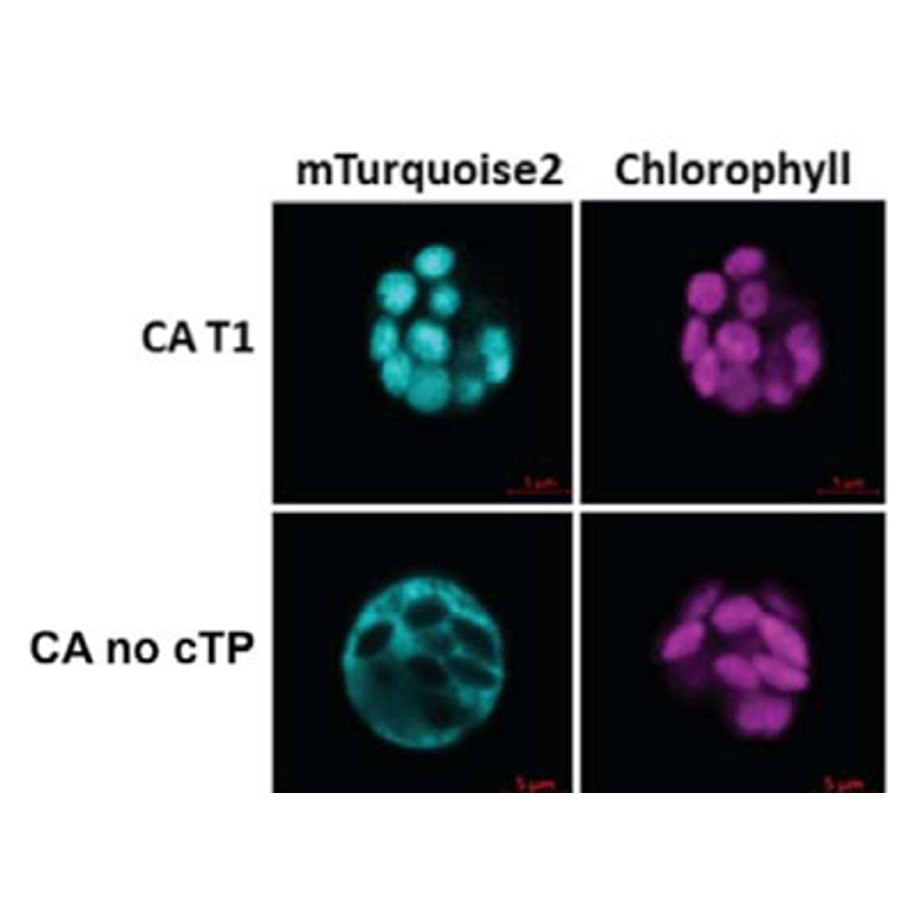
Engineering cytosolic carbonic anhydrase to establish C4 photosynthesis in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn mesophyll cells, carbonic anhydrase is mainly located in the chloroplast, however it is in the cytosol in plants with a C4 carbon concentrating mechanism. There is interest in relocating carbonic anhydrase to the cytosol of C3 plants as a first step in the introduction of a carbon concentrating mechanism.…

Single-nucleus sequencing reveals transition from C3 to C4 photosynthesis
Plant Science Research WeeklySometime in the Cretaceous period (dinosaur time!), some monocots acquired a special pathway for carbon fixation, rendering them more efficient particularly in hot or dry environments. In most monocots, carbon is fixed by Rubisco in the mesophyll cells. In the innovative pathway, carbon fixation is split…
Special issue: Rubisco and its regulation
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase) catalyzes the fixation of atmospheric carbon from CO2 to molecules used for biosynthesis and energy production. Several studies have focused on understanding the nature, complexity, activity, and regulation of Rubisco due to its key role in the production…
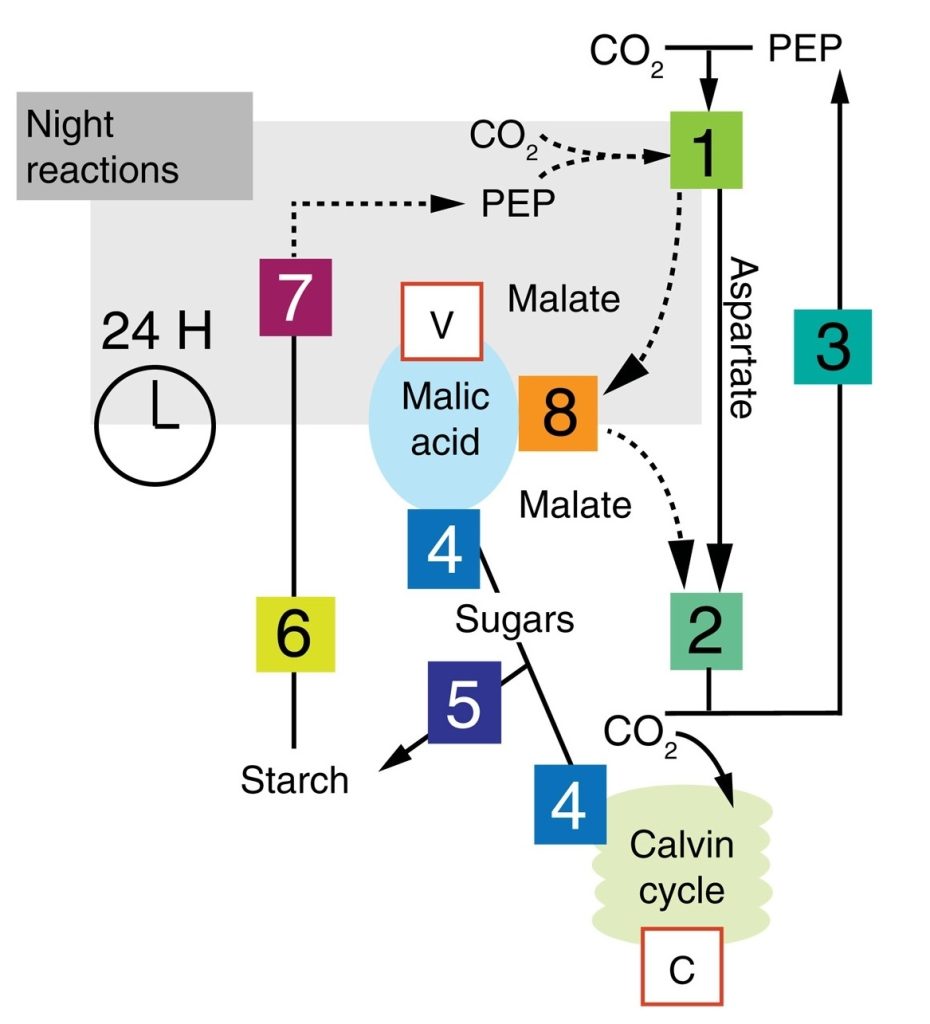
