
miRNA-mediated lateral inhibition controls rhizoid cell patterning in Marchantia polymorpha (Curr. Biol.)
In multicellular organisms, the patterning of different cell types in spatial arrays is regulated through several mechanisms, one of which is lateral inhibition, a process well characterized in metazoans. In this process, an individual cell transmits signals to neighboring cells to instruct a different…
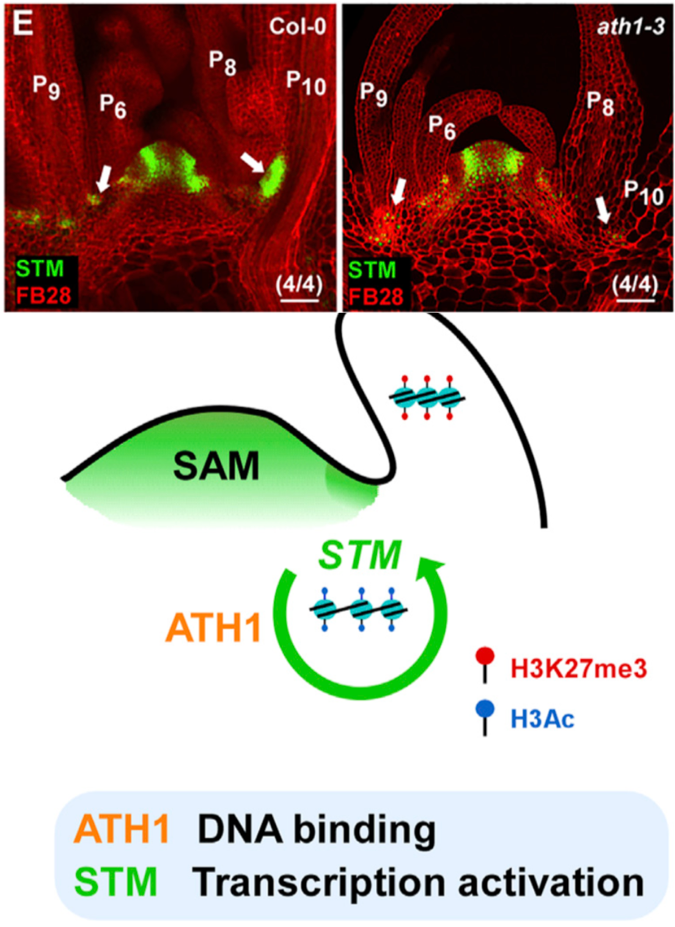
Self-activation loop of STM maintains the meristematic activity of cells at leaf axil (Curr. Biol.)
Plasticity in plant development comes from the meristematic cells that are maintained throughout plant growth and among other things produce lateral organs such as shoot branches. In this paper, Cao et al. show that the self-activation loop of SHOOT MERISTEMLESS (STM), a meristem marker gene that encodes…
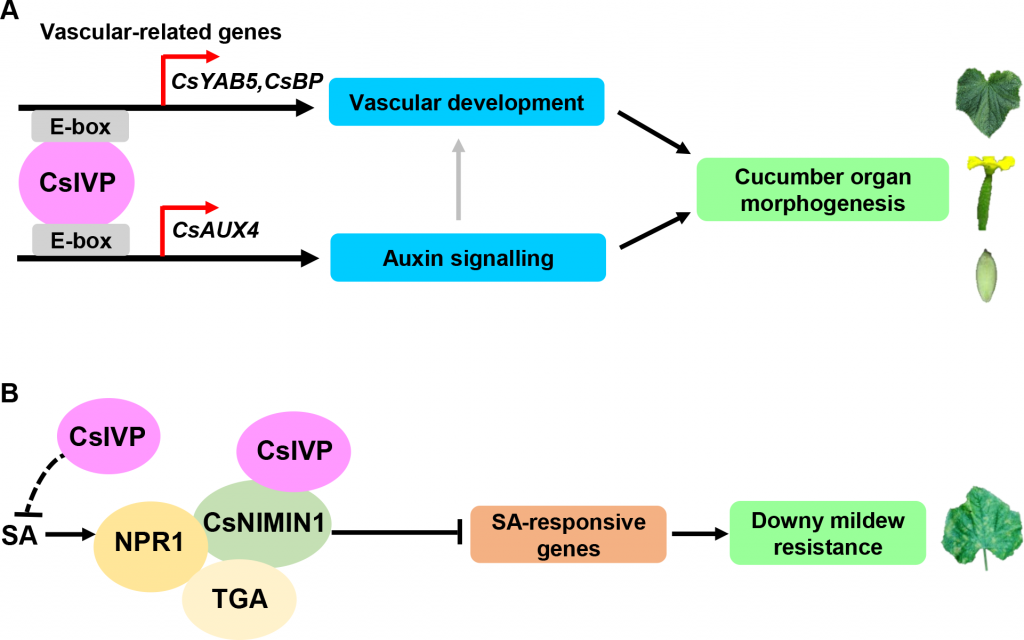
CsIVP functions in vasculature development and downy mildew resistance in cucumber (PLOS Biol)
