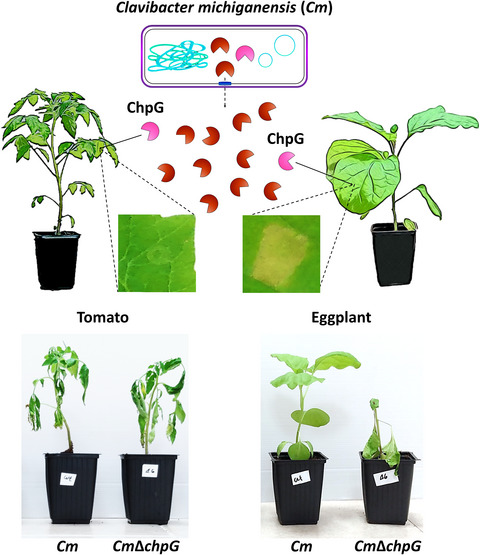
Bacterial avirulence gene encodes for a secreted protease and restricts host range (Mol Plant Path)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant pathogenic bacteria of the genus Clavibacter tend to have a narrow host range, but different species affect many important crops. Clavibacter michiganensis (Cm) causes bacterial wilt and canker in tomato, pepper and a few varieties of eggplant. There are no Cm-resistant tomato varieties but many…
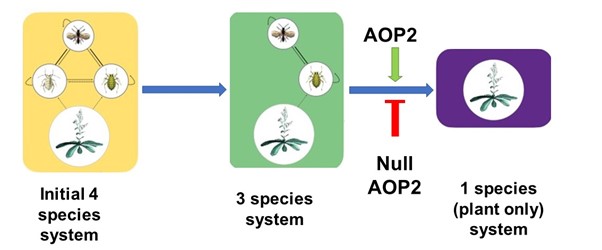
A plant gene that shapes its ecosystem (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyKeystone species shape the structure of an entire ecosystem, but can a gene determine structure of the whole ecosystem? A recent study indicates yes, some genes can, and such genes are called keystone genes. Barbour et al. set up a small ecosystem containing two herbivore aphids, one predator of these…
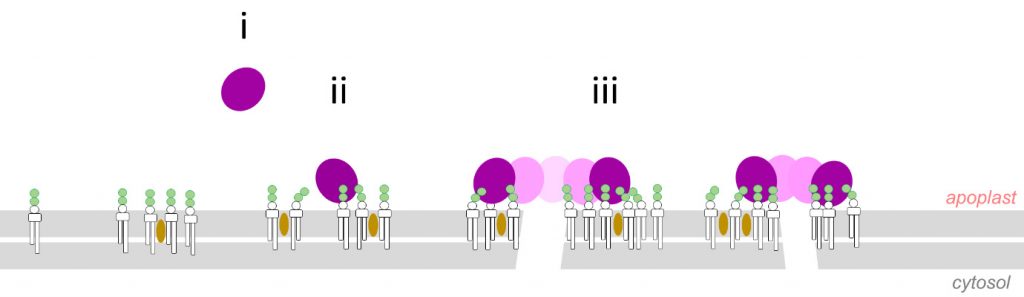