Spatial resolution of an integrated C4+CAM photosynthetic metabolism (Sci. Advances)
Plant Science Research WeeklyC4 and CAM are both photosynthetic strategies that concentrate CO2 upstream of RuBisCO, somewhat uncoupling photosynthetic carbon fixation from transpirational water loss. Both strategies use the enzyme PEP-carboxylase to produce an organic acid, which can then be decarboxylated to provide CO2 to RuBisCO.…

Rubisco accumulation factor 1 and carboxysome biogenesis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Carbon concentration mechanisms (CCMs) refer to a diverse set of strategies by which photosynthetic organisms increase the amount of carbon dioxide available to the carbon-fixing enzyme Rubisco. The cyanobacterial CCM relies on the carboxysome, a membraneless microcompartment with a core of densely…

Conversion of Escherichia coli to generate all biomass carbon from CO2 (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are photosynthetic autotrophs, meaning they use light energy to feed themselves, with carbon dioxide as a carbon source. Heterotrophs like E. coli require organic carbon. Here, Gleizer et al. have rewired the metabolism of E. coli to make it into a (non-photosynthetic) autotroph, meaning it can…
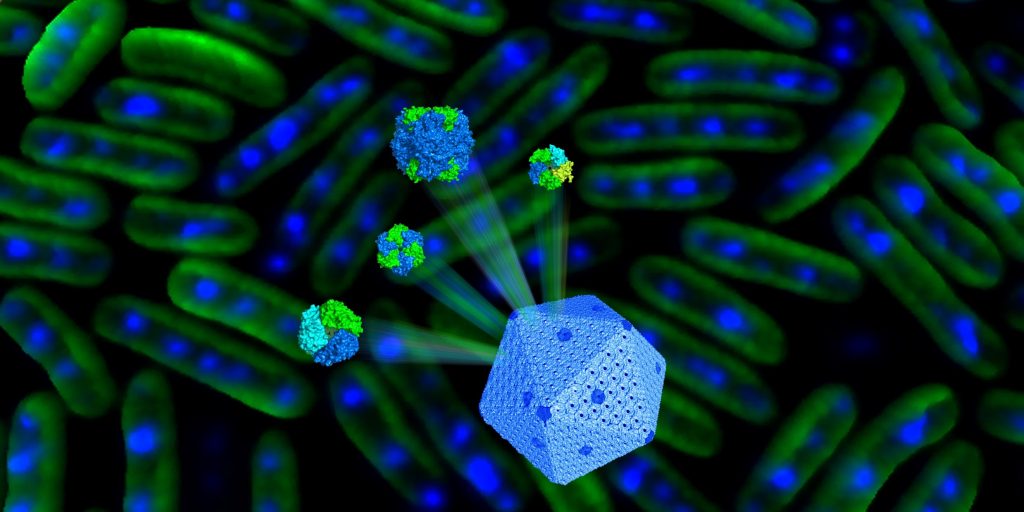
