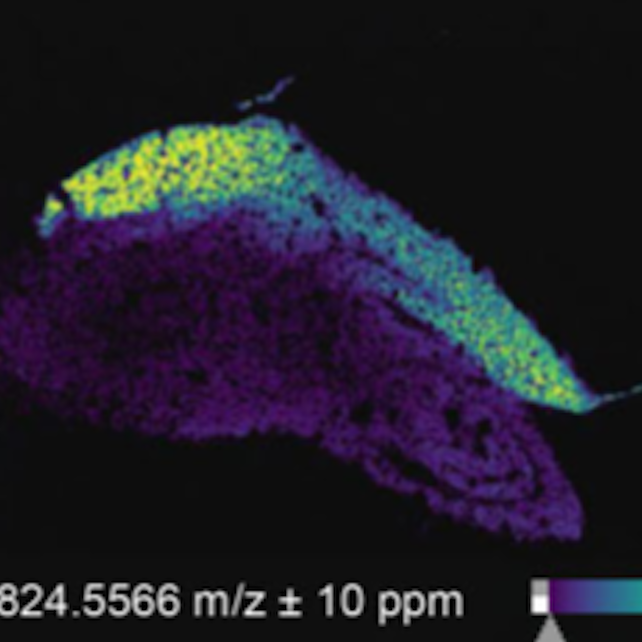
Shielding the oil reserves: the scutellum as a source of chemical defenses (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIf you work with grasses, you are probably familiar with the scutellum –the shield-like cotyledon typical of seeds from these plants. This structure has a renowned role in transferring nutrients to the growing embryo. However, Murphy and colleagues show us that not only does this structure look like…
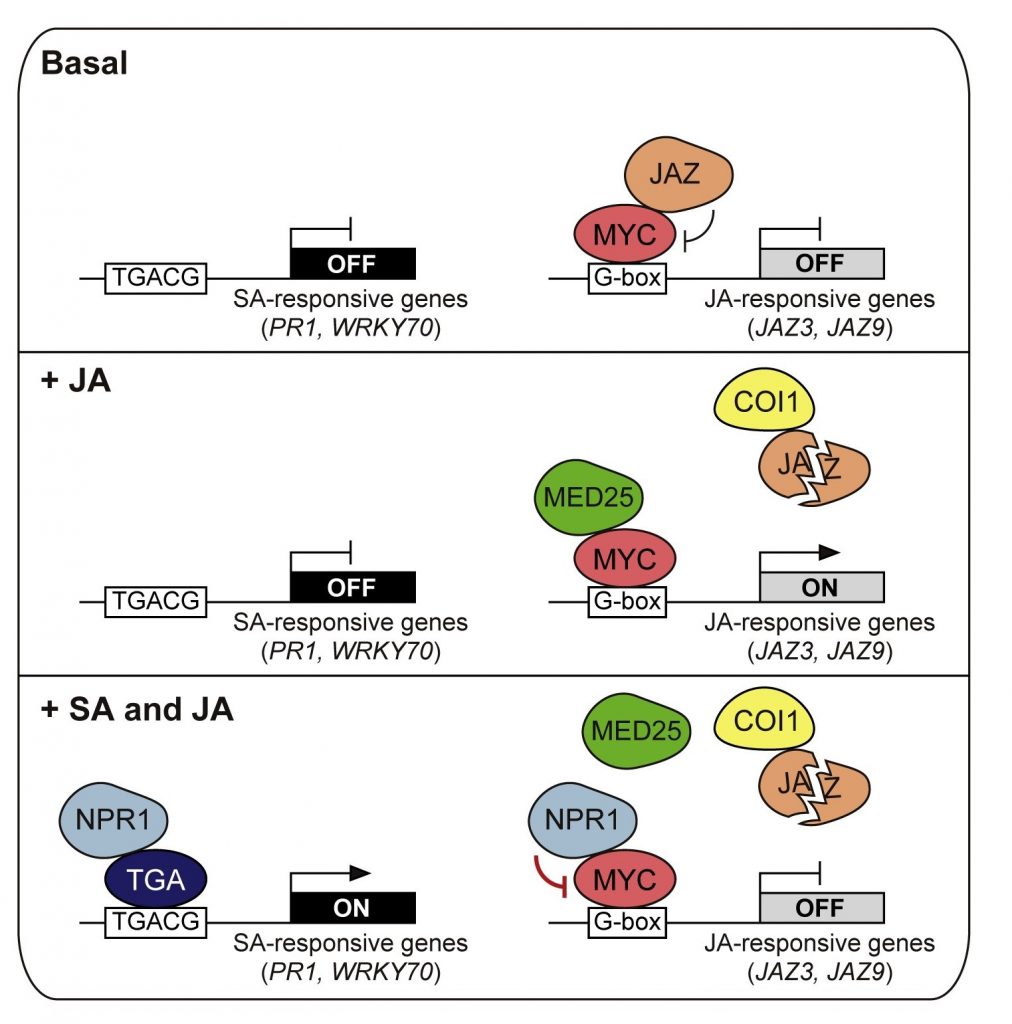
Suppression of MYC transcription activators by the immune cofactor NPR1 fine-tunes plant immune responses (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn Arabidopsis, NONEXPRESSOR OF PR GENES 1 (NPR1) plays an important role in the antagonistic crosstalk of salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) signalling. It activates SA-induced genes that protect against biotrophic pathogens and suppresses JA-induced genes that protect against necrotrophic pathogens.…
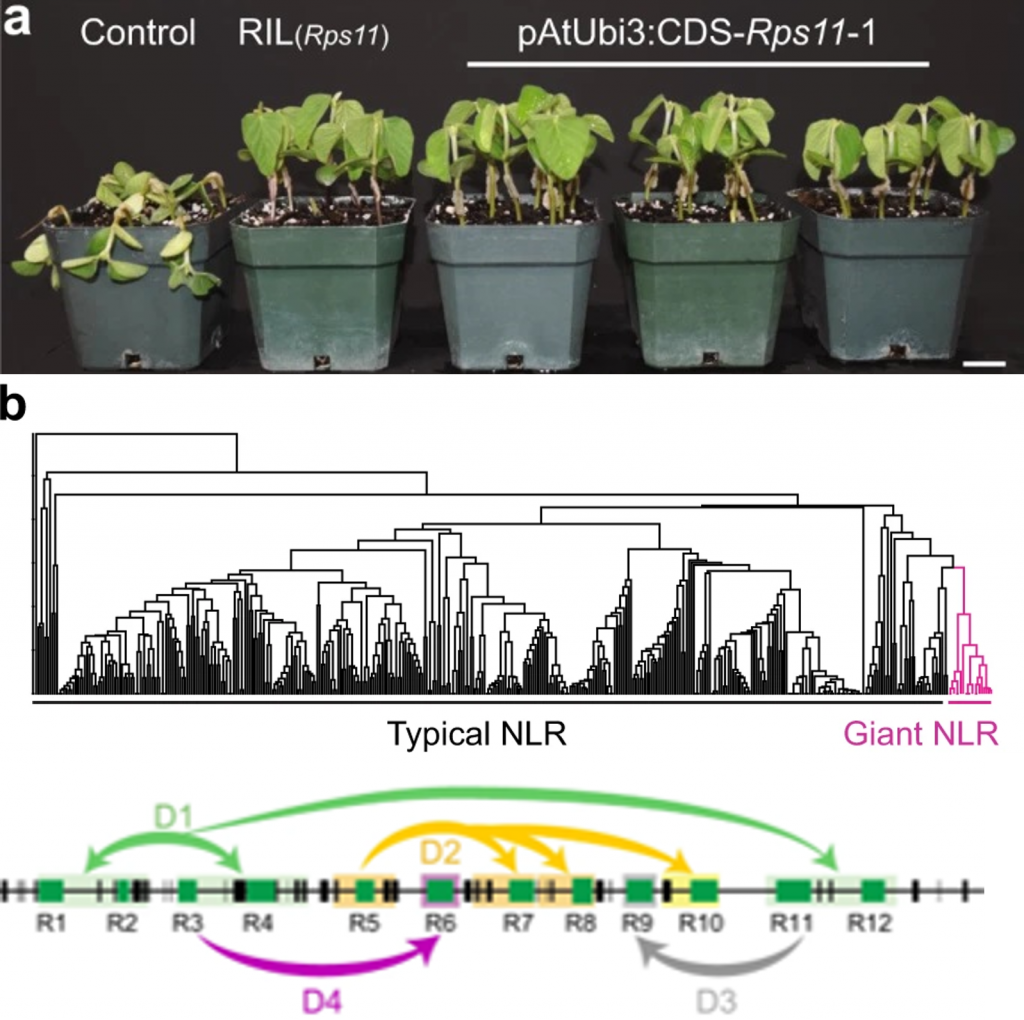
