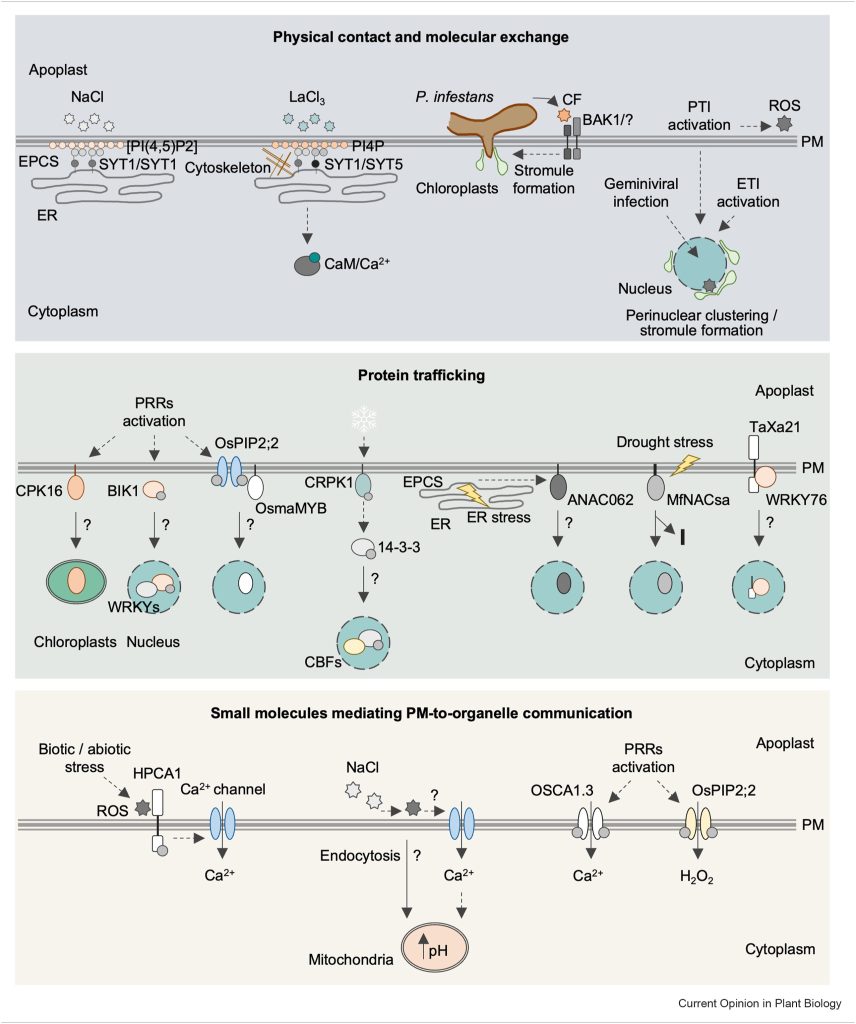
Review: Plasma membrane-to-organelle communication in plant stress signaling (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe plasma membrane (PM) is a critical interface between the cell and its environment and serves crucial sensing and transducing roles. This timely review by Medina-Puche and Lozano-Durán updates exciting new developments in understanding communication between the PM and intracellular organelles, focusing…
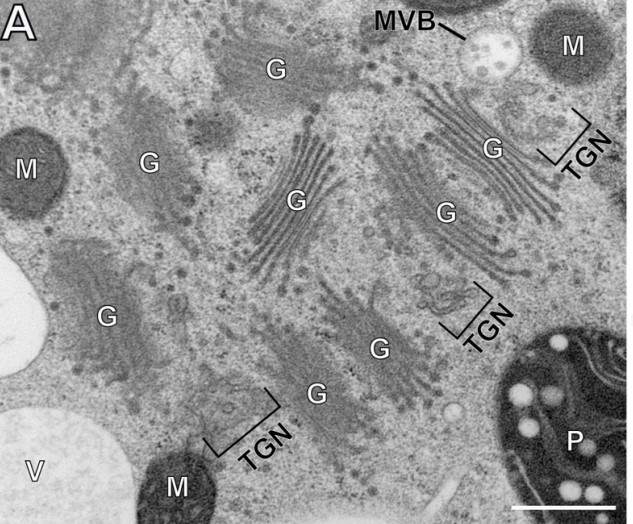
Review. A glossary of plant cell structures: Current insights and future questions (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn a contribution to the January 2022 Plant Cell Focus Issue on Plant Cell Biology, Kang et al. have assembled an updated survey of plant cell structures. This review includes a dozen mini-reviews that describe various compartments or structures within plant cells: the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum,…
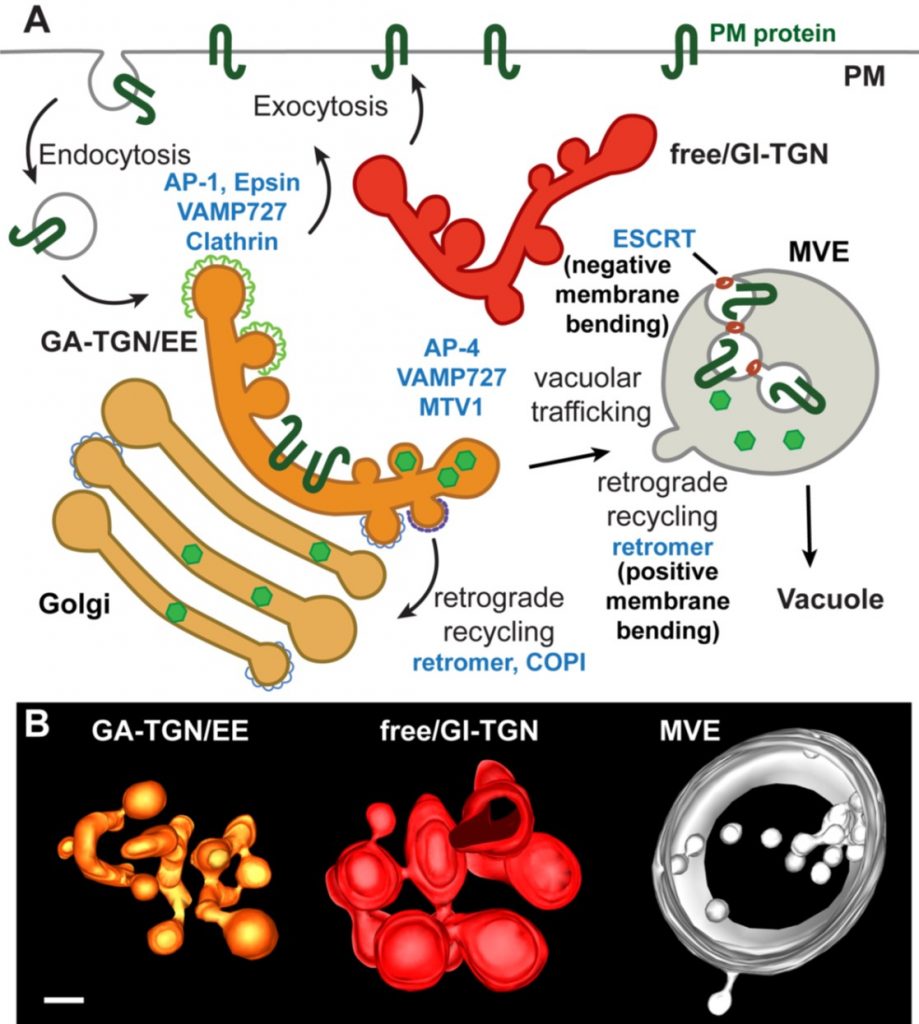
