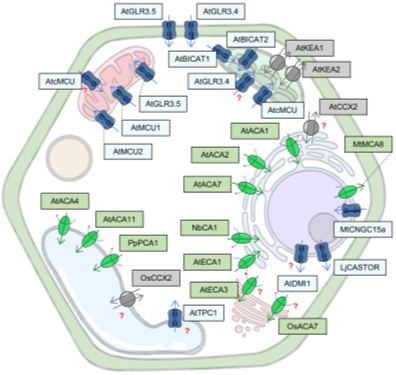
Review: One cell, many signatures: Organellar Ca2+ signaling (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium ions (Ca2+) occupy a primary position in plant cell signaling processes by virtue of their role as the so-called second messengers. Ca2+ signaling underlies plant response to various abiotic, biotic and developmental cues. Whilst this Ca2+ signaling was thought to predominantly occur in the cytoplasm,…
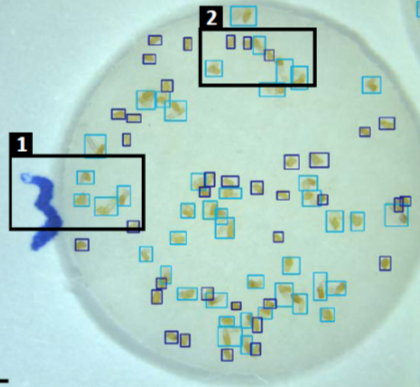
SeedQuant: A deep learning-based tool for assessing stimulant and inhibitor activity on root parasitic seeds (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyParasitic plants can completely wipe out a farmer’s harvest. The seeds can lie dormant in soil until they perceive signals from potential host plants, which stimulate germination. Therefore, germination stimulants applied to fields before the crops are planted can cause the parasitic seeds to germinate…
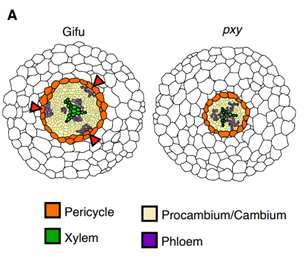
Natural variation identifies a Pxy gene controlling vascular organization and formation of nodules and lateral roots in Lotus japonicus (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiosis between legumes and nitrogen-fixing bacteria such as Mesorhizobium loti requires an exchange of signals. Plants recognize both specific nod factors (lipochitooligosaccharides) as well as cell-surface exopolysaccharides through distinct pathways. The M. loti exoU mutant fails to properly form…

Plantae Presents: Sophia Stone and Sjon Hartman
Blog, Plantae Presents, Research Skills0 Comments
/
Plantae Presents: Sophia Stone and Sjon Hartman
Recorded April 14
Sophia Stone: The ubiquitin-proteasome system at the crossroads of abiotic and biotic stress tolerance
Sophia Stone earned her PhD at York University, Canada, and completed an HFSP long-term fellowship at the University…
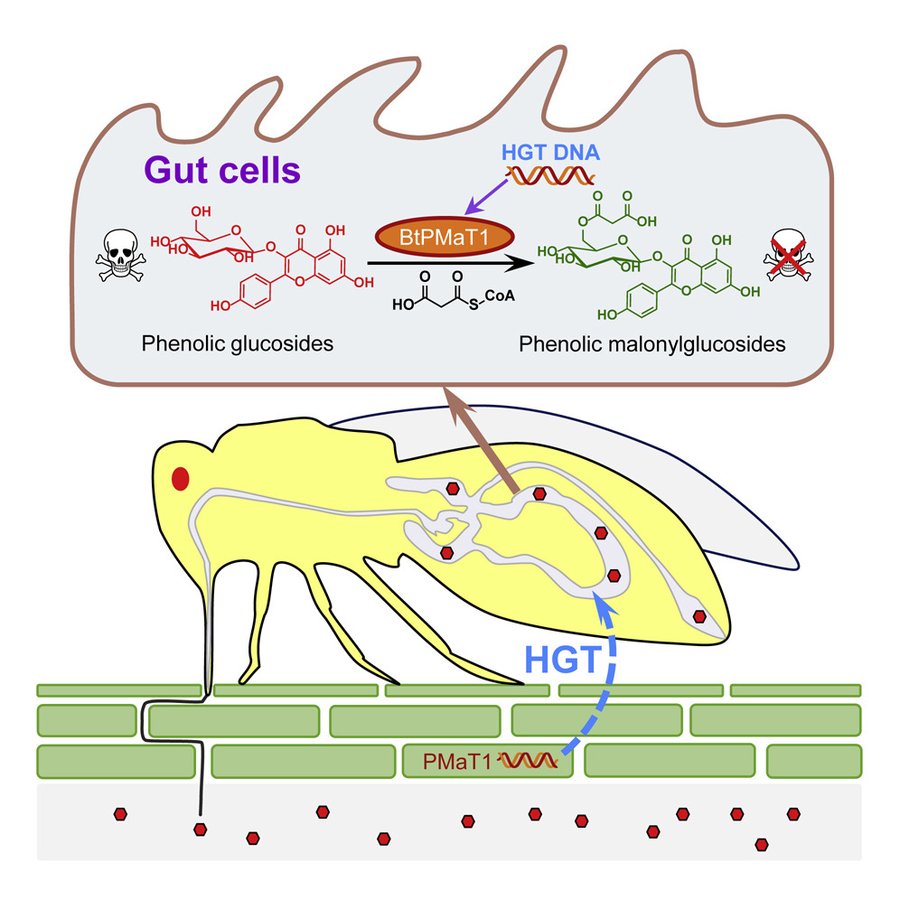
