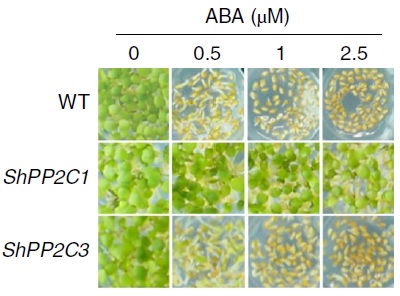
An aberrant protein phosphatase 2C confers abscisic acid tolerance and drives high transpiration during drought conditions in a parasitic plant, Striga ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStriga hermonthica is a parasitic plant which infects major crops in arid environments. The rate of transpiration in Striga is higher than that of the host plant, thus maintaining a water potential gradient from the host to the Striga plant. Until recently, the exact mechanism has been poorly understood.…
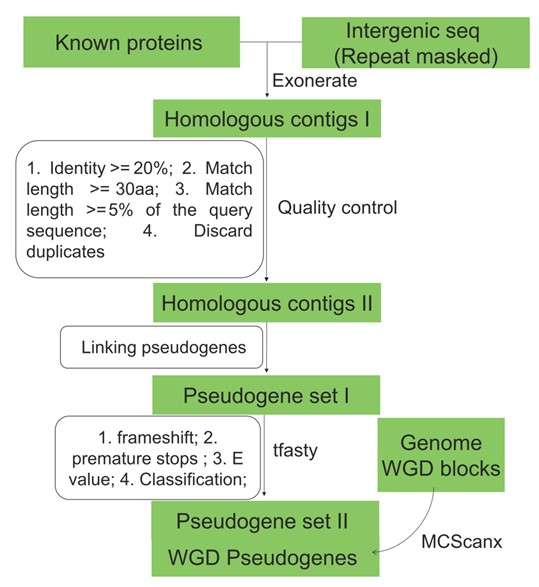
Evolutionary origins of pseudogenes and association with regulatory sequences (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProtein-coding genes have undergone frameshifts, in-frame stop codons, and truncation to produce pseudogenes (Ψs), which had been thought to be non-functional. Recently, Ψs have been shown to play regulatory roles in gene expression by acting as a source of small interfering RNAs or sequestering microRNAs.…
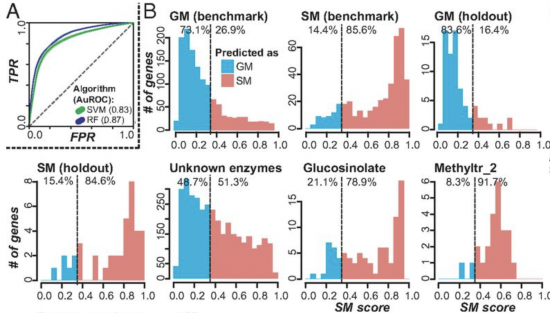
Metabolism gene prediction using diversiform molecular features (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAdvances in sequencing technologies enable scientists to obtain molecular features of genes in high-dimensionality. Features of individual gene like expression, methylation, histone modification, evolutionary signals and sequence itself provide high resolution for distinguishing annotated genes. In plant…
Understanding leaf shape development and diversity in Brassicaceae (New Phytol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany economically important crops are in the Brassicaceae family, such as cabbage, mustard, and the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Recently, the systematics of Brassicaceae has assigned most of the species to 52 monophyletic groupings (tribes). However, relationships along the backbone of the phylogeny…
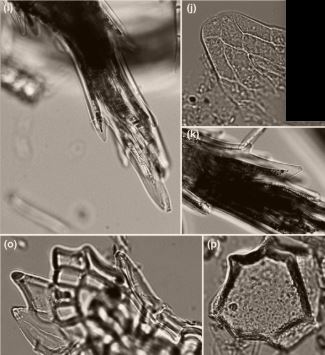
