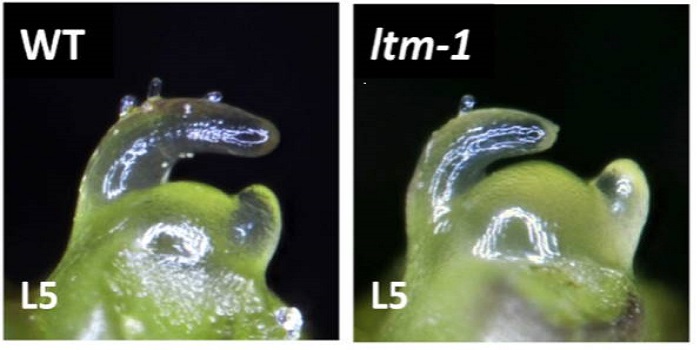
Meristem Doming and the Transition to Reproductive Development in Tomato
Research, The Plant Cell: In Brief0 Comments
/
During vegetative growth, the shoot apical meristem (SAM) produces lateral organ primordia but remains roughly the same size, as WUSCHEL–CLAVATA signaling modulates the balance between cell division and differentiation. During the transition to reproductive growth in many species, the SAM expands in…
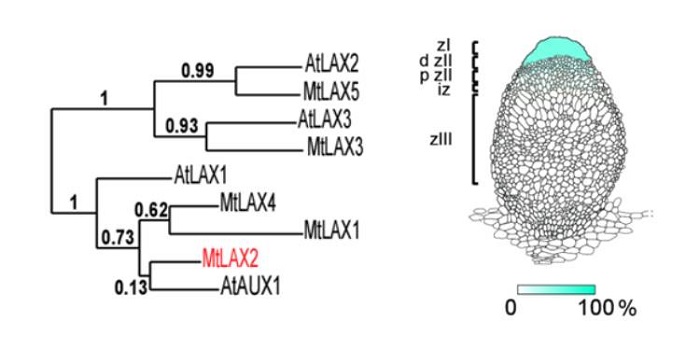
MtLAX2, a functional homologue of the auxin influx transporter AUX1, is required for nodule organogenesis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNodules are specialized structures that form symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing associations with rhizobia on some plants including Medicago truncatula. Previous work has shown that auxin signalling is involved in nodule formation. Roy et al. extend this knowledge through the identification of a Medicago gene…
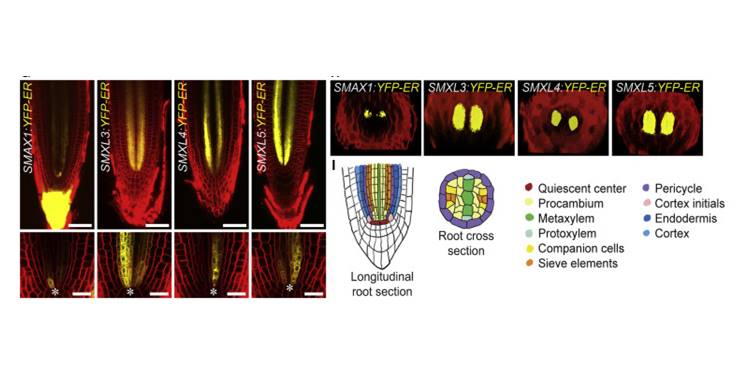
Strigolactone- and karrikin-independent SMXL proteins are central regulators of phloem formation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSMAX1 (SUPPRESSOR OF MAX2 1) was identified genetically as a suppressor of the enhanced seed dormancy phenotype of the max2 mutant, which is affected in both strigolactone (SL) and karrikin (KAR) responses (karrikins are smoke-derived germination promoters). SMAX1 is the founding member of an eight-member…
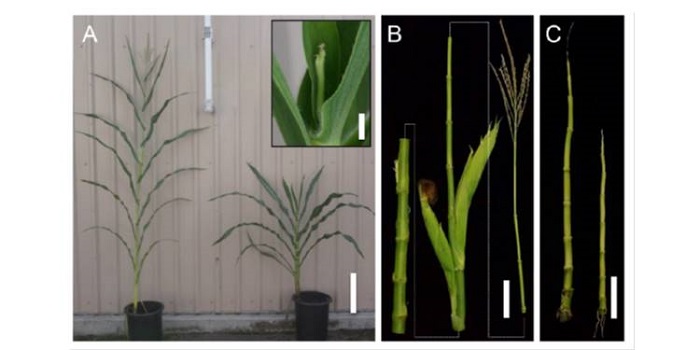
KNOTTED1 cofactors, BLH12 and BLH14, regulate internode patterning and vein anastomosis in maize
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe maize shoot comprises modular domains of leaf, subtending shoot tissue, and an intercalary meristem that sits just above the next leaf down. By contrast to eudicot shoots that form a ring of vascular bundles, maize shoot vascular bundles remain as separate bundles, forming a “disordered” atactostele.…

