
The fungal MAP kinase Pmk1 controls intracellular spread of rice blast fungus in rice cells (Science)
Magnaporthe oryzae is a devastating fungal pathogen that routinely threatens rice crop yields. Rice blast infection occurs when fungal hyphae penetrate into and proliferate within living plant cells, moving intracellulary from cell-to-cell through plasmodesmatal junctions. In a recent article published…

Insight: Phyllosphere microbiology: at the interface between microbial individuals and the plant host (New Phytol)
A bean leaf might not look big to us, but to a bacterium it is huge: authors Remus-Emsermann and Schlechter point out that in terms of scale, a microbe is to a leaf as a human is to the island of Trinidad. Like an island, a leaf has diverse inhabitants and provides diverse microhabitats. Much of what…
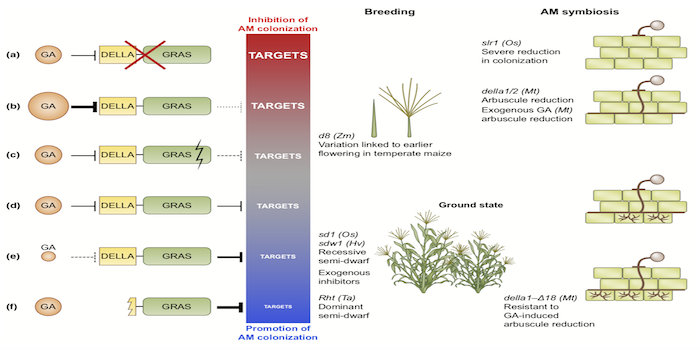
Insight: The impact of domestication and crop improvement on arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in cereals (New Phytol)
Cereals, such as rice, maize, wheat and sorghum are the nutritional base for many human societies, accounting for over 50% of the global caloric intake. Therefore, sustainability of (cereal) agriculture and quality of the cereals consumed is a great concern. This has led to an increasing interest into…

Review: Venus Flytrap: How an excitable, carnivorous plant works ($) (Trends Plant Sci)
The one sure-fire way to get children excited about plants is to show them how a Venus flytrap works. But how does it work? We’ve all heard that the trap “counts” the number times it is triggered, and that it requires two or more touches in quick succession to close – but how does it count? Hedrich…
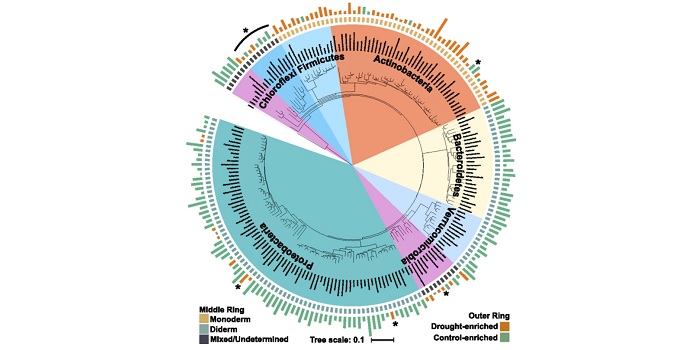
Increase in monoderm bacteria in drought-delayed early sorghum root microbiomes (PNAS)
Drought stress drastically decreases crop productivity. Some root-associated bacteria have been shown to decrease the negative effects of drought stress on plants, but the role of drought in the development of the root microbiome has not been studied. Xu and colleagues use root metabolomics and 16S rRNA…
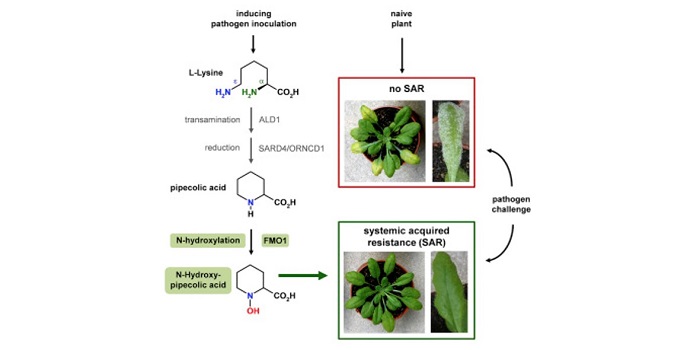
Emergence of N-hydroxy-pipecolic acid as a key long-distance immunity signal in Arabidopsis
Systemic acquired resistance is a form of long-distance immunity employed by plants to protect distal uninfected tissues upon localized pathogen attack. Over the past two decades, a number of putative long-distance signals have been described as regulators of systemic immunity including the lysine catabolite…
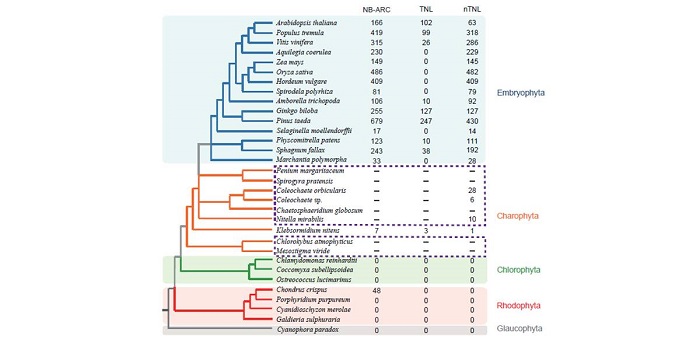
Origin of Plant R Genes
Plants rely on two branches of the innate immunity system to prevent or eliminate microbial infections: one involves cell surface receptors to respond to pathogen- or microbe- associated molecular patterns, and the other acts inside plant cells by using proteins with nucleotide-binding site (NBS) and…

Phytophthora palmivora establishes tissue-specific intracellular infection structures in the earliest divergent land plant lineage (OA)
Surprisingly little is known about the pathogens of liverworts. Carella et al. explored the interaction between the broad-host range pathogenic oomycete Phytophthora palmivora and the model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. They found that the pathogen enters the host tissues and proliferates in intercellular…
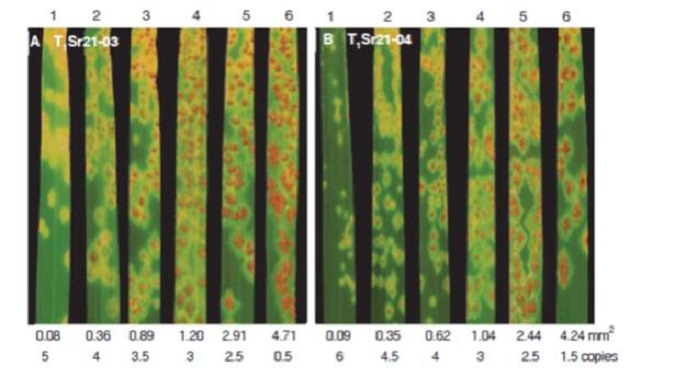
Identification and characterization of wheat stem rust resistance gene Sr21 effective against the Ug99 race group at high temperature (OA)
Stem rust is a fungal disease of wheat caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici (Pgt). The Ug99 race group of the fungus has evolved the ability to overcome most stem rust (Sr) resistance genes. Previously, Sr21, an Sr gene that confers partial resistance to Ug99, was found in diploid wheat. Chen et…

