roots do amazing things, particularly in terms of how they optimize their growth in response to their very local environment including water, nutrients, microbes, and physical obstructions. Branching in regions of contact with water is called hydropatterning, and previous studies showed that an auxin…
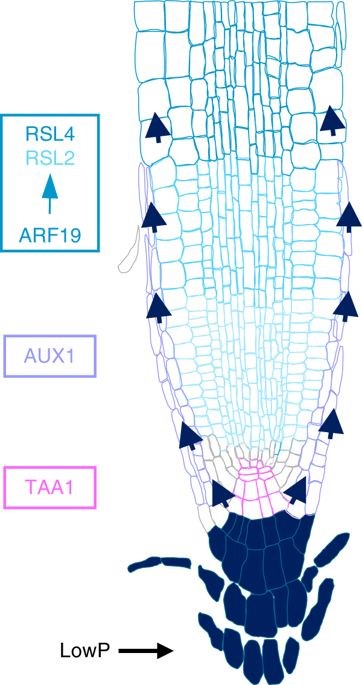
A mechanistic framework for auxin dependent Arabidopsis root hair elongation to low external phosphate (Nature Comms)
Plants respond to a low phosphate environment through increased elongation of root hairs. Bhosale et al. showed that low external P increases levels of the auxin (IAA) in Arabidopsis roots through the TAA1 (TRYPTOPHAN AMINO TRANSFERASE 1)-mediated auxin biosynthesis pathway. At the same time, the auxin…
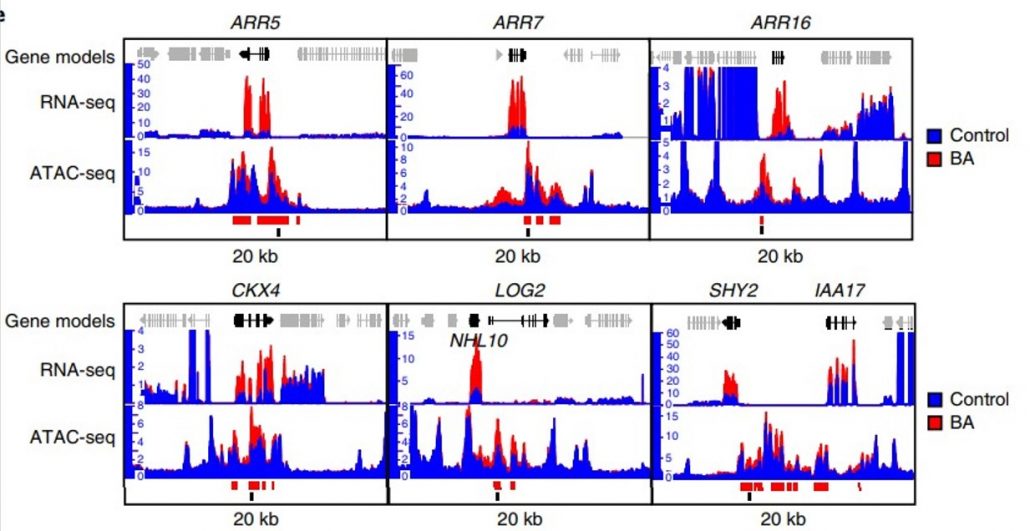
Cytokinin modulates context-dependent chromatin accessibility through the type-B response regulators ($) (Nature Plants)
The cytokinin-based response is assumed to be achieved through context-dependent transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Potter et al. analyzed cytokinin-induced alterations in chromatin accessibility using ATAC-seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using Sequencing) and combined these results…
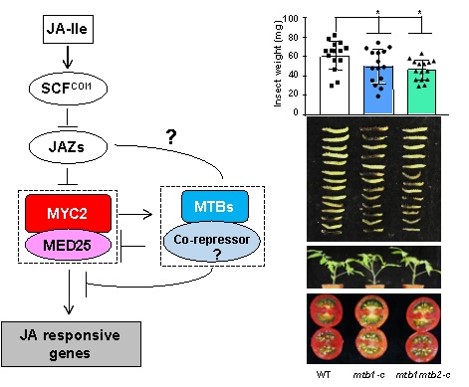
The mechanism by which MYC2 regulates the termination of jasmonic acid signaling
Source: Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology Published: 2019-01-11. Translated from the original.
As an important plant hormone, jasmonic acid regulates plant defense responses and adaptive growth. When the plant is exposed to pests or other stresses, the active jasmonic…

New Teaching Tool: "Molecular Control of Plant Shoot Architecture"
We’re excited to announce the publication of The Plant Cell’s latest Teaching Tool, “Molecular Control of Plant Shoot Architecture,” by Agustin Zsögön and Lázaro E. P. Peres, available without subscription at Plantae.org.
Manipulation of plant form and height has been instrumental in…

