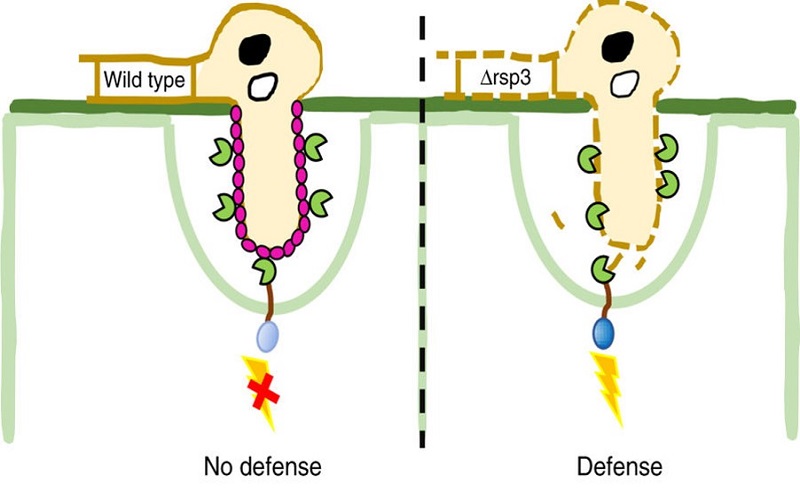
The repetitive effector Rsp3 promotes the virulence of the corn smut fungus Ustilago maydis
The corn smut fungus Ustilago maydis manipulates maize tissues and cells through the secretion of effectors that modulate host protein activities. In a recent article published in Nature Communications, Ma et al. characterize a highly repetitive effector protein family (Rsp3, repetitive secreted protein…
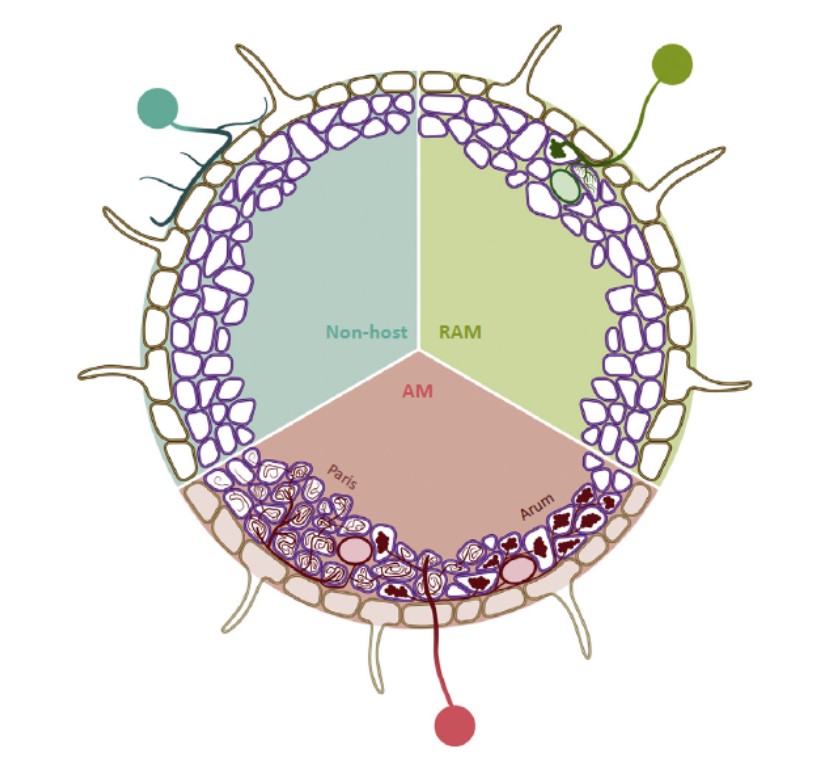