Self-assembling organelles for CO2 fixation: stoichiometry and structural plasticity
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSun et al. investigate how carboxysomes are constructed and regulated in cyanobacteria. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00787
By Luning Liu
Background: All cells are composed of well-defined compartments to encase enzymes and reactions to increase the efficiency of biological processes.…
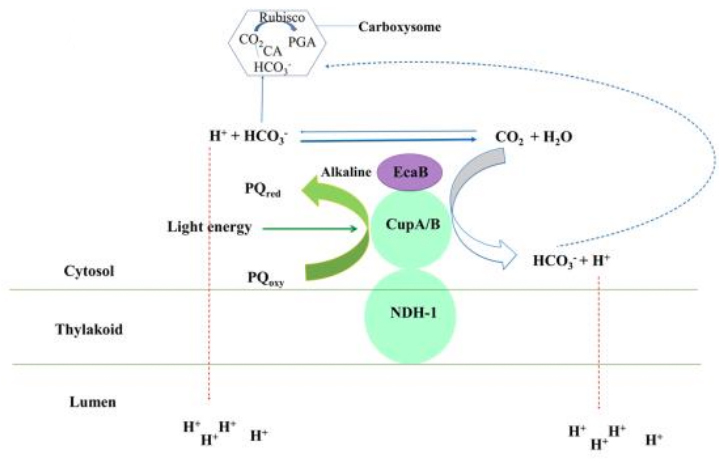
A thylakoid-located carbonic anhydrase regulates CO2 uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism (CCM) is dependent on a continuous supply of inorganic carbon (Ci) to rubisco inside carboxysomes in order to function optimally. CO2 uptake pathways are therefore of great importance for a full understanding of the cyanobacterial CCM. Sun et al demonstrate…

Review: Increasing metabolic potential: C-fixation (Essays Biochem) $
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIncreasing carbon fixation through the Calvin-Benson-Bassham (CBB) cycle is a viable strategy to boost crop yields, as has been demonstrated through both experimental and modelling approaches. In this review, Andralojc et al outline the most recent advancements in this research field. The authors…