High yielding crops are often less resistant to pathogens and vice versa, suggesting that there is an underlying mechanism co-regulating development and disease resistance in plants. Yan et al. identified a transcription factor in cucumber (CsIVP) that regulates vascular development and resistance to…
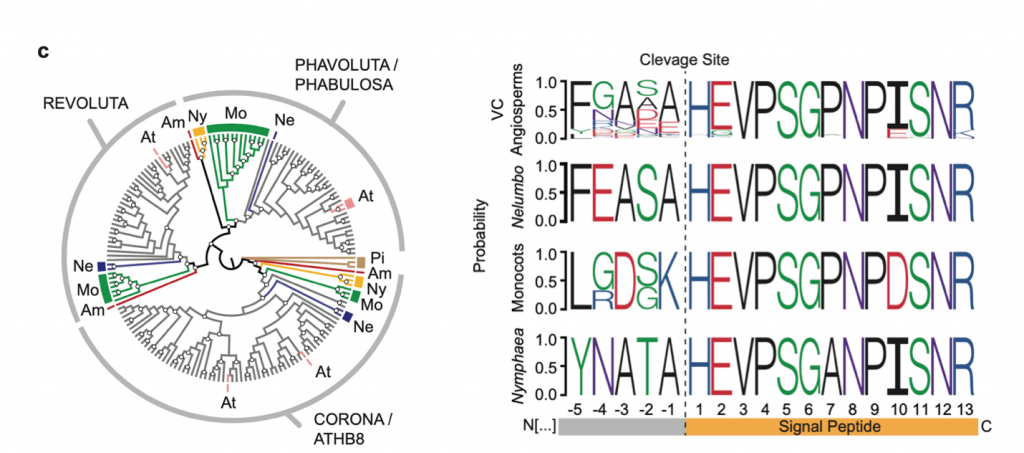
Water lily (Nymphaea thermarum) draft genome reveals variable genomic signatures of ancient cambium losses (bioRxiv)
The vascular cambium, a meristematic tissue responsible for xylem and phloem production, is an ancestral trait in angiosperms, however, its loss has independently occurred in at least 5 flowering plant lineages. One of such is the Nymphaeales, which includes Nymphaea thermarum, an emergent model for…
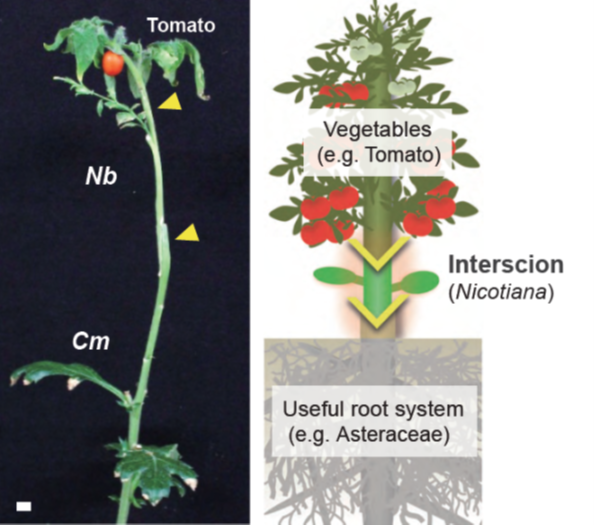
Unlocking interspecies grafting (bioRxiv)