Opinion: Non-mycorrhizal Plants: The exceptions that prove the rule (TIPS)
Most vascular plants establish in their roots a multifunctional symbiosis with arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi. Among the 29% that do not host AM fungi are 66-92% of the members of the Brassicaceae family, including some major crops (broccoli, oilseed rape) as well as the model plant Arabidopsis…
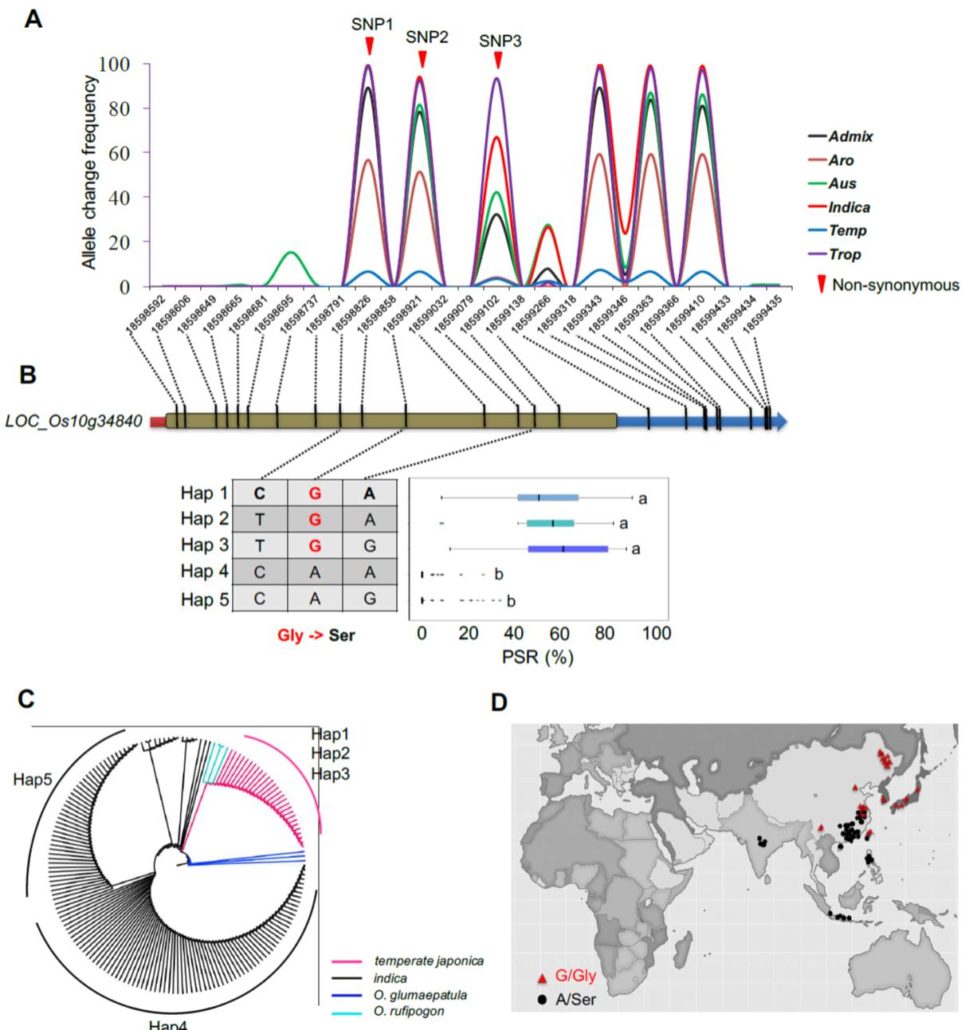
Identification of cold tolerance genes and a functional allele that confers cold tolerance ($) (Plant Physiol.)
