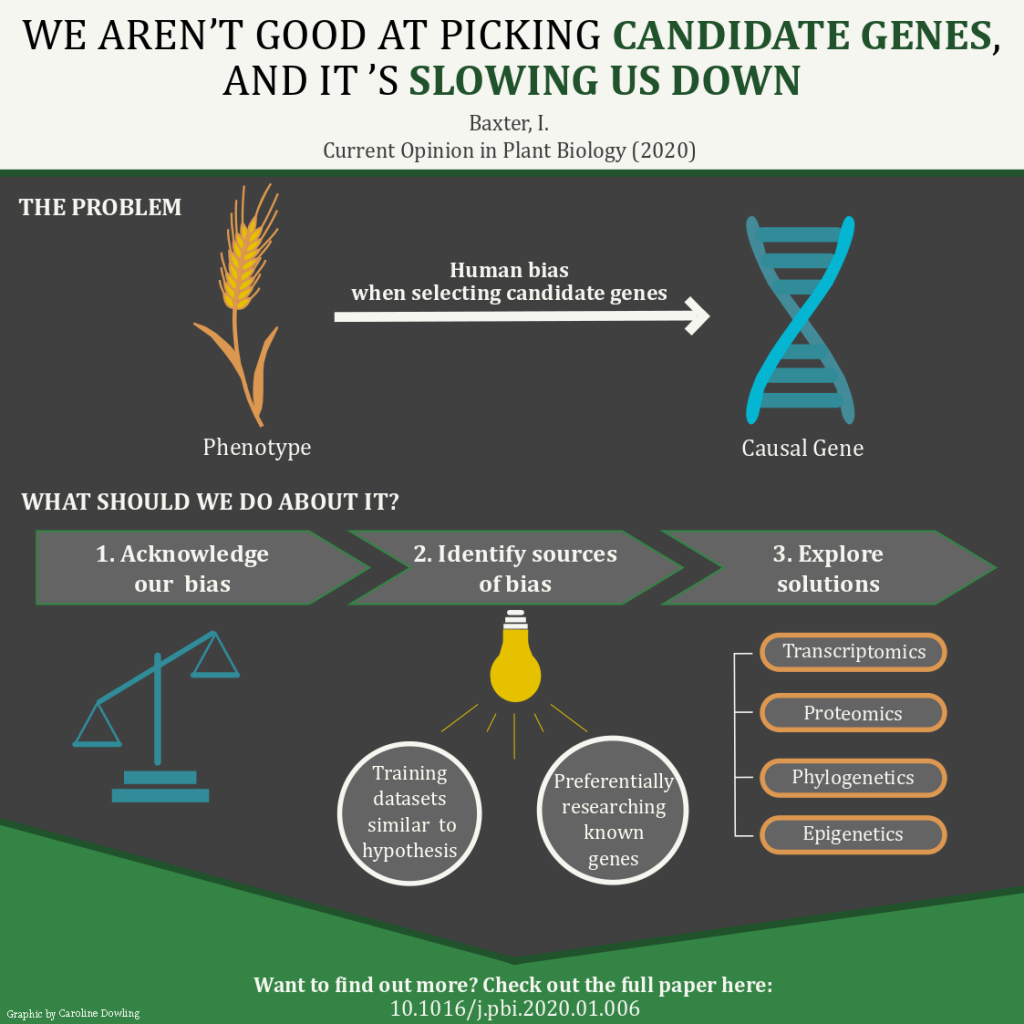
Opinion: We aren’t good at picking candidate genes, and it’s slowing us down (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRecent advances have facilitated the generation of huge phenotypic datasets from plant populations. However, the means to inexpensively organise such datasets to unequivocally determine causal genes has evaded researchers. Here, Baxter discusses how human bias when selecting candidate genes is compromising…
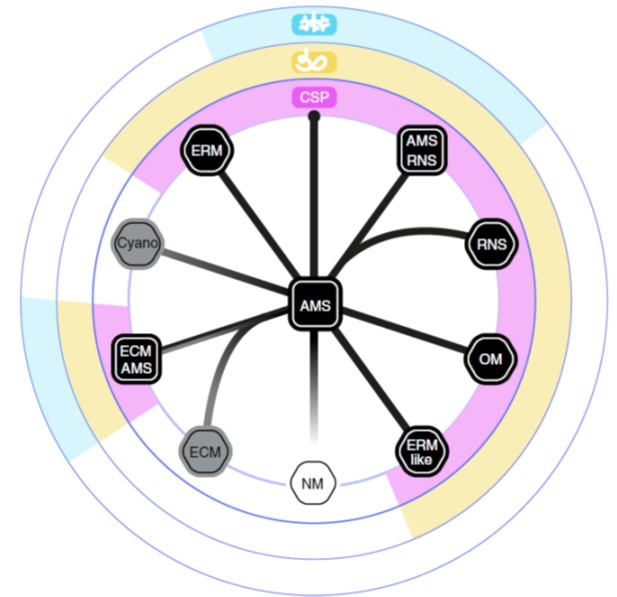
An ancestral signalling pathway is conserved in intracellular symbioses-forming plant lineages ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt’s widely thought that plants acquired the ability to live on land thanks to a little help from their friends, specifically arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Even now, most land plants form mutually beneficial associations with fungi or bacteria, and these often involve the plant cells acting as hosts…
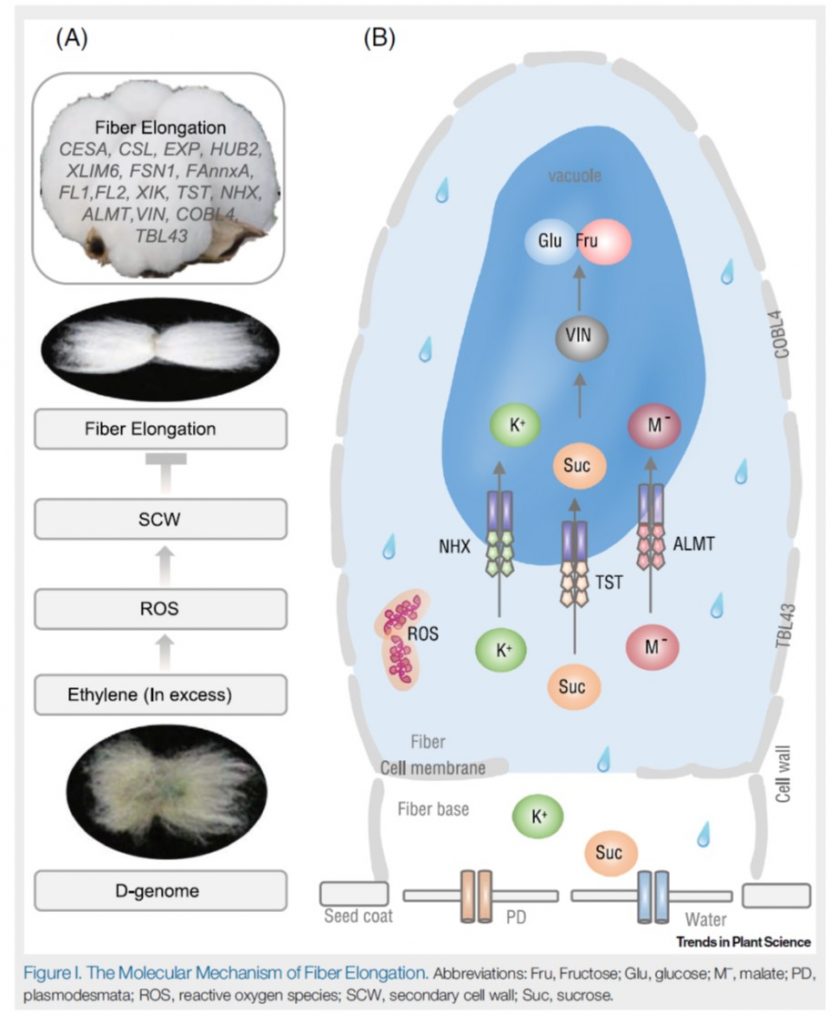