Plant grafting is an agricultural technique that joins plant tissues (e.g., the shoot and root) to confer beneficial traits from one plant to another. Although interfamily grafting is difficult in general, Notaguchi et al. found that Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb) has a strong potential to graft with phylogenetically…
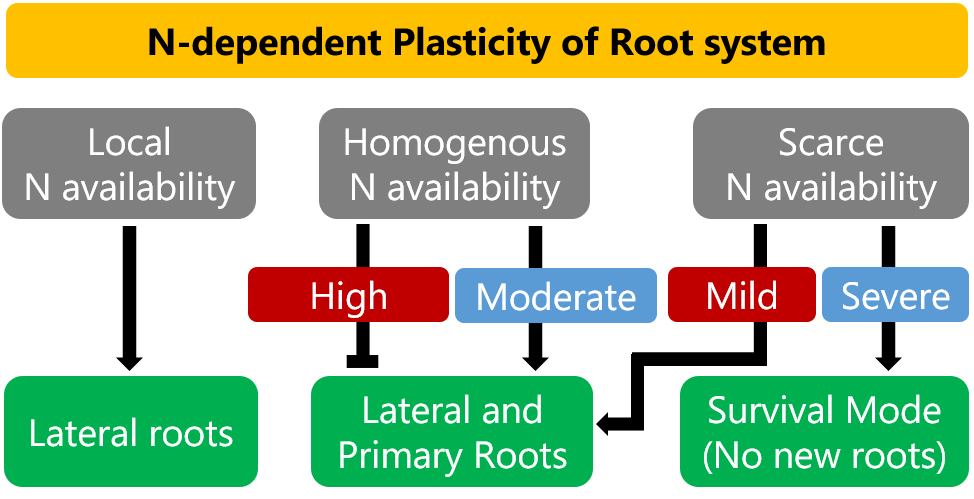
Review. Signalling pathways underlying nitrogen-dependent changes in root system architecture: from model to crop species (J. Exp. Bot.)
Nitrogen (N) is one of the seventeen essential nutrients for a plant to complete its life cycle and is one of the most important determinants of productivity of various crops globally. Nitrate (NO3‑) and ammonium (NH4+) are the major plant-available forms of N. The spatiotemporal heterogeneity of N…
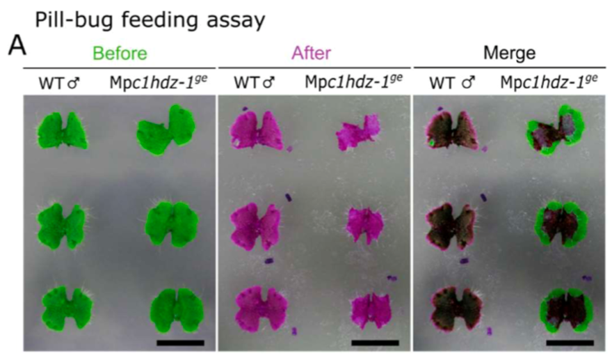
How Marchantia polymorpha avoids bug bites (bioRxiv)
Plants took hundreds of million years to evolve from aquatic to land environments. Biotic and abiotic stress adaptation contributed to the transition. In this preprint, Romani et al. elucidated functions of the transcription factor CLASS I HOMEODOMAIN LEUCINE-ZIPPER (C1HDZ) in the early land plant Marchantia…
