
Striga hermonthica – a beautiful but devastating plant…
GPC Blog, Research0 Comments
/
This week’s post was written by Caroline Wood, a PhD candidate at the University of Sheffield.
When it comes to crop diseases, insects, viruses, and fungi may get the media limelight but in certain regions it is actually other plants which are a farmer’s greatest enemy. In sub-Saharan Africa,…
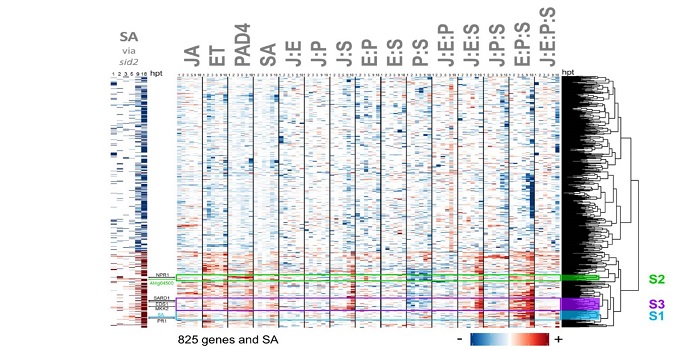
The highly buffered Arabidopsis immune signaling network conceals the functions of its components
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchClassic genetic approaches have been instrumental in identifying genes that control developmental and defense networks, but as Hillmer et al. point out, analysis of single mutants is complicated by network buffering. They describe network buffering as occurring when the effect of losing a gene’s function…
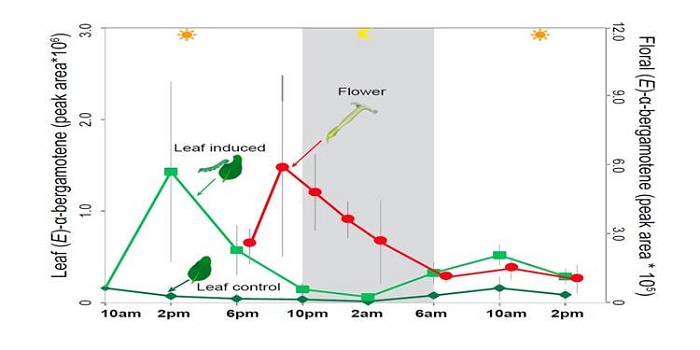
When pollinators are also herbivores ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe interaction between wild tobacco (Nicotiana attenuata) and the moth Manduca sexta, which is both a pollinator and a herbivore, is a model for plant/ arthropod interactions and has revealed insights into chemical signals and defenses. Zhou et al. show that a single compound, the sesquiterpene (E)-α-bergamotene,…

Review: Communication in the phytobiome ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAn old ad stated, “Without chemicals, life itself would be impossible,” but it’s only more recently that we’ve begun to understand the importance of semiochemicals – chemicals produced for communication. Leach et al. pull together insights from chemical ecologists, soil scientists, plant pathologists…

Australia's giant parasitic Christmas tree, with blades sharp enough to cut telephone wire
Blog, Education, Education General, Education General PublicHere's a fascinating plant in honor of Fascination of Plants Day #PlantDay
By Tim Low, published in Australian Geographic
AUSTRALIA HAS A PARASITE believed to be the largest in the world, a tree whose greedy roots stab victims up to 110m away. The Christmas tree (Nuytsia floribunda) has blades…
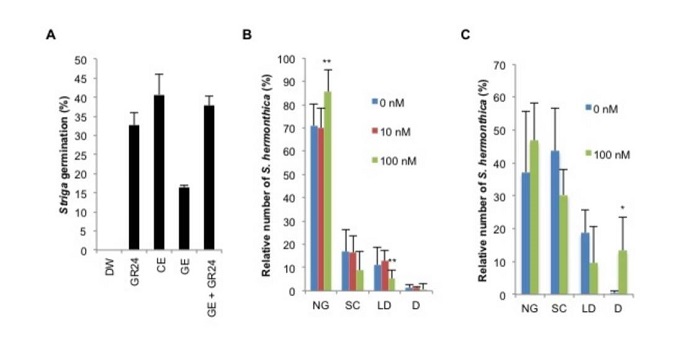
Strigolactone-Gibberellin Cross Talk
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchStrigolactones Root parasitic weeds, such as broomrape (Orobanche spp.) and witchers weed (Striga spp.), are harmful plants in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and Asia that maintain seed dormancy in the absence of host plant. Both parasitic plant species require germination stimulants released from…
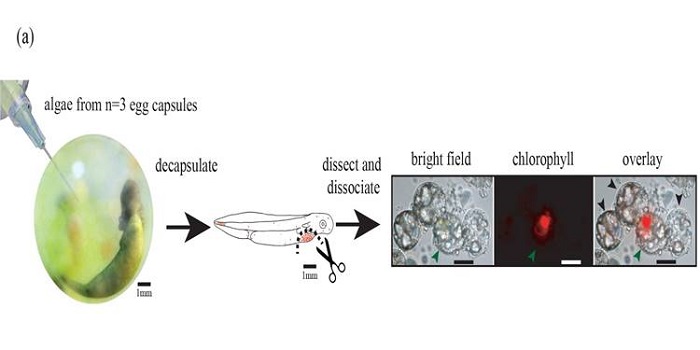
Transcriptome analysis illuminates the nature of the intracellular interaction in a vertebrate-algal symbiosis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchChloroplasts are of course the descendants of ancient endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. While there are examples of photosynthetic bacteria or algae living in animal tissues (e.g., anemones and corals), vertebrate endosymbiosis is rare. One exception is the interaction between a salamander Ambystoma maculatum…
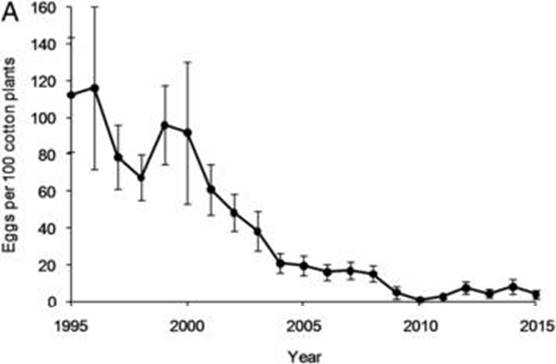
Hybridizing transgenic Bt cotton with non-Bt cotton counters resistance in pink bollworm
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBiotic interactions are complex; any effort by the prey/host to defend against the predator/pathogen provides selective pressure towards overcoming those defenses. As new herbivore control methods are developed they quickly lose effectiveness as the pests evolve resistance; this is true whether the control…

Review: Transfer and engineering of immune receptors to improve recognition capacities in crops
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCell-surface localized immune receptors are one of the ways that plants detect pathogens. Traditionally, these receptors have been introgressed from resistant to susceptible varieties through classical breeding. More recently, it has become possible to use genetic engineering methods to move immune receptor…

