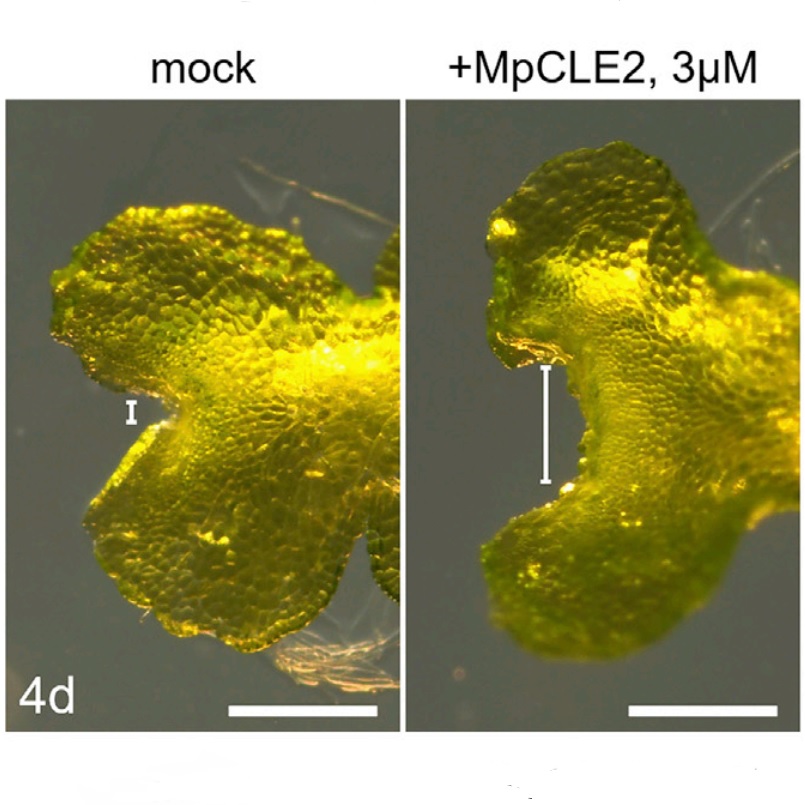
Molecular regulation of meristem development in liverworts (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants grow through meristems, pools of undifferentiated cells that produce and develop into all varieties of cell types. Flowering plants such as Arabidopsis regulate meristematic cell division through CLAVATA3/EMBRYOSURROUNDING REGION-related (CLE) peptide signaling, but the molecular mechanisms in…
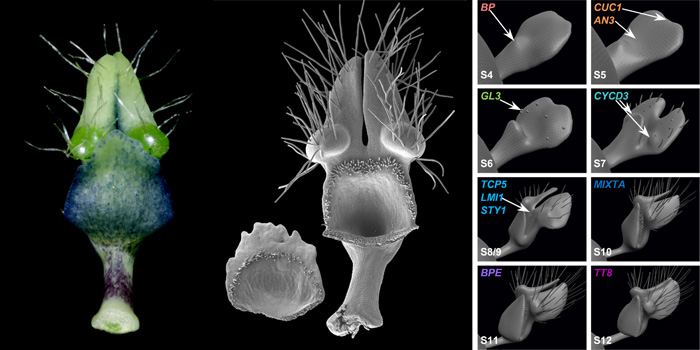
Towards Uncovering the Developmental Mechanisms of Elaborate Petals: Nigella damascena as a Beginning
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. explore the mechanisms underlying elaborate petal development and specialized character formation in Nigella damascena. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00330
By Rui Zhang, Xuehao Fu, Caiyao Zhao, Jie Cheng, Hongyan Shan, and Hongzhi Kong
Background: Petals can be simple or…
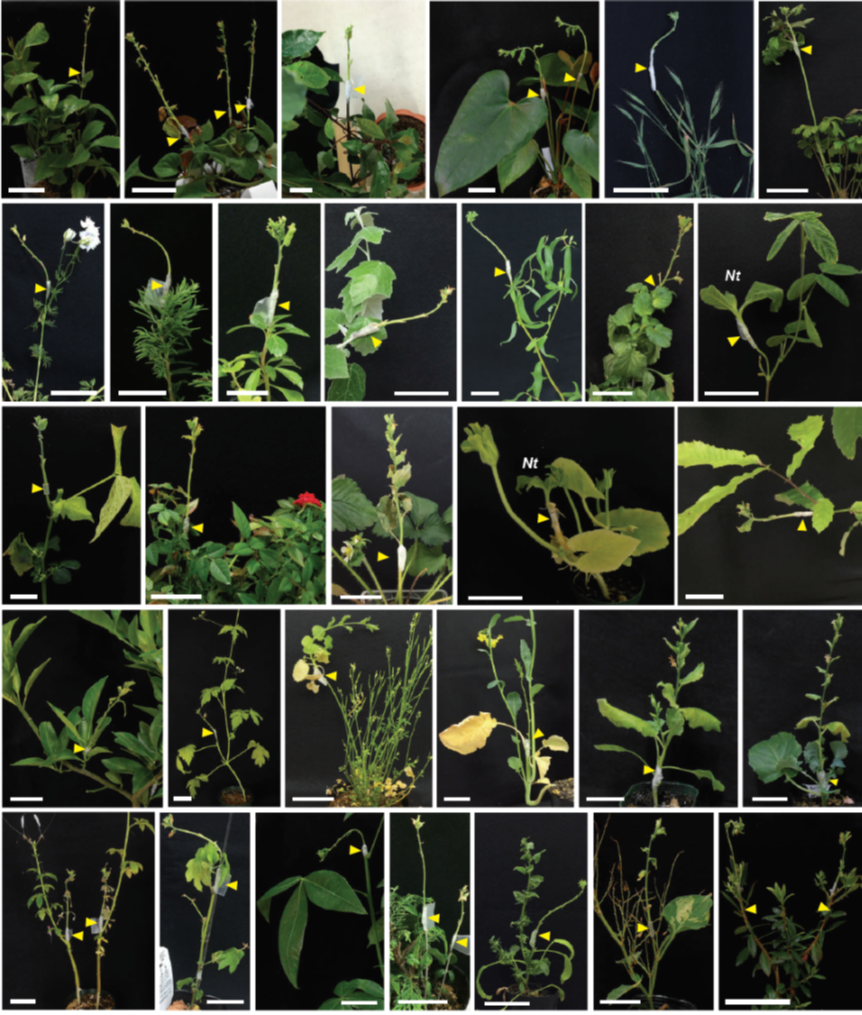