Review: 3D electron microscopy for imaging organelles in plants and algae (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHave you noticed that the quality and resolution of cell images has been getting better and better? Weiner et al. review the recent advances in 3D electron microscopy (EM) technologies that have provided these strikingly beautiful and informative images. Like “classic” transmission EM, EM tomography…
Review: Fifteen compelling open questions in plant cell biology (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs part of The Plant Cell’s upcoming celebration of plant cell biology, Roeder et al. write about fifteen of the “open questions” in the field. This, and the other reviews that make up the focus issue, provide valuable insights into the leading edge of the discipline. Among the questions posed:…
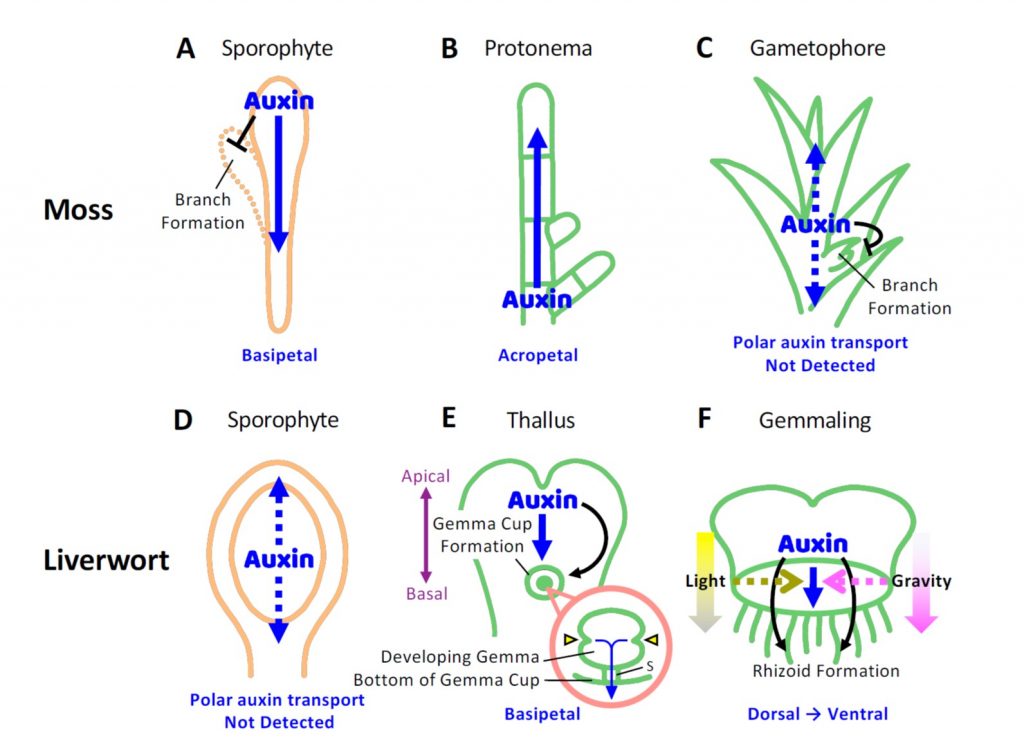
