
Snapshot of a TF Network in Plants
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLi et al. investigate a transcription factor network that transmits environmental signals to regulate secondary metabolism in plants. The Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00805.
By Baohua Li and Daniel Kliebenstein
Background: Plants produce specialized secondary metabolites to survive…
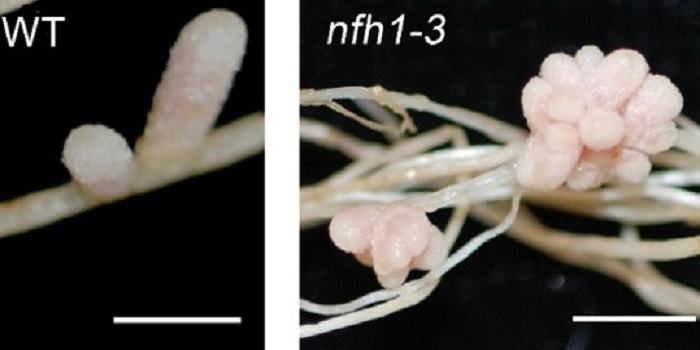
Goldilocks Principle: MtNFH1 Ensures Optimal Nod Factor Activity
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPartner selection is a critical step that must occur early during establishment of Root Nodule Symbiosis (RNS). RNS refers to the mutualistic interaction between legumes and some non-legumes with soil bacteria that help convert atmospheric nitrogen into plant usable ammonia. In legumes such as Medicago…
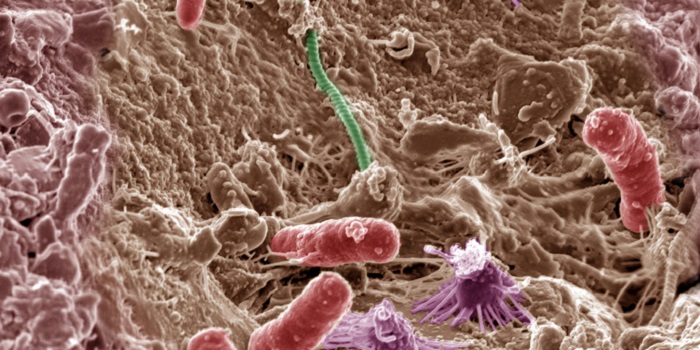
Opinion: Plant pathogen effector proteins as manipulators of host microbiomes? (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTo understand disease development, effector research has mainly focused on the direct interaction of pathogen-derived molecules with plant host targets, or their sensing by surface or intracellular receptors. Recently, attention has turned to the plant microbiome and its key role in maintaining plant…

Review. Rhizobia: From saprophytes to endosymbionts (Nat. Rev. Microbiol.) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogOne of the best characterized plant-bacteria interactions is that between legumes and rhizobia. This review by Poole et al. explores rhizobia in their non-plant associated state (as saprophytes that derive energy and nutrients from organic matter in the soil), through the complex signals that lead to…
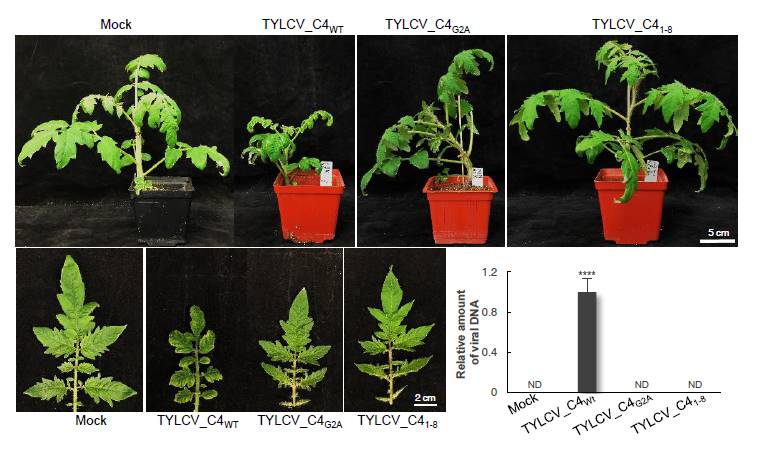
A virus-targeted plant receptor-like kinase promotes cell-to-cell spread of RNAi (PNAS) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogViruses can move from cell to cell through plasmodesmata. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are key components in the plant's arsenal against viruses. They function by harnessing the AGO system to target and cleave viral RNA, thus silencing the viruses. Like the viruses they target, siRNAs move from cell…