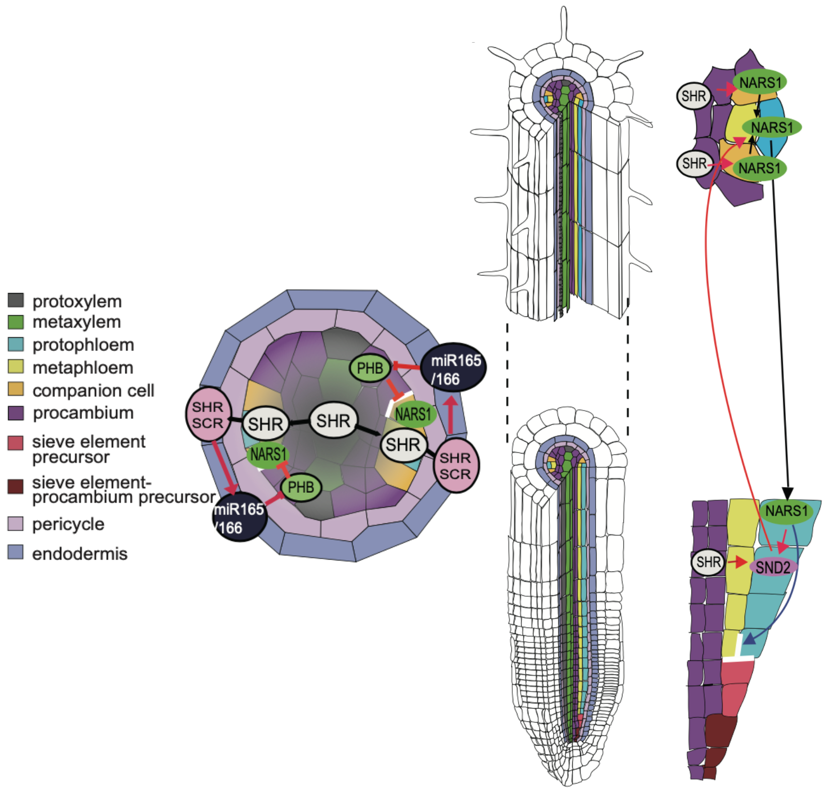
A feedforward loop controls vascular regeneration and tissue repair through local auxin biosynthesis (Plant Cell)
Plant cells are entrapped in rigid cell walls, so morphogenesis relies on asymmetric cell division (ACD) and positional cues to regulate tissue patterning. The Arabidopsis phloem is a good system to study tissue patterning due to its relatively simple composition: sieve elements (SEs) and companion cells…
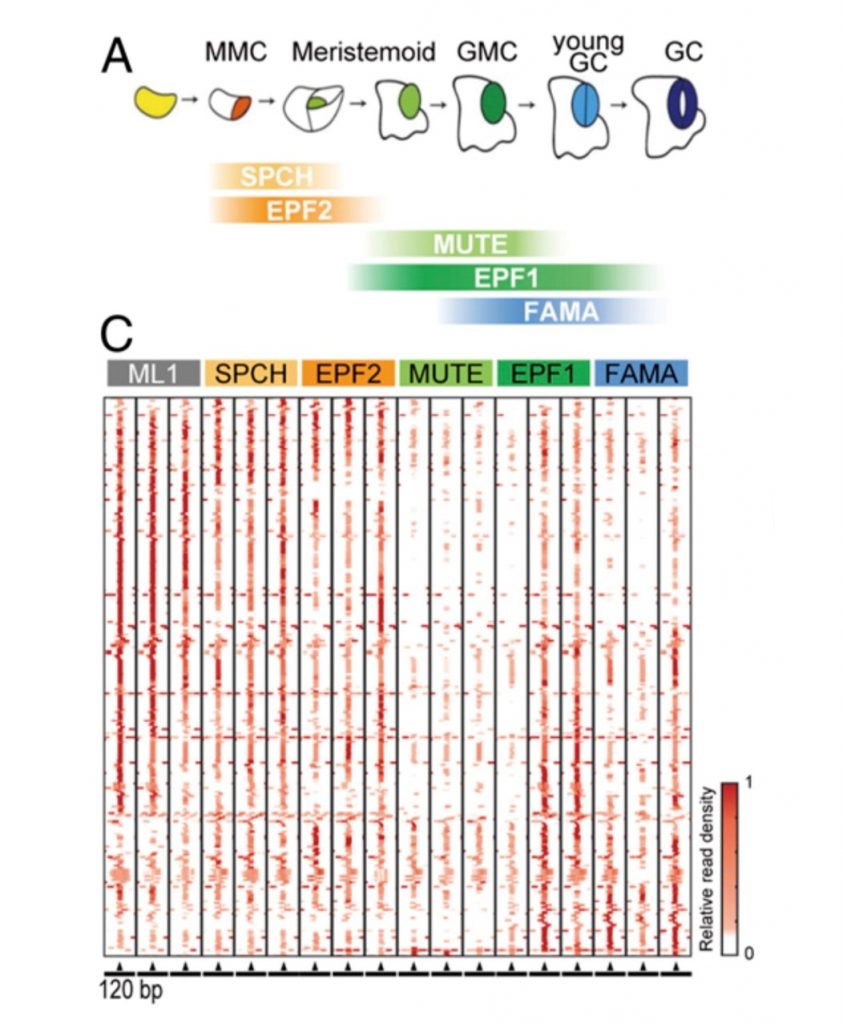
MicroRNAs and the control of stomatal development (PNAS)
Stomata mediate critical functions in plant life: gas exchange, water loss, and some environmental responses. At the molecular level, some bHLH transcription factors and a MAP-kinase pathway control a series of asymmetric and symmetric cell divisions of stomatal stem cells to form a guard cell. In…