An oomycete peptide cytolysin forms transient small pores in lipid membranes (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNLPs (Necrosis and ethylene-inducing peptide 1–like proteins) are small peptides produced by a variety of plant pathogens. Some NLPs are cytolysins meaning that they trigger lysis of their target cells. Here, Pirc et al. use an assortment of tools including molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, neutron…
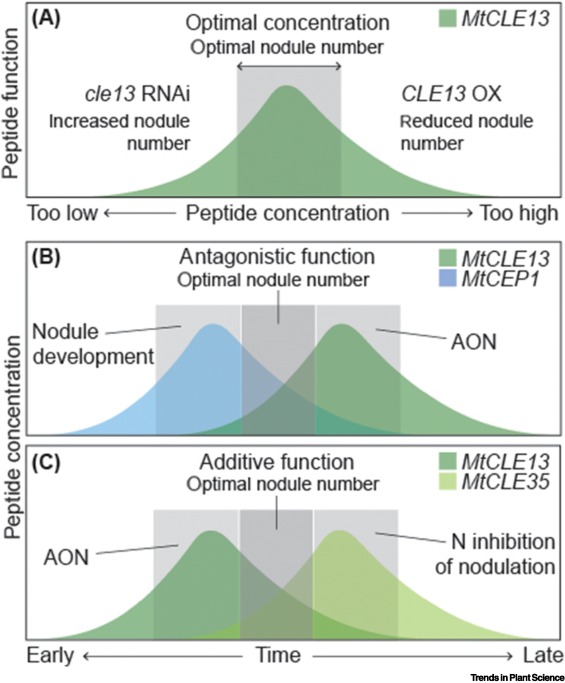
Review: A rulebook for peptide control of legume–microbe endosymbiosis (Trends in Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiotic associations with bacterial or fungal partners enhance nutrient uptake for most plants, and recent years have uncovered the very sophisticated means by which these associations are established and controlled. Peptides have emerged as key regulators of many facets of mycorrhizal and rhizobial…
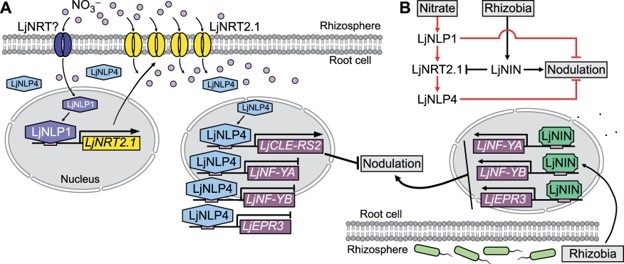
Nitrate transporter NRT2.1 is a determinant of a nitrogen acquisition switch between nitrate uptake and symbiosis in Lotus japonicus (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen nitrogen or nitrate availability is