Auxin synthesis contributes to virulence of Pseudomonas syringae (PLOS Pathogens)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant pathogens have developed a large range of strategies to allow them to have successful interactions with their plant host, including physiological manipulation. For example, Pseudomonas syringae, the cause of speck disease in many plant systems, manipulates the auxin phytohormone physiology in its…
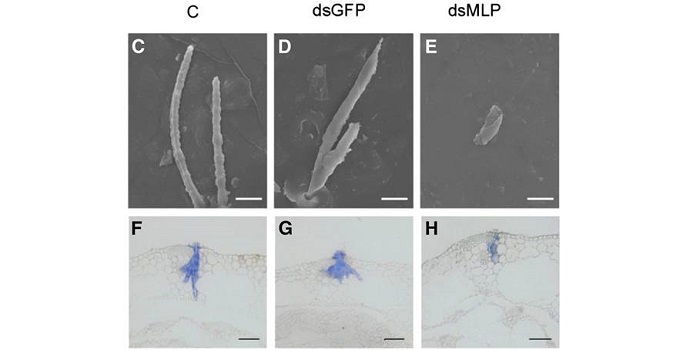
A mucin-like protein of planthopper is required for feeding and induces immunity response in plants (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPiercing-sucking insects secrete saliva while feeding through specialized mouth parts called stylets. Saliva plays critical roles in insect digestion and nutrition, and regulates plant defense responses, but the specific metabolites involved have not been characterized. Shangguan et al. reported the…
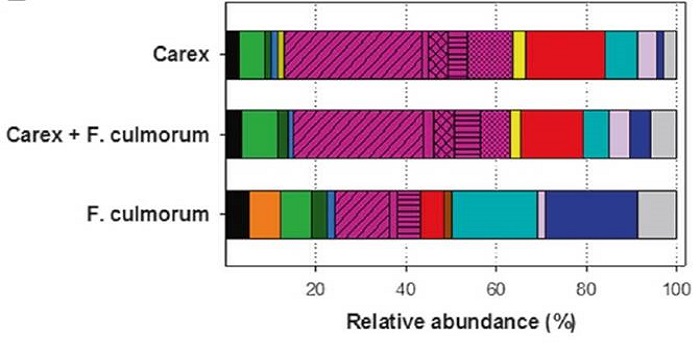
Calling from distance: attraction of soil bacteria by plant root volatiles (ISME J.) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant interactions with beneficial microbes are good strategies to survive biotic and abiotic challenging conditions, but the mechanisms that plants use to recruit these interactions, specially belowground, remain scarcely known. Schulz-Bohm et al. designed an olfactometer system to analyze the long…
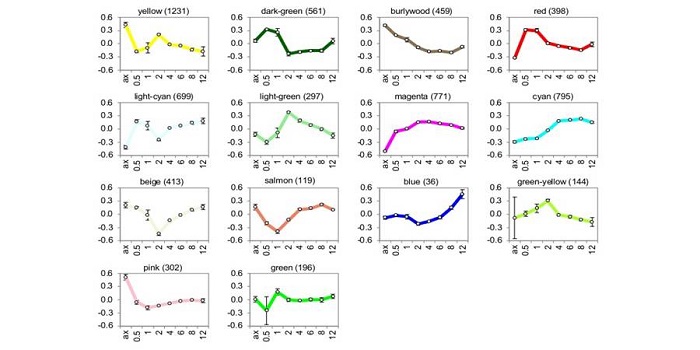
The Shifting Transcriptional Response of Corn Smut Fungus
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAs a biotrophic fungus, Ustilago maydis (corn smut fungus) relies on living plant tissues for sustenance. Once U. maydis cells of compatible mating types fuse on a leaf surface, they produce a dikaryotic filament with a specialized infection structure—the appressorium—that penetrates epidermal cells.…