Whitefly hijacks a plant detoxification gene that neutralizes plant toxins (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci, are devastating crop pests that lower yields and transmit viruses. They feed off more than 600 species, most of which produce toxic phenolic glycosides. Xia et al. investigated how the whiteflies manage to avoid the effects of the toxin. They found convincing…

Review: Microbiota-root-shoot-environment axis and stress tolerance in plants ($) (COPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots and shoots exist in different environments and have different functions, but each depends on the actions of the other. In recent years, many factors have been identified that move from root to shoot or vice versa to integrate their actions; these include hormones, small RNAs, peptides, and transcription…
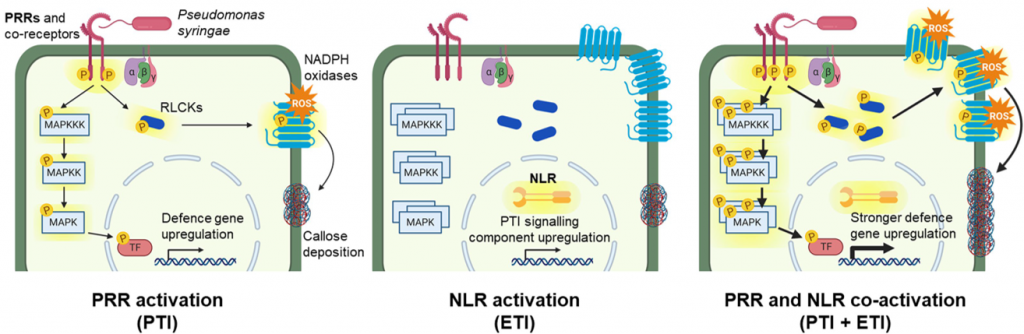
Not PTI or ETI: PTI and ETI (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTwo very exciting papers have come out this week in Nature that address a long-standing question about the relative contributions of two different plant immunity pathways. PTI (pathogen-triggered immunity) recognizes conserved pathogen signatures at the plant cell surface; a model system for PTI is the…
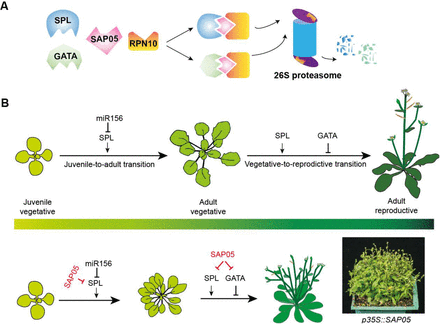
Phytoplasma effector physically interacts with host proteasome to promote bacterial growth
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs a way to circumnavigate the plant innate immune system, phytopathogens evolved effector molecules that protect the pathogen from the plant’s defenses. SAP05, an effector from the insect-vectored phytoplasma Candidatus (a bacterial obligate parasite), is responsible for the plant phenotype observed…
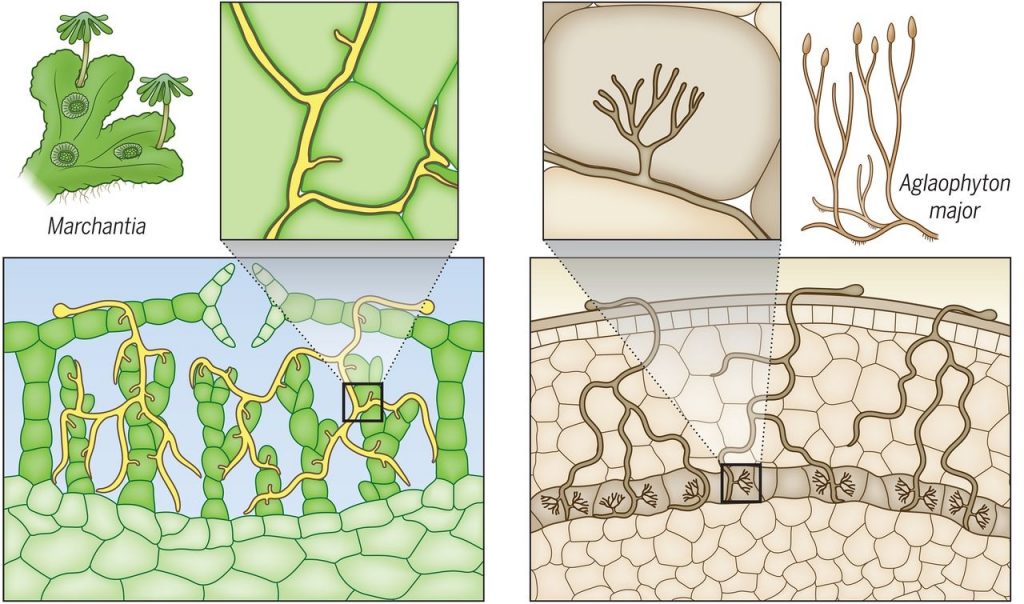
Review: Plant evolution driven by interactions with symbiotic and pathogenic microbes (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the great questions in plant science has been, “How do plants recognize friend from foe?” Like most great questions, this one benefits from a historical perspective. In their new review, Delaux and Schornack look at plant evolution through the lens of plant interactions with symbiotic and…