Review: Bryophytes as model systems for studying evolutionary cell and developmental biology (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe development of Arabidopsis as a model system greatly advanced the field of plant cell biology by bringing in molecular approaches, so much of our conceptual foundation rests on studies from angiosperms. More recently, model bryophytes, particularly Marchantia polymorpha (liverworts) and Physcomitrium…

URM Plant Scientist Highlights - Manuel Mora (he/him)
BlogManuel Mora (he/him) is a doctoral student in the Molecular Biology Interdepartmental Developmental Program (MBIDP) at UCLA. Born in Santa Ana, CA, Manuel was raised between California and the town of Santiago Tangamandapio in Michoacan, Mexico. Growing up he enjoyed playing soccer, but when living…
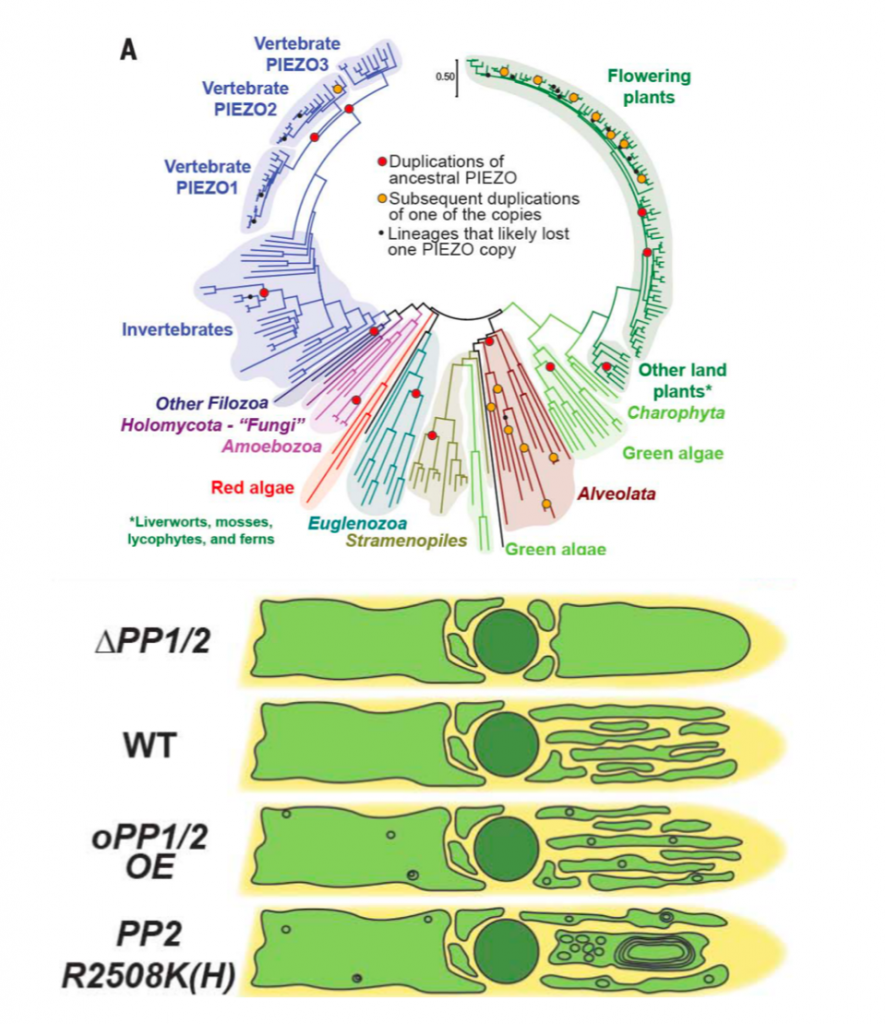
Plant PIEZO homologs modulate vacuole morphology during tip growth (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability to perceive and respond to mechanical stimuli and forces, such as gravity or touch, is an extremely well conserved property that is key for proper cellular function. This ability is fueled by mechanosensitive ion channels activated by mechanical disturbances in the membrane, which leads to…