Review. Gossypium genomics: Trends, scope, and utilization for cotton improvement (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCotton (Gossypium spp.) provides the world’s most important natural fiber, and I suspect with our growing realization of the problems with plastics there will be still more demand for it. Yang et al. review the current state of Gossypium genomics. As a crop that has been domesticated for millennia,…

Expression atlas of Selaginella moellendorffii provides insights into the evolution of vasculature, secondary metabolism, and roots (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLycophytes, including the model species Selaginella moellendorffii, are extant (still alive today) seedless vascular plants that were particularly abundant around 400-300 million years ago (and major contributors to the formation of coal). To further understand the biology of some of these oldest extant…

Gene duplication accelerates the pace of protein gain and loss from plant organelles (Mol. Biol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrganelles, such as the chloroplast and nucleus, are structures with specific functions within a plant cell. It has been reported that many related, or homologous, proteins function in different organelles. However, how and why organellar proteins have diverged over evolutionary time remains unclear.…

Mitochondrial fostering: the mitochondrial genome may play a role in plant orphan gene evolution (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrphan genes are those that are found in only a single species. In trying to understand the origin of orphan genes, O’Conner and Li have found that many of these orphan genes are likely to have originated as mitochondrial genes, as many are nuclear genes whose encoded proteins are targeted to the mitochondria…
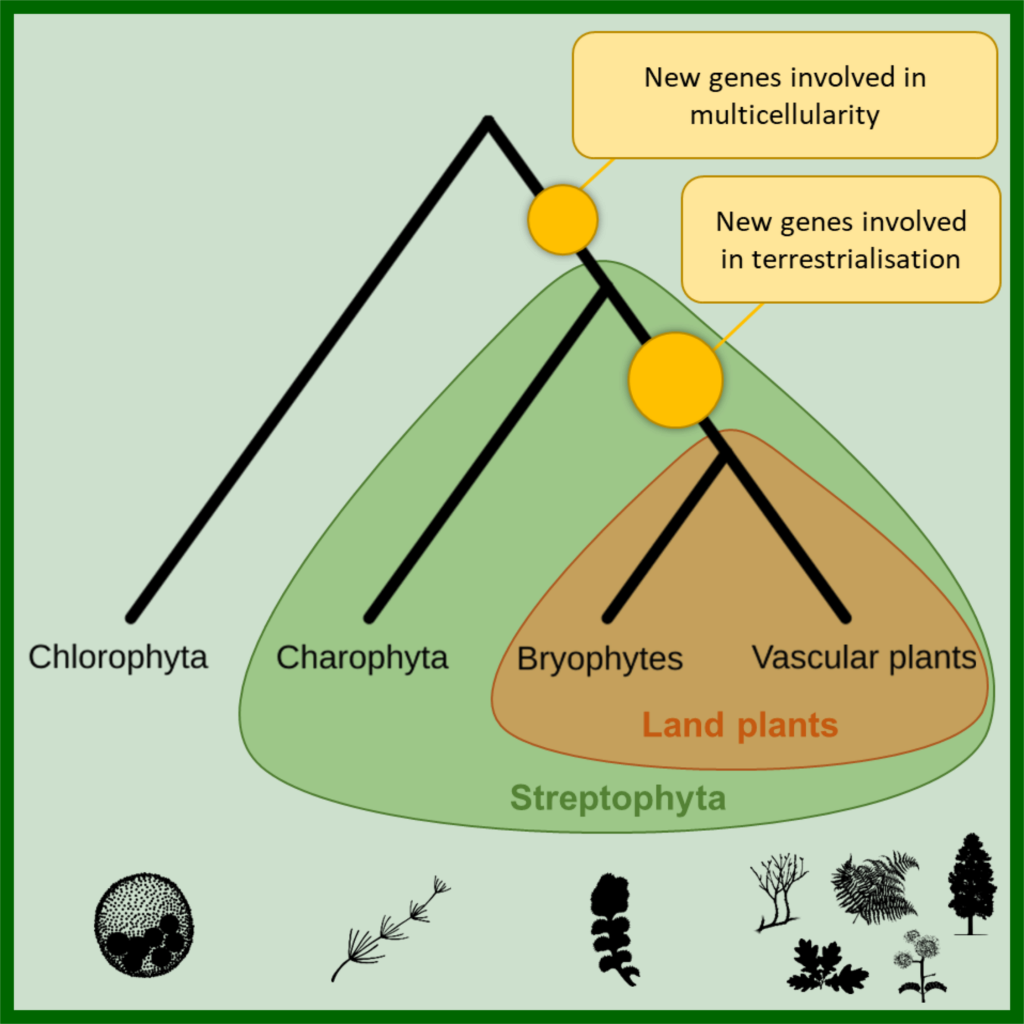
The origin of land plants is rooted in two bursts of genomic novelty (Curr. Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe transition of plants from water to land is one of the most momentous shifts in the history of life on Earth. 500 million years ago, the first land plants dramatically changed the environments on the planet, creating soils, rivers and the oxygen-rich atmosphere. However, the factors that enabled early…

