
A slicing mechanism facilitates host entry by plant-pathogenic Phytophthora (Nature Microbiol)
A plant has many layers of defense against a pathogen. One of the first challenges a pathogen faces is how to get inside the plant. Some bacteria sneak in through open stomatal pores, and some fungi form high-pressure appressoria that burst through walls. Here, Bronkhorst et al. investigated how the…
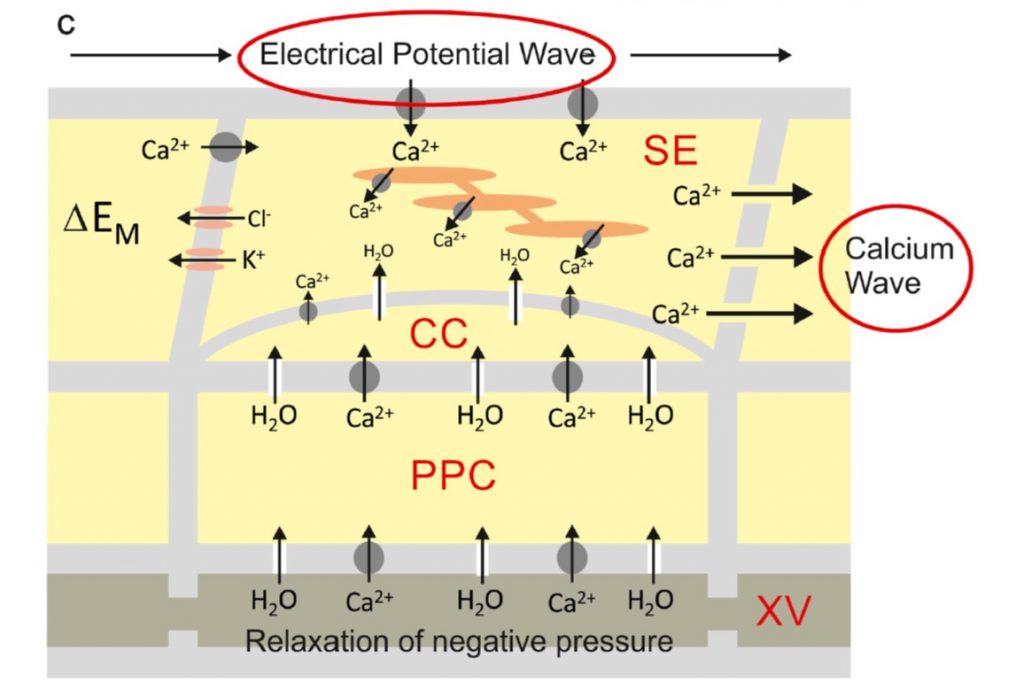
Opinion: Plants have neither synapses nor a nervous system (J. Plant Physiol)
The question “Are plants intelligent?” is raised regularly, with answer often “Well, it depends how you define intelligence.” Another interesting question is whether or not plants have cellular structures that are analogous to those that make up the animal nervous system. Robinson and Draguhn…
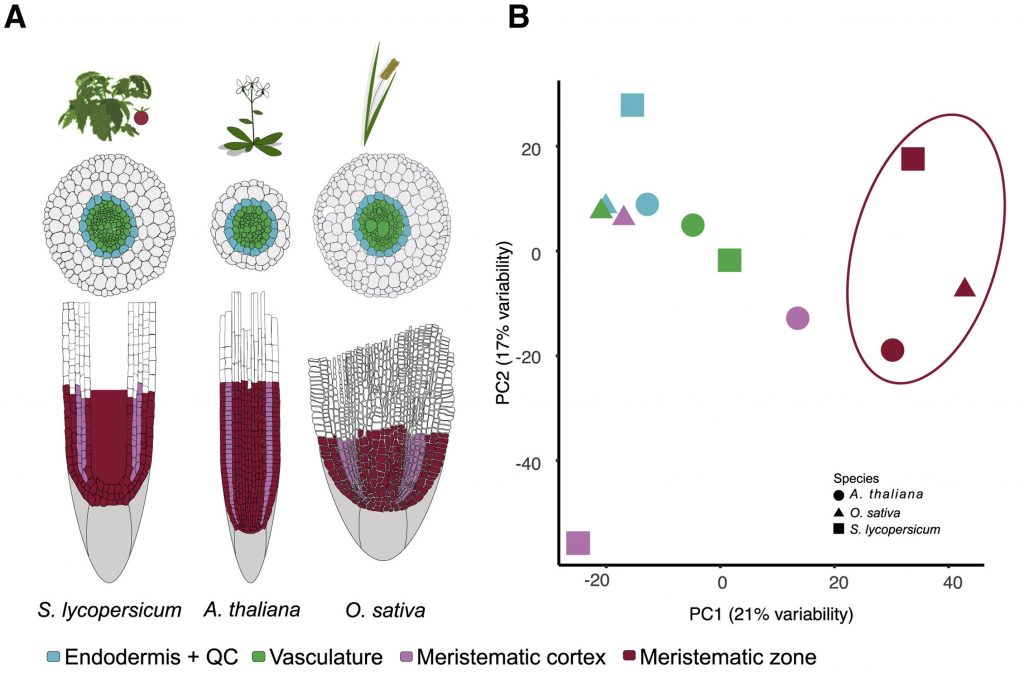
Innovation, conservation, and repurposing of gene function in root cell type development (Cell)
Plants demonstrate a gorgeous diversity in cell types to adapt to their unique environments. Certain cell types, such as the epidermal, cortex, and vascular cells within plant roots, or the classically-defined root developmental zones (meristematic, elongation, and maturation), are homologous in angiosperms.…