high, symbiotic nodule generation is curtailed to conserve the associated energy cost. But how does the presence of nitrate interfere with nodulation and symbiosis? Previously, genetic studies identified nitrate unresponsive symbiosis (nrsym) mutants in Lotus…
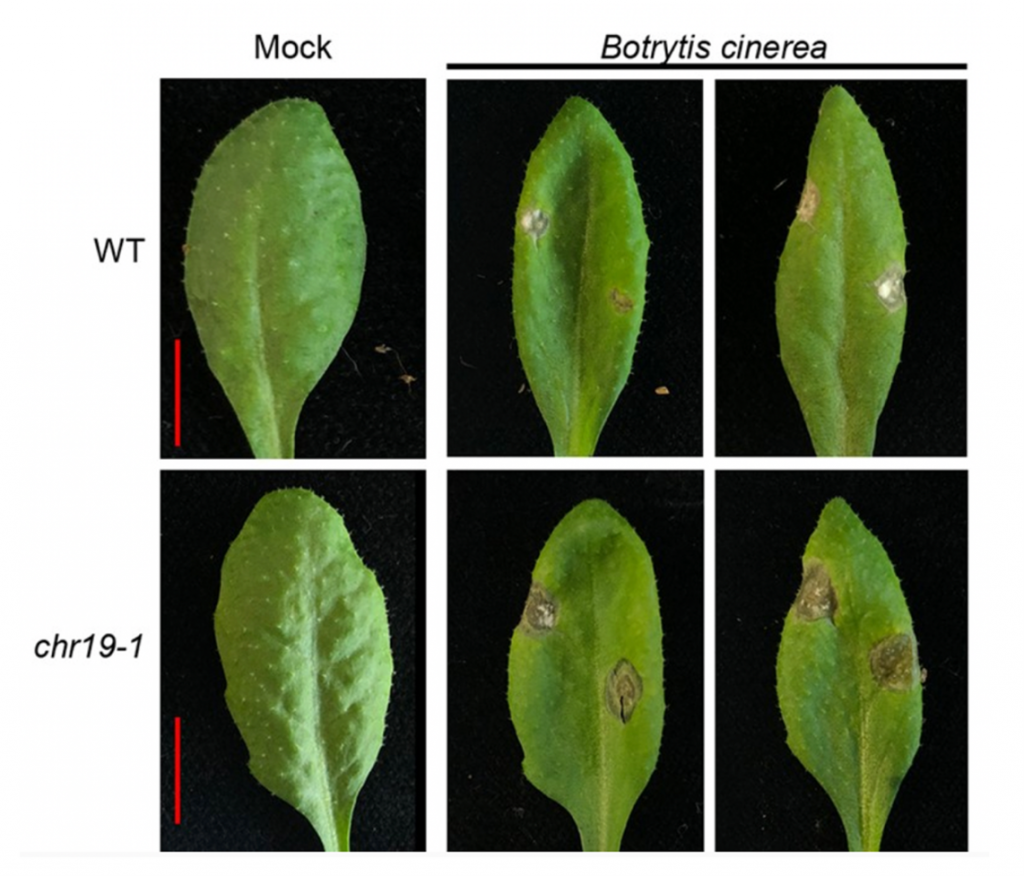
Arabidopsis CHROMATIN REMODELING 19 acts as a transcriptional repressor and contributes to plant pathogen resistance (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChromatin remodellers are highly conserved eukaryotic proteins with regulatory roles in various aspects of DNA metabolism including DNA repair, gene expression and mitosis. Here, Kang et al. examine the function of the CHROMATIN REMODELLING19 (CHR19) in Arabidopsis thaliana. Using two T-DNA insertion…
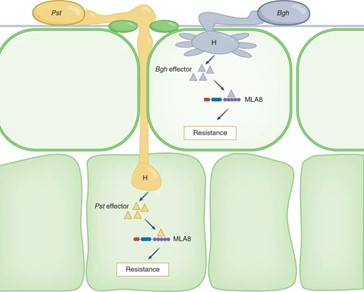
Serendipity: Story of breeding dual resistance (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHow would you feel if you developed a plant that is tolerant to a particular stress stimulus and found out that it can also tolerate another stress? Bettgenhaeuser and found that this happened when plant breeders developed barley varieties resistant to the powdery mildew disease (caused by the fungal…