Review. Diatom molecular research comes of age: Model species for studying phytoplankton biology and diversity (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDiatoms are photosynthetic eukaryotes and contribute substantially to global carbon fixation. They are distantly related to green plants, having shared the same primary endosymbiotic event, although they subsequently underwent additional secondary endosymbioses. There are over 100,000 species of diatoms,…
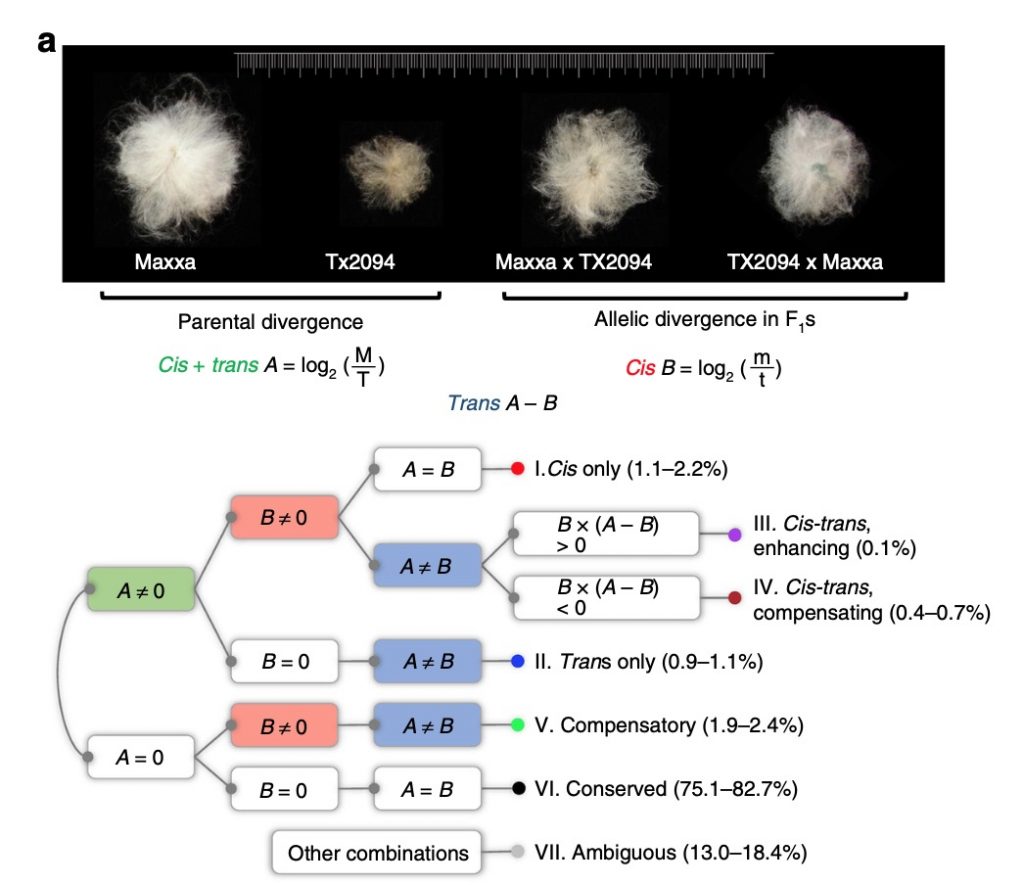
Unraveling cis and trans regulatory evolution during cotton domestication (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPolyploidization leads to a myriad of changes in gene expression and organization of genomes and can supply the material for speciation, adaptation, and morphological innovation. The most cultivated cotton species, Gossypium hirsutum, is an allotetraploid species (AD genome) containing two subgenomes…