A giant NLR gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytophthora sojae is an oomycete pathogen that causes huge yield losses in soybean. Genetic studies have identified several loci that confer resistance (Resistance-to-P. sojae loci, or Rps). Here, Wang et al. have cloned Rps11 and found that it encodes a very large NLR (nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich…
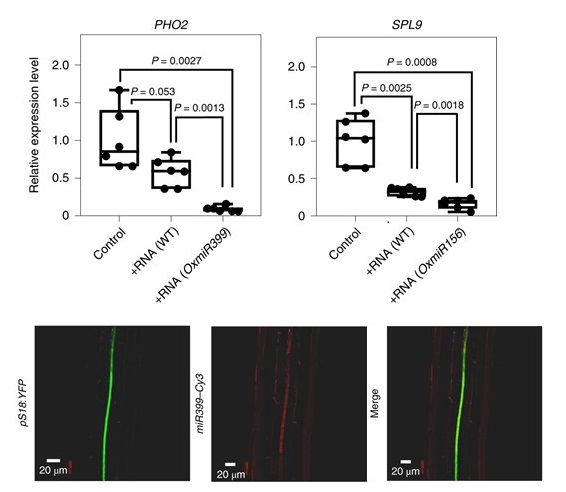
Exogenous miRNAs induce post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklySmall RNAs (sRNAs) are 21- to 24-nucleotide non-coding RNAs that induce gene silencing by targeting specific mRNAs for degradation. They regulate a plethora of developmental and physiological processes. Based on their biogenesis they are classified into two groups: micro-RNAs (miRNAs) and siRNAs. Within…
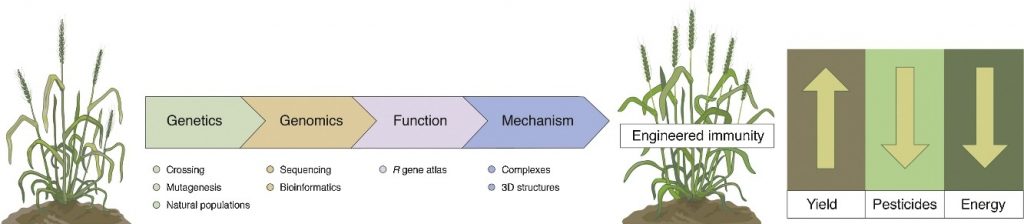
Review: The long road to engineering durable disease resistance in wheat (Curr. Opin. Biotechnol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis review by Wulff and Krattinger is a beautifully