Transcription factor interplay between LEAFY and APETALA1/ CAULIFLOWER during floral initiation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSeveral transcription-factor encoding genes involved in the transition from vegetative to reproductive growth have been identified. One of these, LEAFY (LFY), is expressed at the flanks of the inflorescence meristem at the site of newly forming floral meristems; loss-of-function lfy mutants produce leaves…

Special issue: Flowering of jasmonate research
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchJasmonates are a family of compounds including jasmonic acid and its derivatives that regulate many plant processes from germination to defense. The Journal of Experimental Botany has a special issue on jasmonate research, which commemorates the advances in this field in the ten years since the JAZ proteins…

BRC1 expression regulates bud activation potential, but is not necessary or sufficient for bud growth inhibition in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchShoot branching patterns are determined by whether lateral buds are activated or inhibited. Classic studies showed that auxin transport both in the stem and from the bud affects bud outgrowth, and more recent studies have demonstrated a role for strigolactones in regulating bud outgrowth, probably through…
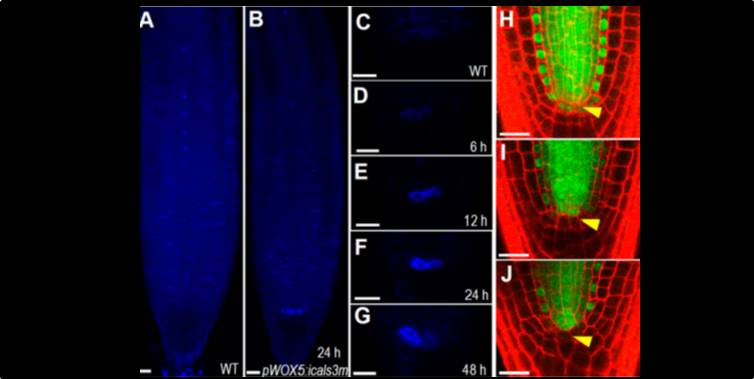
Symplastic communication spatially directs local auxin biosynthesis to maintain root stem cell niche in Arabidopsis ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAlthough plant cells are surrounded by walls, cytoplasmic strands connect adjacent cells through junctions called plasmodesmata. Liu et al. investigated the contributions of plasmodesmata to signaling between root quiescent center (QC) cells and the cells that surround the QC by expression of an inducible…
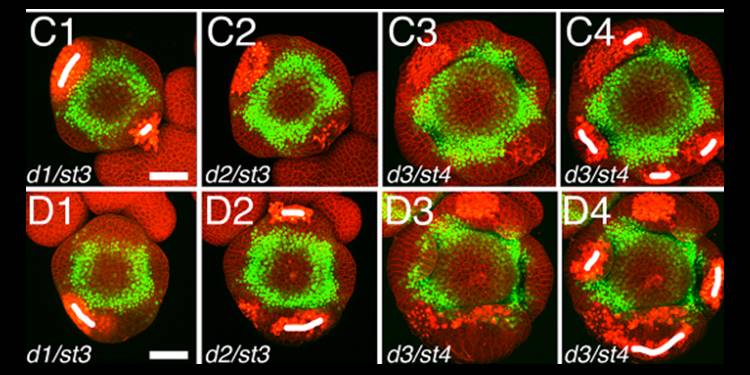
Live Confocal Imaging of Developing Arabidopsis Flowers
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMonitoring cells and their activities in real time provides exceptional insights into their mechanisms and strategies of growth. Prunet has used live confocal imaging of Arabidopsis flowers to study the placement of floral organs and the dynamics of floral stem cells. Here, he presents a detailed protocol…

