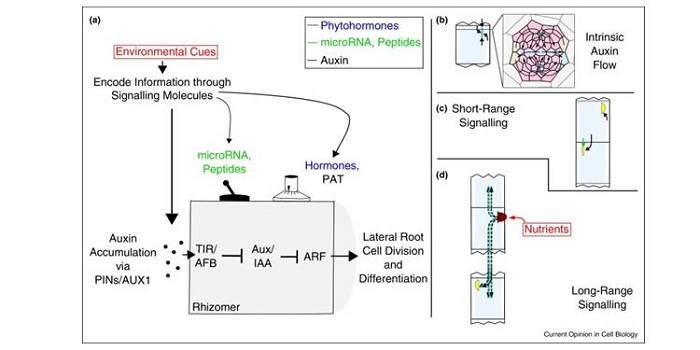
Review: Root branching plasticity: collective decision-making results from local and global signalling
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Roots are extraordinary examples of developmental plasticity, and hundreds of papers have reported on the mechanisms by which root system architecture responds to the environment and the global nutritional status of the plant. McCleery et al. propose a model that synthesizes evidence of intrinsic, local…

TOPLESS mediates brassinosteroid control of shoot boundaries and root meristem development
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSteroids play a role as essential hormones in plants as well as in animals. In plants, steroids termed brassinosteroids (BR) regulate plant growth and development. BR has been shown to be involved in many processes such as light response, stomata and root development, and flowering in plants. BR-regulated…
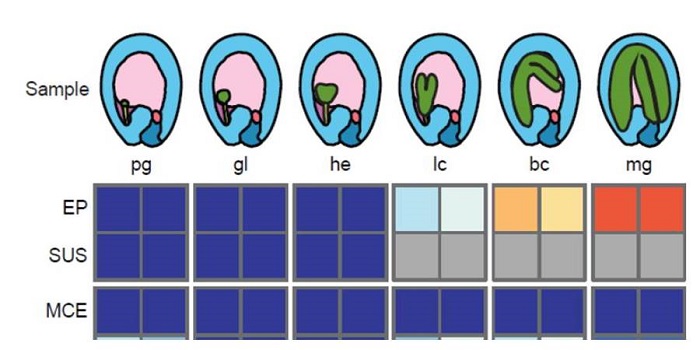
Commentary: Widespread contamination of Arabidopsis embryo and endosperm transcriptome datasets
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchKnowing where a gene is expressed provides valuable information about its function, but that information is compromised if the RNA source is contaminated by other tissues. Schon and Nodine investigated the extent to which Arabidopsis embryo and endosperm transcriptome datasets are affected by tissue…

Review: The evo-devo of plant speciation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSpeciation events result from a combination of molecular, environmental and stochastic (random) factors. Several models developed in the last 150 years help to explain how species emerge, but more recently evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) approaches give us tools to decipher plant speciation.…
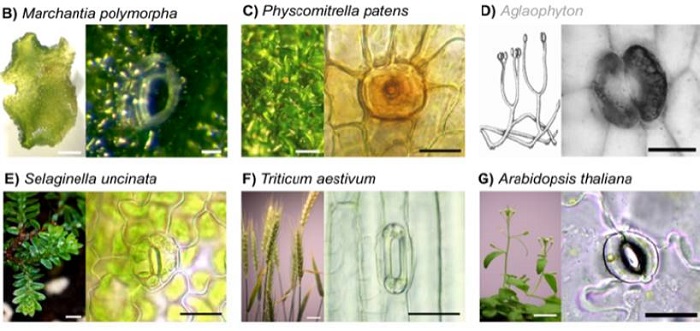
Update: Origins and evolution of stomatal development