Evolution of phytolith deposition in modern bryophytes (New Phytol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen monosilicic acid is present in the soil, many plants absorb it through their roots and precipitate rigid silica aggregates known as phytoliths. Phytolith deposition has been observed in all major groups of vascular plants, however the patterns of deposition in bryophytes are comparatively under…
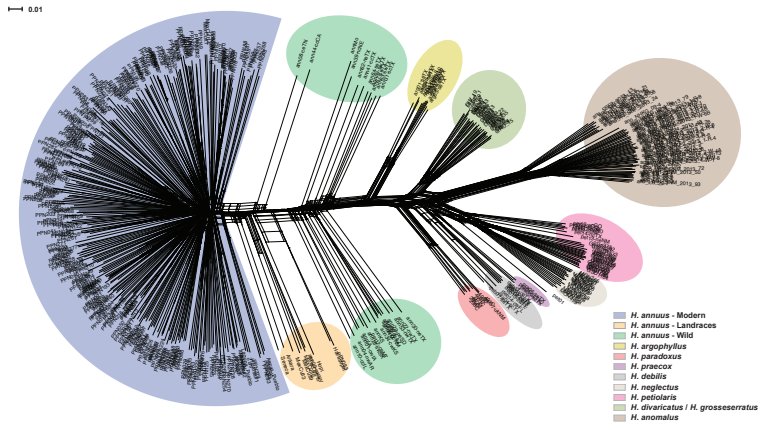
Sunflower pan-genome, evidence for hybridization-altered disease resistance ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklySunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) is an important oil-producing crop, which was domisticated in North America about 4000 years ago with elite varities being developed through the 19th and 20th centuries, narrowing its genetic variation. It retains the ability to hybridize with wild relatives, providing…
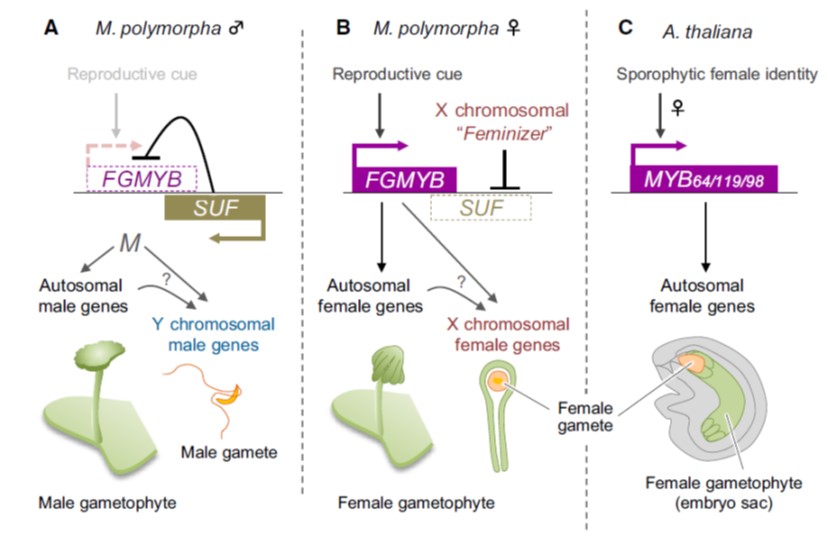
A bidirectional switch controls sexual dimorphism in the liverwort (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBryophytes spend most of their lifecycle in the haploid, gametophytic form, of which there are two types, male (sperm forming) and female (egg forming). Hisanaga et al. investigated the genetic basis that determines sex in the model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. Their findings are fascinating. A single…
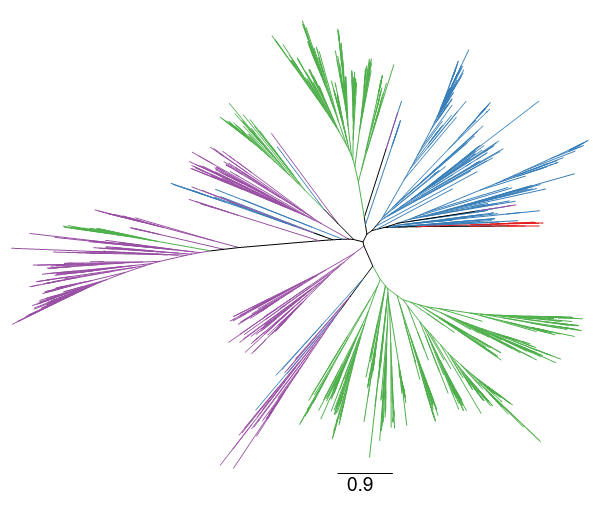
The Terpene Synthases of Red Algae Have a Bacterial Origin
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe red algae (Rhodophyta), encompassing over 8,000 species, are the richest source of marine secondary metabolites. Among red algae, many genera produce terpenes, which constitute the largest class of secondary metabolites. Despite the rich diversity of terpenes in red algae, little is known about how…
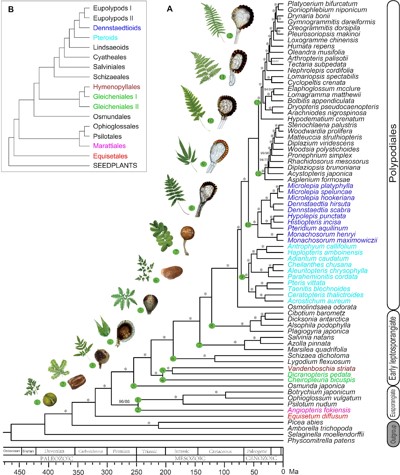
Large-scale phylogenomic analysis resolves a backbone phylogeny in ferns (GigaScience)
Plant Science Research Weekly
A look back at the most popular articles shared on Plantae social media in 2018.
Plantae Social Media Interns Katie Rogers and Juniper Kiss have been reviewing the 2018 stats. Previously they shared the most popular posts overall. Here, they share the posts to research and review articles that…