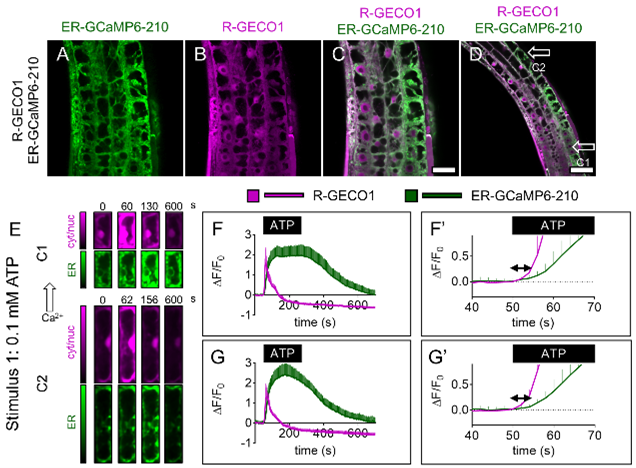
Waves of information: Simultaneous imaging of ER and cytosolic Ca2+ dynamics reveals long distance ER Ca2+ waves in plants (Plant Physiol.)
Calcium (Ca2+) signaling regulates a host of stress and developmental responses in plants. Apart from increases in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]Cyt.), organellar signals play a key role in shaping the cytosolic signaling events. In an attempt to understand the Ca2+ dynamics in the endoplasmic…
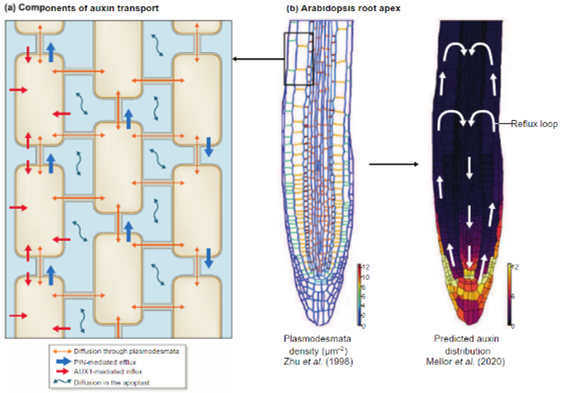
Review: Auxin fluxes through plasmodesmata (New Phytol)
Plasmodesmata, the tubular connections that form continua between neighboring cells in plants, play vital roles in long-distance transport of ions, RNA, proteins, and small molecules. While it is known that plasmodesmata are permeable to phytohormones, including auxin, the physiological significance…
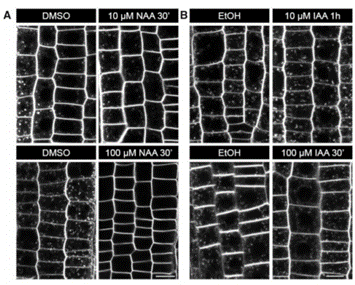
Trapped in traffic – redefining cellular responses to auxin pharmacology (Plant Physiol.)