Cell-cell adhesion in plant grafting is facilitated by b-1,4-glucanases (Science) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant grafting has been used in crop improvement for centuries and more recently to study systemic and long-distance signaling in the plant vascular system. In order to better understand graft compatibility and its mechanism, Notaguchi et al. used Nicotiana to study interfamily graft combinations. Interfamily…
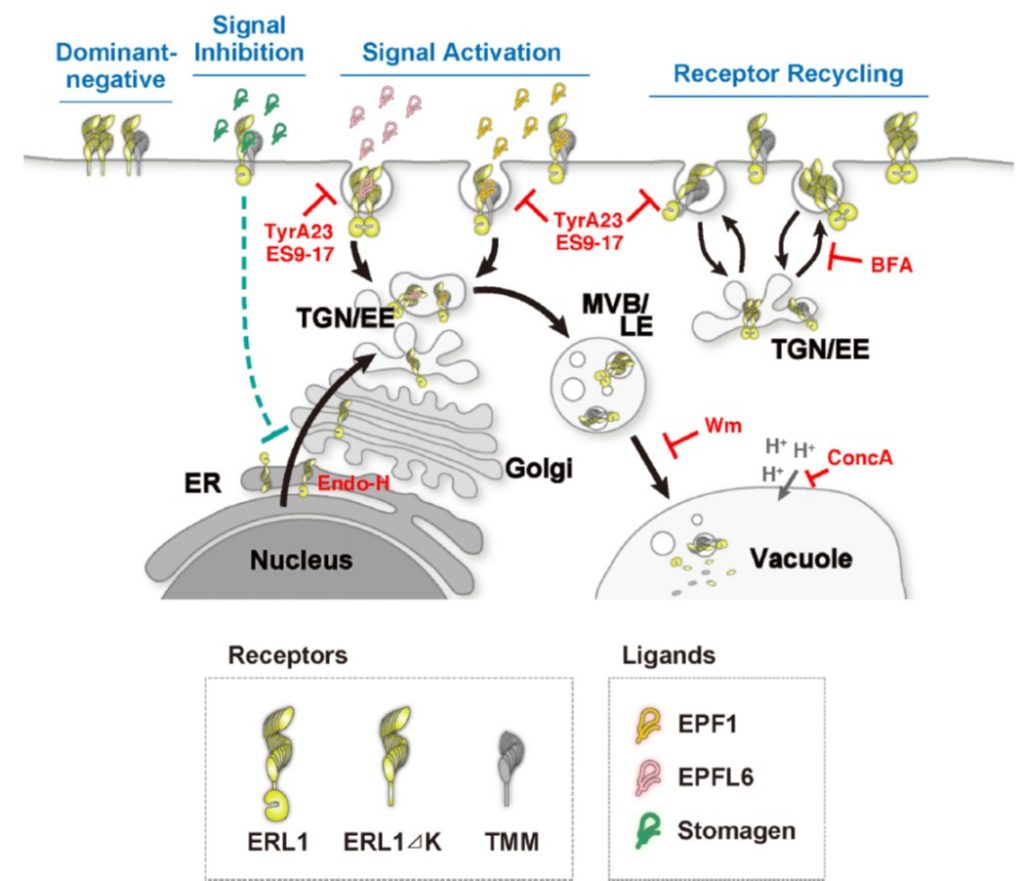
The manifold actions of signaling peptides on subcellular dynamics of a receptor specify stomatal cell fate (eLife)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomatal development requires cell-to-cell communication and follows one cell spacing, with a minimum of one cell space between two stomata. Key to this communication are the ERECTA and ERECTA LIKE (ERL) Leucine-Rich Repeat domain-Receptor Like kinases (LRR-RLKs) and their ligands, the EPIDERMAL PATTERNING…

DNA damage triggers reprogramming of differentiated cells into stem cells in Physcomitrella (Nature Plants) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWounding and other types of cellular damage, such as DNA damage-induced stem cell death, trigger