Xiao et al. used 1,033 rice accessions for GWAS to identify QTLs associated with cold tolerance. In general, japonica-type varieties showed greater cold tolerance than indica types. The authors identified many QTLs for cold tolerance at the seedling and booting (initiation of panicles) stages. They…
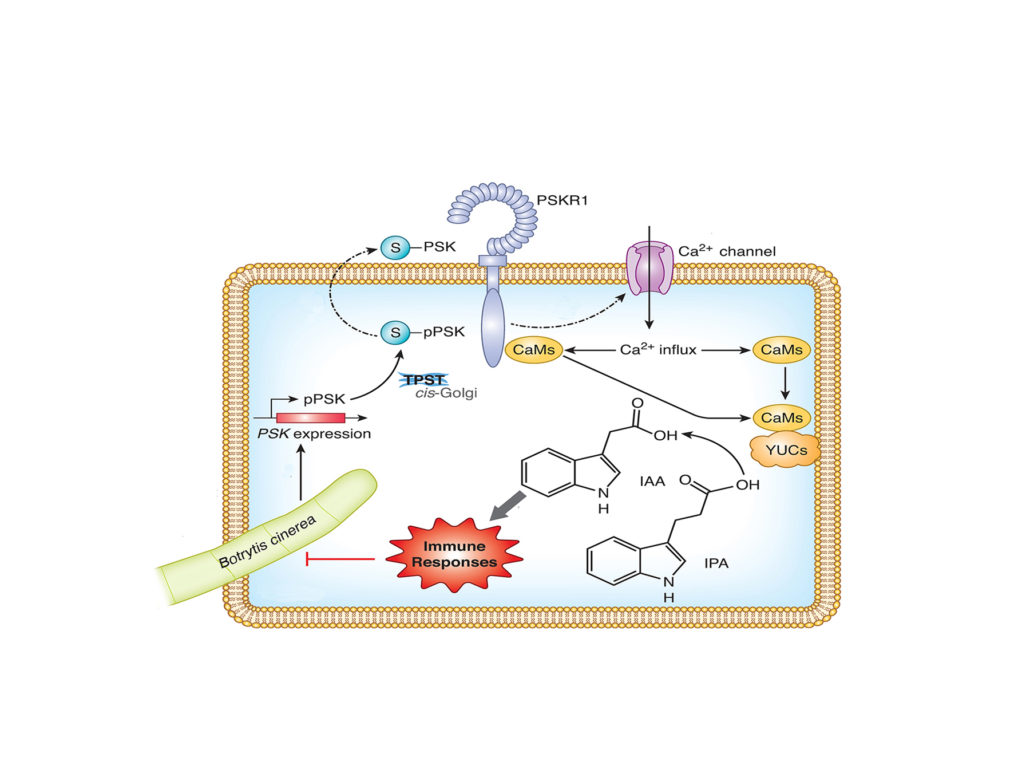
Small Peptide PSK Induces Plant Immunity Against Botrytis cinerea
Zhang et al. show how PSK initiates Ca2+- and auxin-dependent immunity https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00537.
By Huan Zhang, Zhangjian Hu and Kai Shi
Background: During plant-microbe interactions, some small secreted peptides are secreted into the apoplast between plant cells as damage-associated…
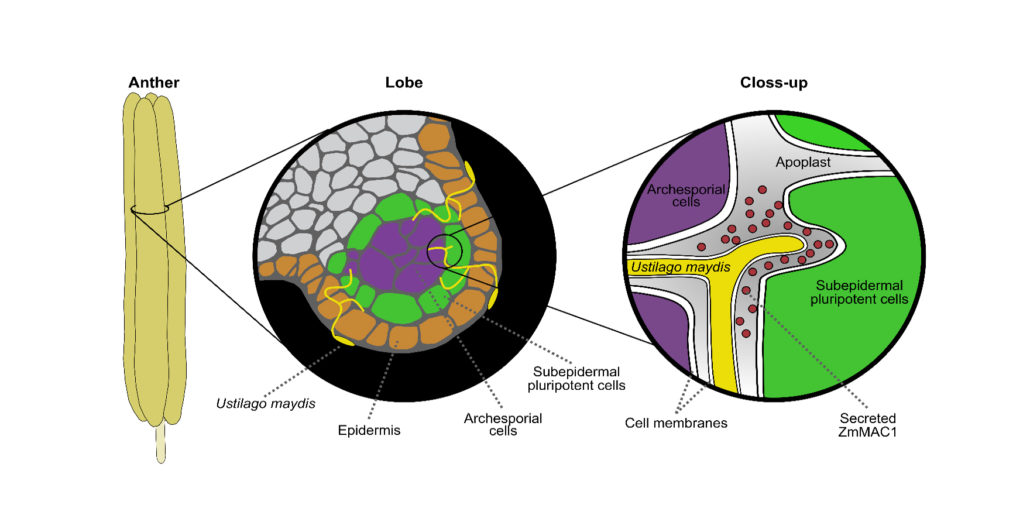
PLANT PROTEIN MEETS HOMER´S TROJAN HORSE
By Karina van der Linde and Virginia Walbot
Background: In contrast to animals in which meiotically competent cells develop in embryos, plants switch from vegetative to reproductive growth only during flowering. In maize, the most productive cereal crop, the tassel contains male flowers in which…
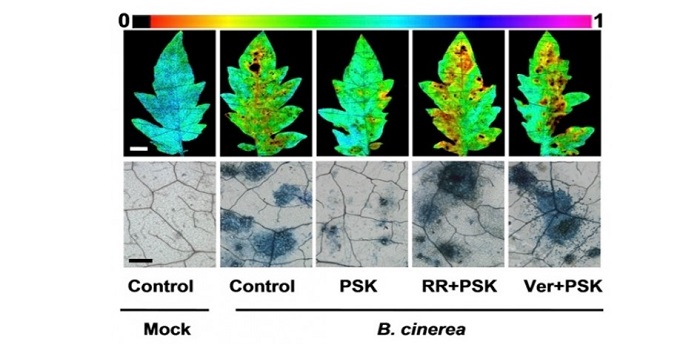
A plant phytosulfokine peptide initiates auxin-dependent immunity through cytosolic Ca2+ signaling (Plant Cell)