Understanding cellular responses to the phytohormone auxin has always been a challenge and decades of work has constantly renewed our knowledge of the same. Here, Narasimhan and colleagues attempted to revisit and resolve the basis of differential action of naturally occurring auxin indole-3-acetic acid…

GABA signalling modulates stomatal opening to enhance plant water use efficiency and drought resilience (Nature Comms)
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a non-protein amino acid produced by animals and plants, but is its function conserved across kingdoms? In mammals, GABA acts as chemical messenger in the central nervous system by inhibiting neurotransmission. In plants, GABA accumulates in response to stress but its…
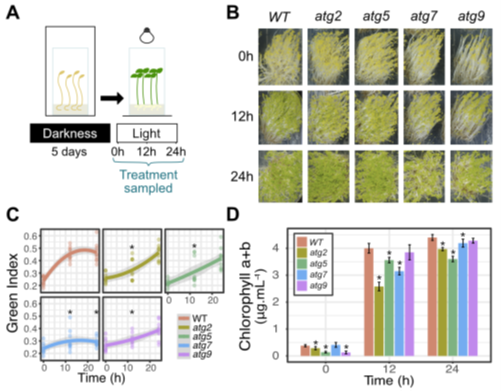
Autophagy promotes photomorphogenesis during seedling development (bioRxiv)
Autophagy is an intracellular evolutionarily conserved catabolic process that degrades cytoplasmic constituents and organelles in lytic vacuoles (micro- and macro-autophagy) or in the cytosol (mega-autophagy). Autophagy can be induced by biotic or abiotic stresses, sugar, carbon and nutrient starvation…
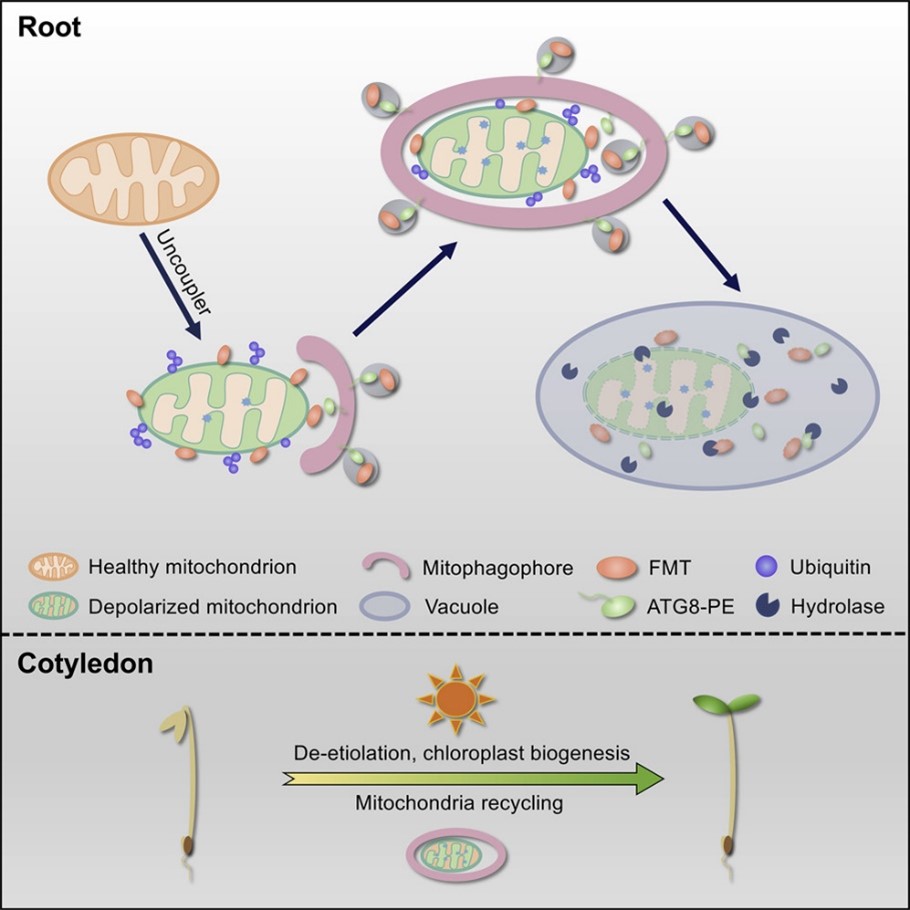
A clustered mitochondria family protein mediates the plant mitophagy (Curr. Biol.)
Mitochondria function as cellular powerhouses to generate energy via oxidative phosphorylation and facilitate the synthesis of essential macromolecules. To protect against proteotoxic stress, damaged mitochondria are selectively removed by autophagy via a process known as mitophagy. In mammalian cells,…