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Updates, ResearchThe fossil record suggests stomata-like pores were present on the surfaces of land plants over 400 million years ago. Whether stomata arose once or whether they arose independently across newly evolving land plant lineages has long been a matter of debate. In Arabidopsis, a genetic toolbox has been identified…
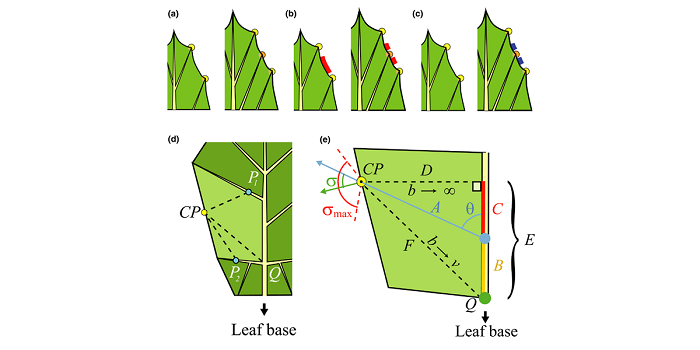
A common developmental program can produce diverse leaf shapes
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe plethora of diverse leaf shapes results from variations of shared molecular mechanisms that govern leaf growth and development. To better understand the molecular underpinnings of diverse leaf morphologies, Runions et al. constructed a computational model of leaf development that included multiple…
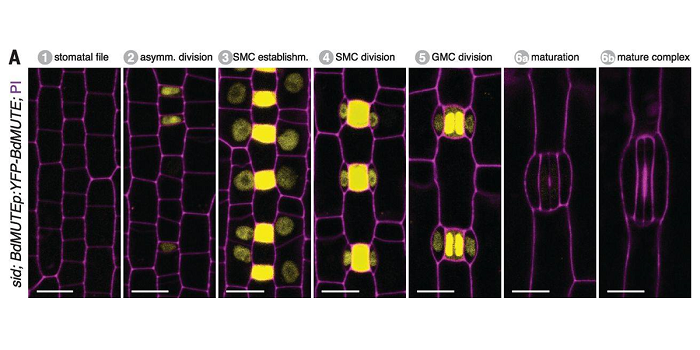
Mobile MUTE specifies subsidiary cells to build physiologically improved grass stomata ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlants breathe through pores called stomata on leaf surfaces. Stomata are the point of contact with the outside world as they allow gas exchange (e.g., CO2 for photosynthesis) and transpiration. Grasses have evolved to form more efficient stomata in which the guard cells are flanked by additional subsidiary…
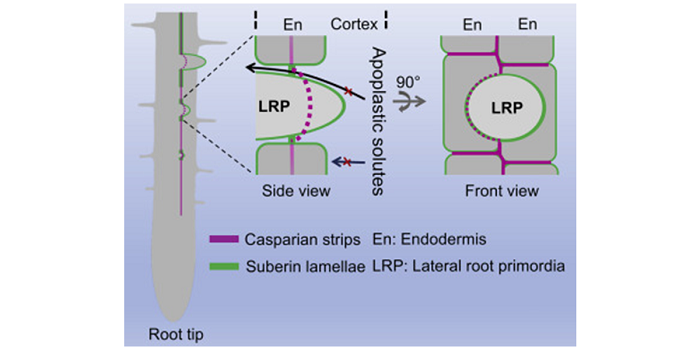
Role of LOTR1 in Nutrient Transport ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCasparian strips, named after the German botanist Robert Caspary who discovered them, are a cellular feature found in the roots of all higher plants. They are ring-like lignin polymers deposited in the middle of anticlinal cell walls (parallel to the root radius) between endodermal cells. Along with…
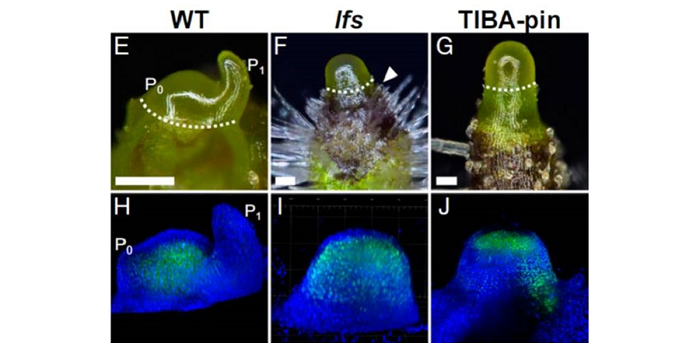
Coordination of auxin-triggered leaf initiation by tomato LEAFLESS ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCapua and Eshed explored the link between auxin and leaf initiation at the shoot apical meristem, using the tomato mutant leafless (lfs), which is an ortholog of the Arabidopsis DORNRONSCHEN (DRN) and DRN-like (DRNL) genes that encode AP2-type transcription factors. The lfs mutant and the drn/drnl double…