cellular reprogramming to confer stem cell identity to damage-adjacent cells, thus establishing a new stem cell niche capable of repairing the injury. Studies in angiosperm models have identified the phytohormone…
Lipo-chitooligosaccharides as regulatory signals of fungal growth and development (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring symbiosis, the rhizobia bacteria rely on their lipo-chitooligosachharide signals (LCOs) to associate with plants. This signal is perceived by plant receptor like kinase, LysM-containing receptors which activate the common symbiosis signaling pathway (CSSM). Fungal symbiosis with plants has also…
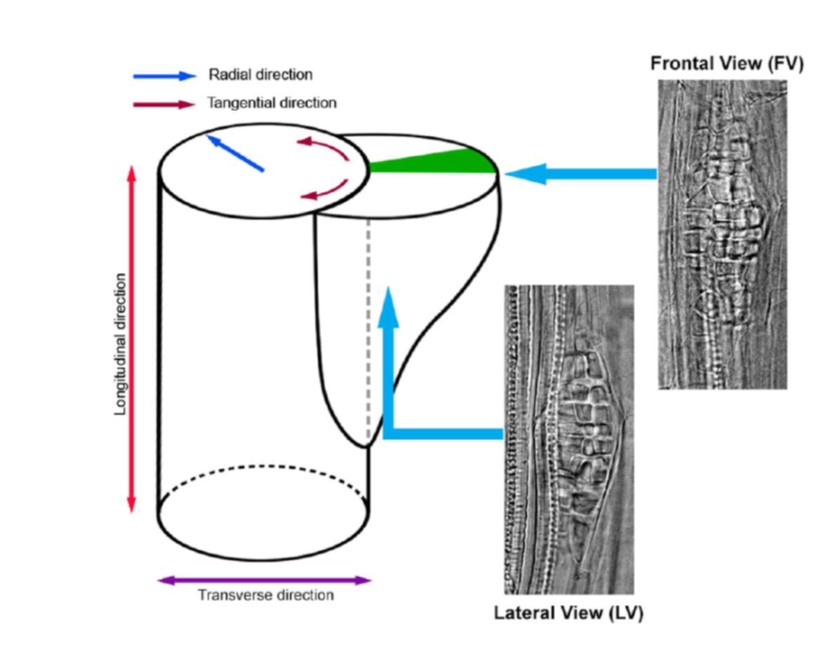
From one cell to many: Morphogenetic field of lateral root founder cells in Arabidopsis is built by gradual recruitment (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBecause plant cells don’t usually move within an organ, it is possible to trace the developmental program cell by cell, through a technique called clonal analysis. If a single cell can be labeled in some heritable way, then all its progeny will also carry this label. Torres-Martínez et al. randomly…