Plants are exposed to a wide variety of biotic stressors such as herbivores and microbial pathogens. Thus, they have developed a sophisticated response system which involves different signal molecules and accurate signaling pathway responses. Among them, phytosulfokine (PSK), a disulfated pentapeptide,…

Bacteria exploit autophagy for proteasome degradation and enhanced virulence in plants (Plant Cell)
Autophagy has been defined as non-specific self-eating to obtain material that will be used for key processes within the cell. Even through authophagy has been demonstrated to be very important, its role during plant-bacteria interactions is not well known. Üstün et al. examined interactions between…
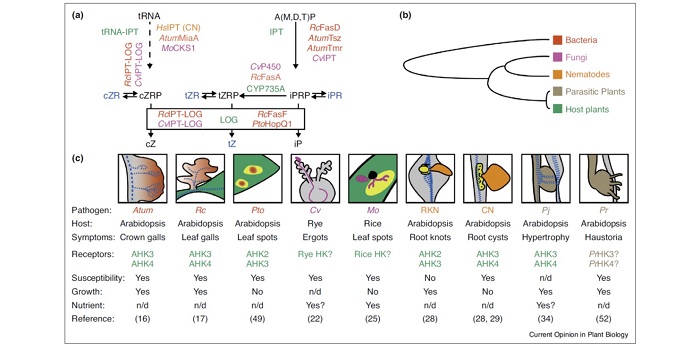
Review: Same tune, different song — cytokinins as virulence factors in plant–pathogen interactions? (COPB)
Many pathogens produce virulence factors that improve their pathogenicity, including in some cases compounds produced by the host, such as the hormone cytokinin. Spallek et al. review the various plant pathogens — spanning from bacteria to parasitic plants — that use cytokinins as virulence factors;…

Differential roles of NPR proteins in regulating SA signalling (Cell) ($)
Salicylic acid is a small phenolic hormone that plays a prominent role in the regulation of plant immune responses. Exactly how SA is perceived in planta has been an intensive area of research, with differential paradigms proposed for the perception of SA through negative regulators NPR3/NPR4 or through…

