
Review: Mechanisms of plant–soil feedback: interactions among biotic and abiotic drivers
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe often think about how the soil environment influences plants, but two new papers focus on how plants influence the soil environment (through abiotic and biotic effects), in turn affecting other plants. These plant-soil feedbacks (PSFs) can be negative (resource depletion, natural enemy accumulation)…
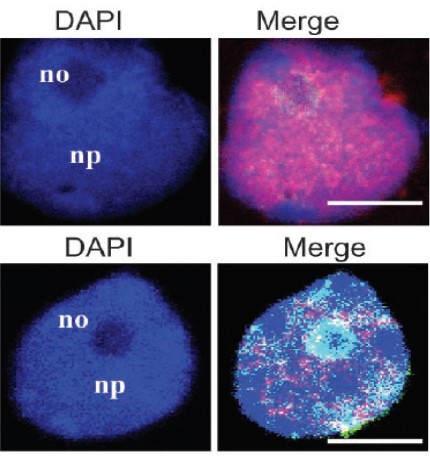
Worming into the Plant Chromatin: A Nematode Effector Influences Host Histone Acetylation
Blog, The Plant CellPlants encounter myriad invaders, including bacteria, fungi, insects, and other parasites. These pathogens generally deliver effector proteins into plants, increasing their virulence and targeting various host processes (Toruño et al., 2016). Although advances in the past two decades have led to significant…
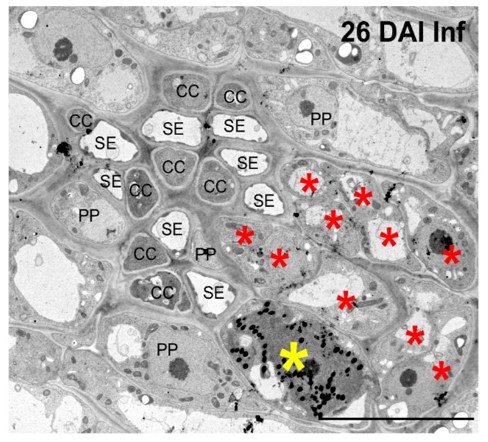
Sugar architect: the Brassicaceae pathogen Clubroot manipulates plants on multiple levels to secure sucrose supply
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe soil-borne pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae can infect most members of the Brassicaceae family. The infections, which can lead to extensive crop losses, typically involve development of galls in the underground tissues of the plant, giving the pathogen its common name, ‘clubroot’.
Although…
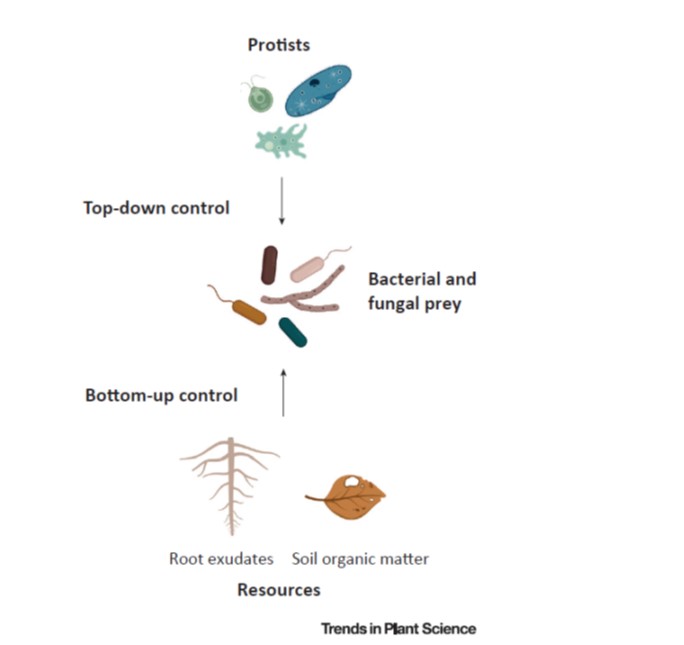
Review. Protists: Puppetmasters of the rhizosphere microbiome ($) TIPS
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe enemy of my enemy is my friend, right? Gao et al. argue that we should be more aware of the beneficial impacts of friendly protists that eat potentially harmful microbes in the rhizosphere (they deliberately exclude plant pathogenic protists in their discussion). Protists are a diverse paraphyletic…
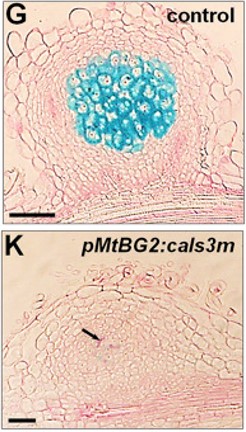
Symplastic coordination of root nodule development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe establishment of root nodule symbiosis in legume roots involves the perception, infection, and accommodation of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia. The de novo formation of root nodules relies on complex developmental programs coordinated through different tissues via unknown cellular routes. Gaudioso-Pedraza…

