
Field-based species identification of closely-related plants using real-time nanopore sequencing
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDNA sequencing was slow before the development of high throughput sequencing. Portable DNA sequencing, which would make sequencing on-site a reality, was impossible until recently. Parker et al. report on the on-site use of MinION from Oxford Nanopore Technologies for DNA barcoding, which yields data…
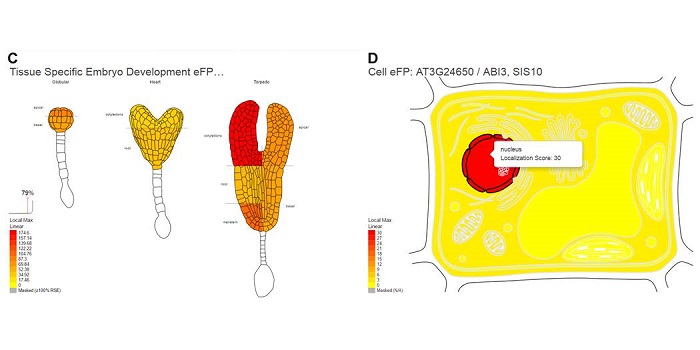
So Much Data, So Little Time: ePlant Steps into the Breach for Plant Researchers
Blog, Research, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In Brief0 Comments
/
The ever-increasing amount of data available to researchers has come with similarly increasing cognitive loads in efforts to use these data. Even when data sets are stored in well-curated databases, it can be time-consuming to master the specific tools harbored at each site and cumbersome to move between…
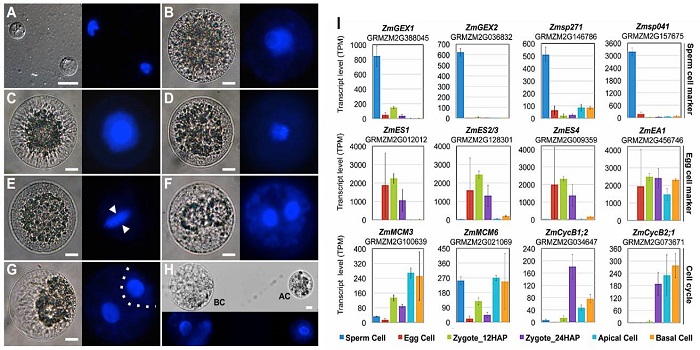
Zygotic genome activation occurs shortly after fertilization in maize
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogA plant’s life begins with the fusion of haploid egg and sperm cells to produce a diploid zygote. Many of the processes that control early development are under the control of the maternal genome, but at some point there is a shift towards zygotic control. Chen et al. investigated when this shift occurs…

Emergence of subgenome dominance across time and ploidy
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMany plants are not simple diploids (two copies of each chromosome) but are instead are the result of various forms of polyploidization (for example, whole-genome duplication or interspecific hybridization). Polyploidization can disrupt well-established controls over gene expression levels, transposon…

Temporal and spatial transcriptomic and miRNA dynamics of CAM photosynthesis in pineapple ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCAM (crassulacean acid metabolism) is the form of photosynthesis in which carbon assimilation occurs at night. CAM allows plants, especially those growing in arid regions, to avoid excessive water loss. With the long-term goal of eventually engineering this water-conserving trait into crop plants, Wai…

Ash dieback epidemic in Europe: How can molecular technologies help?
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe fungal pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus that infects European ash (Fraxinus excelsior) has caused a huge epidemic and cost millions of trees their lives. Downie describes the employment of molecular techniques to trace the origin of the fungus in Europe, and describes how the fungal life cycle…

The sequences of 1,504 mutants in the model rice variety Kitaake facilitate rapid functional genomic studies
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchLi et al. describe an important new genetic resource, a huge database of Kitaake rice mutants. Kitaake is a short-generation variety of Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica well suited for genetic studies. The authors sequenced more than 1500 fast-neutron-induced mutants and identified more than 91,000 mutations…
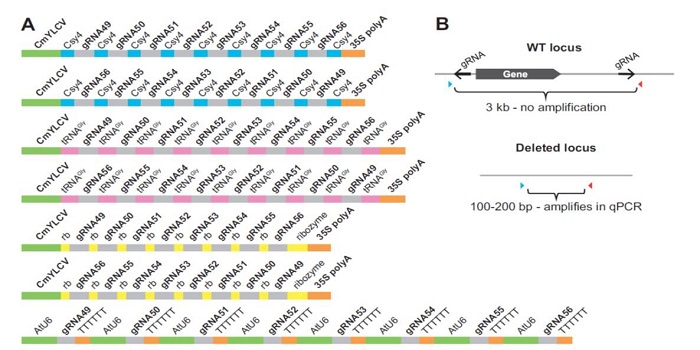
A multi-purpose toolkit to enable advanced genome engineering in plants
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPrecise genome editing holds tremendous promise for meeting future food security needs and sustainable agriculture. Čermák et al. describe a set of reagents that facilitate genome editing in plants, based on both TALEN (Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases) and CRISPR/Cas technologies. Precise…

The sunflower genome provides insights into oil metabolism, flowering and Asterid evolution
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) is an important oil crop and, according to the authors, “the only major crop domesticated in North America.” Assembling its genome has been difficult as more than three quarters of it is made up of young (less than one million years old) long-terminal repeat retrotransposons.…