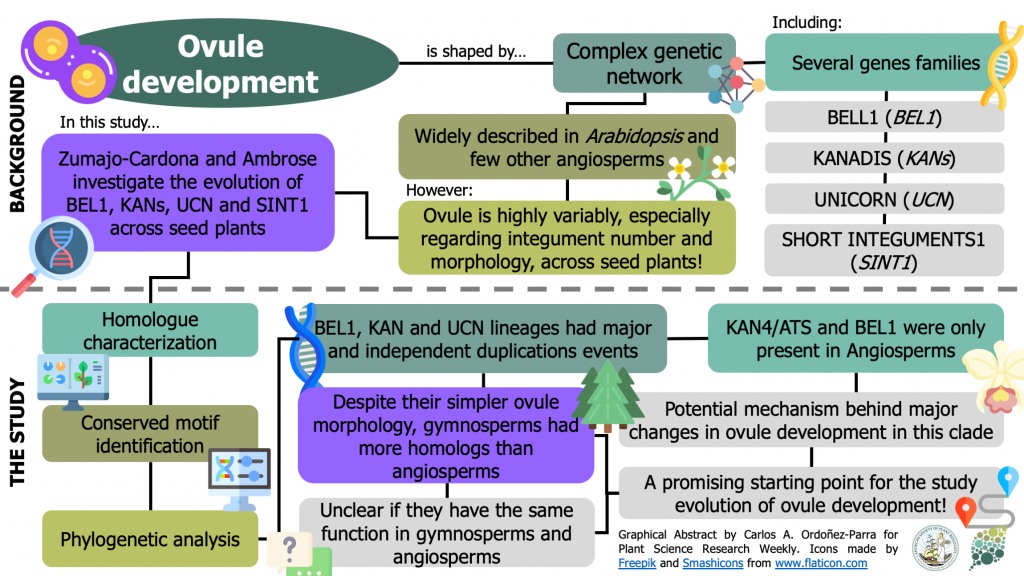
Phylogenetic analyses of key developmental genes provide insight into the complex evolution of seeds ($) (Mol. Phylogenet. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe complex genetic network behind the development of the ovule –the cell that will give place to seeds after fertilization– has been widely described in some model plants. However, ovules hold a high variability in integument number and morphology across seed plants. To understand the genetic mechanism…
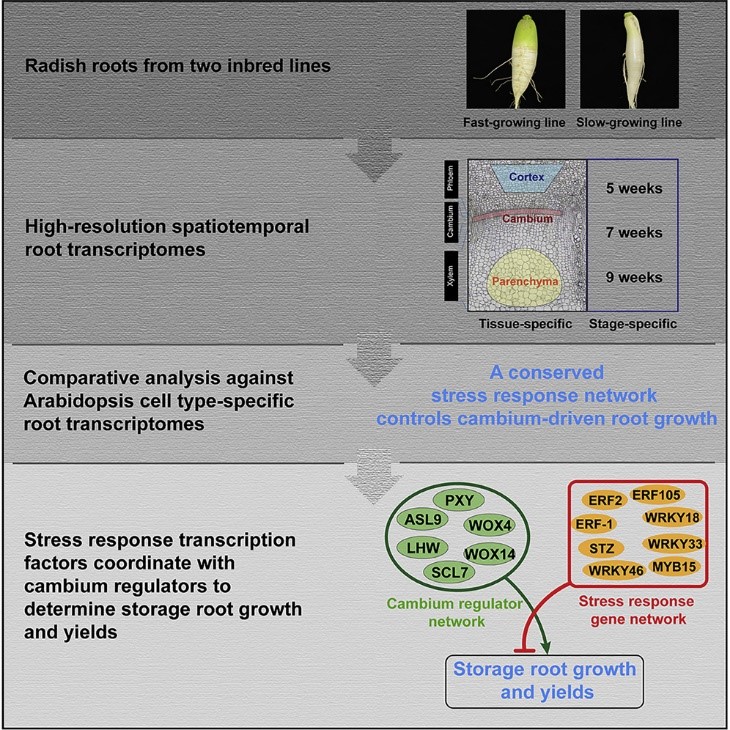
Conserved gene regulatory network integrated with stress response factors in radish and Arabidopsis root cambium (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe cambium is a layer of actively dividing cells between xylem and phloem tissues that is responsible for the thickening of primary or lateral roots and stems. Root crops are tightly associated with the cambium regulatory mechanism which is less characterized in root as compared to shoot development.…