A slicing mechanism facilitates host entry by plant-pathogenic Phytophthora (Nature Microbiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA plant has many layers of defense against a pathogen. One of the first challenges a pathogen faces is how to get inside the plant. Some bacteria sneak in through open stomatal pores, and some fungi form high-pressure appressoria that burst through walls. Here, Bronkhorst et al. investigated how the…
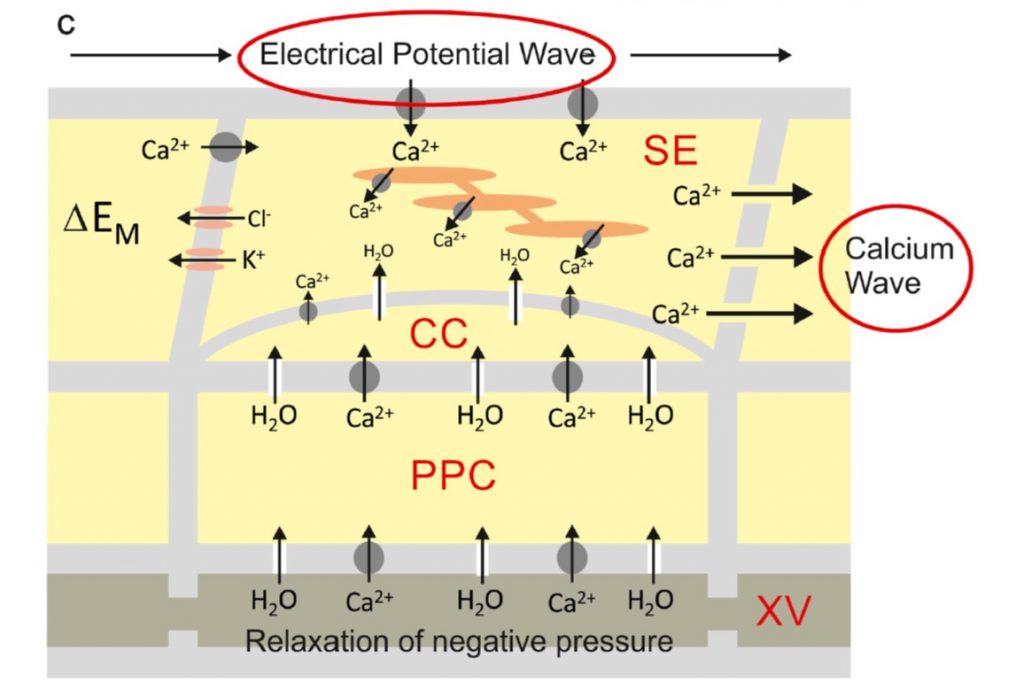
Opinion: Plants have neither synapses nor a nervous system (J. Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe question “Are plants intelligent?” is raised regularly, with answer often “Well, it depends how you define intelligence.” Another interesting question is whether or not plants have cellular structures that are analogous to those that make up the animal nervous system. Robinson and Draguhn…