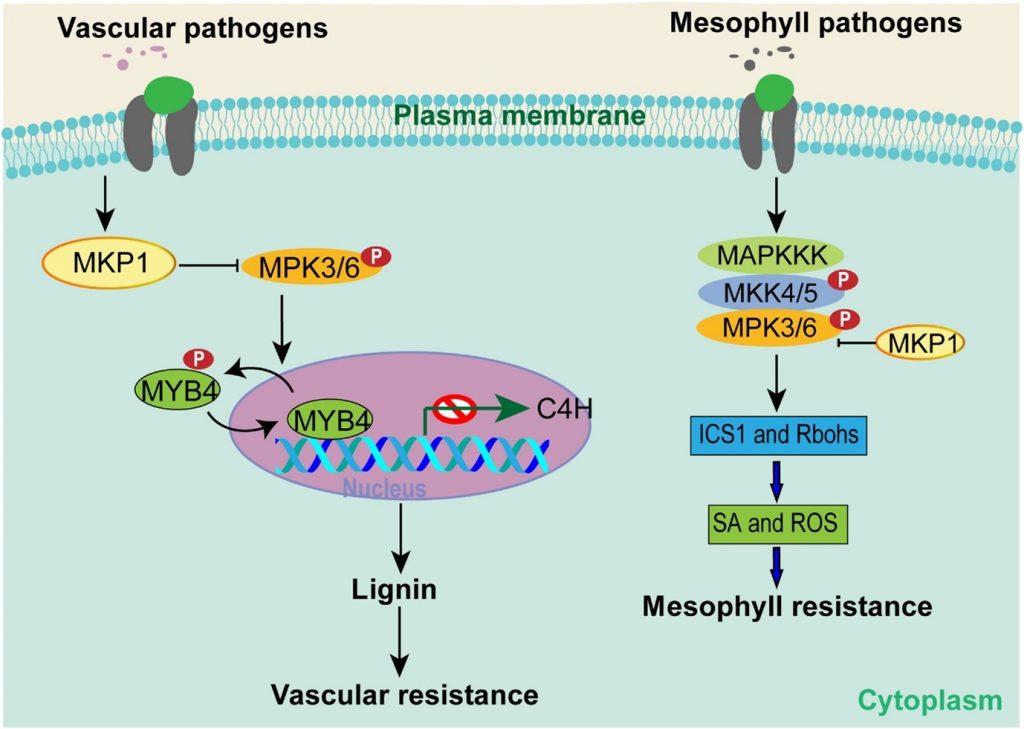
MAP kinase cascade acts as a hub to decide the ways to fight infection (Sci. Adv.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch of our understanding of plant immunity comes from studies of pathogens that infect mesophyll tissues, (e.g., Pseudomonas syringae). However, there are many pathogens that specifically invade vascular tissues (e.g., Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; Xoo), which causes rice bacterial blight. In a recent…
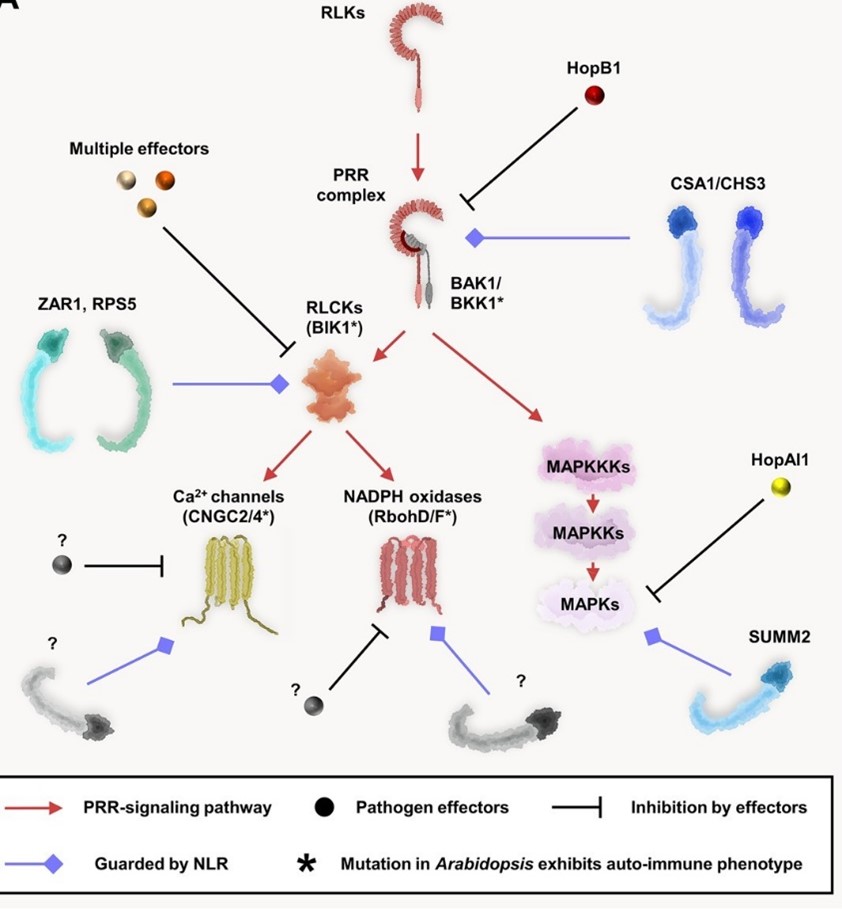
Review. The complex zigzagging in the plant immune system (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyI remember when I joined my PhD lab, the first article I was recommanded was a review by Jones and Dangl (2006) titled “The plant immune system”. Even today it remains the first article given to newbies in the lab. But the field has progressed way ahead in the more than fifteen years since that article…