written “must read”. As the title suggests, it takes the reader on a journey of scientific progress, starting from the “first controlled cross between two wheat species” to the present, with a look into the future. Triticum aestivum (bread…

Plants People Planet Special Issue: Mycorrhizas for a changing world
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants People Planet is a relatively young journal that launched in 2019. It’s aim is to explore aspects of plant science directly relevant to our daily lives, and how plant science is communicated to the public. The Sept 2021 issue has a focus on mychorrhizas, which it explores through several opinion,…

A slicing mechanism facilitates host entry by plant-pathogenic Phytophthora (Nature Microbiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA plant has many layers of defense against a pathogen. One of the first challenges a pathogen faces is how to get inside the plant. Some bacteria sneak in through open stomatal pores, and some fungi form high-pressure appressoria that burst through walls. Here, Bronkhorst et al. investigated how the…
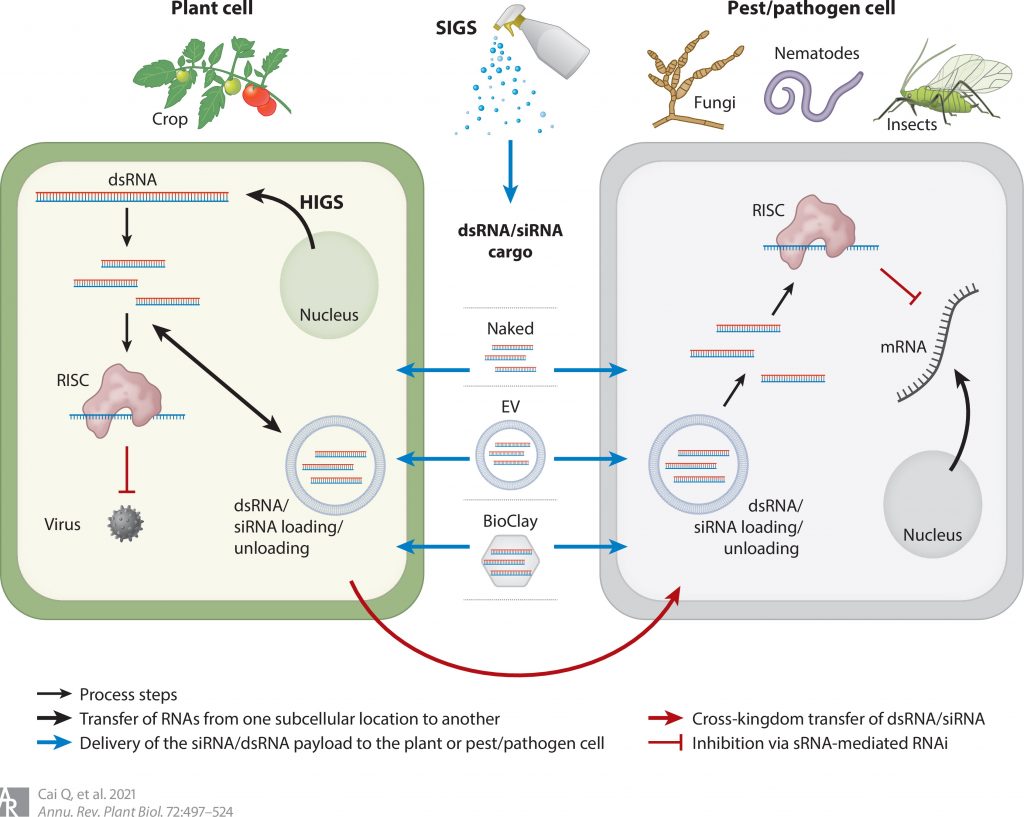
Review. Message in a Bubble: Shuttling small RNAs and proteins between cells and interacting organisms using extracellular vesicles (Annu. Rev. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySmall RNAs have big effects and can serve to shut down or silence gene expression. Recently, studies have found that small RNAs can contribute to plant defense beyond the boundary of the plant, by being packed into extracellular vesicles (EVs) and delivered to a pathogen. Cai et al. review our current…

A bacterial effector targets a plant iron sensing protein, and benefits pathogen growth (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens often appropriate iron from their hosts, as acquisition of iron is vital to sustain life for most organisms. As demonstrated in this paper by Xing et al., an effector protein, AvrRps4, from a common bacterial plant pathogen, Pseudomonas syringae, directly interacts with BRUTUS (BTS), an iron…