Plant extracellular vesicles contain diverse small RNA species and are enriched in 10-17 nucleotide "tiny" RNAs (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklySmall RNAs are known to move between cells and even between organisms. Studies in mammals have shown that extracellular vesicles (EVs) can contribute to small RNA transport, and recently small-RNA containing EVs were identified in plants. Baldrich et al. extend this work with an analysis of the types…
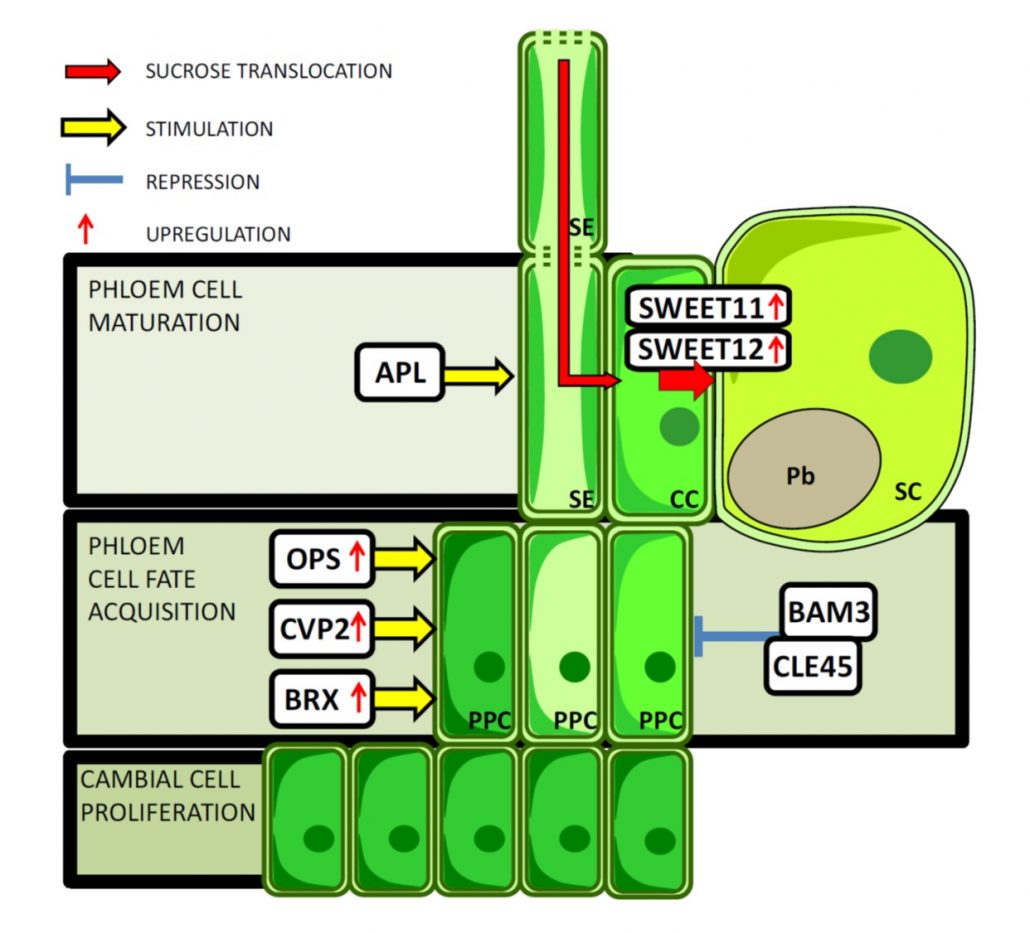
Brassica clubroot disease protist pathogen promotes phloem differentiation and expression of SWEET sucrose transporters (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClubroot is a disease of brassicas (including oilseed crops and Arabidopsis) caused by the protist Plasmodiophora brassicae. The infection is characterized by the formation of swollen tissues called galls that are metabolic sinks in which the pathogen propagates. Walerowski et al. took advantage of Arabidopsis…

Towards Pathogen-Resistant Apples
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. show that a single-nucleotide polymorphism in a hairpin RNA promoter contributes to Alternaria alternata leaf spot resistance in apple and could serve as a marker to distinguish susceptible versus resistant apple cultivars. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00042.
Background: Apple Alternaria…

Aphid-borne viral spread is enhanced by virus-induced accumulation of plant reactive oxygen species (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAphids are major vectors for viral spread. Guo et al. have identified an interesting interaction that affects aphid feeding behavior and viral spread. They showed that reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in plants infected with cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) affects aphid feeding behavior; specifically,…

