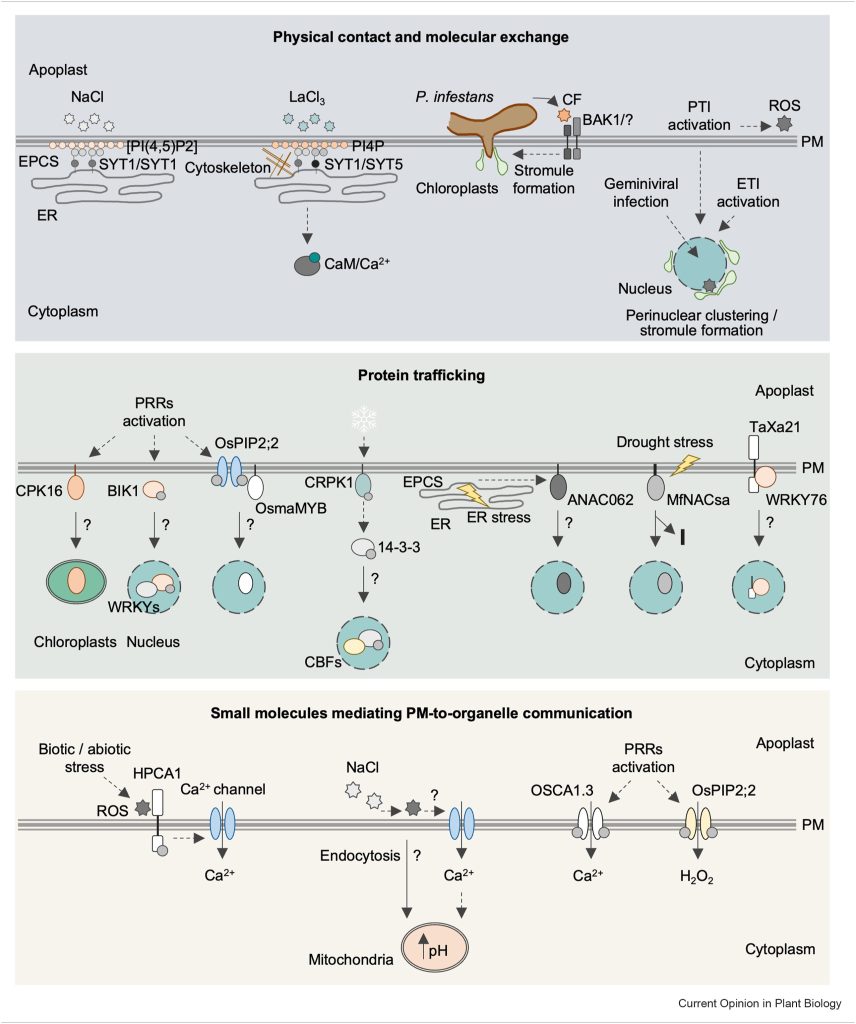
Review: Plasma membrane-to-organelle communication in plant stress signaling (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe plasma membrane (PM) is a critical interface between the cell and its environment and serves crucial sensing and transducing roles. This timely review by Medina-Puche and Lozano-Durán updates exciting new developments in understanding communication between the PM and intracellular organelles, focusing…
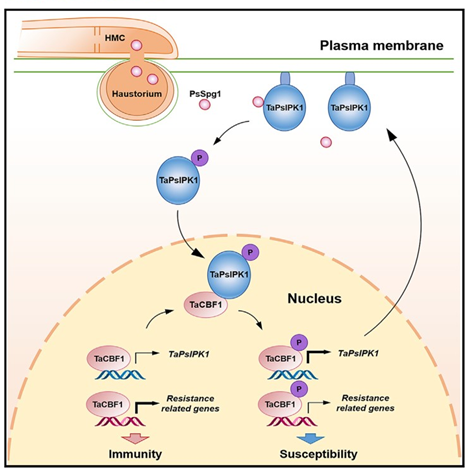
Removing one wheat protein kinase provides resistance to rust fungi (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTolerance against a pathogen can be achieved by either overexpressing a resistance-related gene, or removing a susceptibility-related gene. Overexpression of defense-related genes generally comes with side effects such as decreased growth and yield. On the other hand, a susceptibility factor might have…
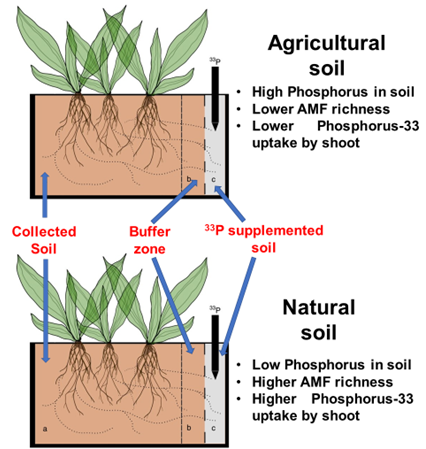
Modern agriculture practices negatively affect functions of beneficial plant microbes (Nature Ecol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAre modern agricultural practices good for the environment? Or at least for the crops? If we look at a small field at a particular time point, it may seem they are good. But looking at a broader picture gives a different notion. In a recent study, Edlinger et al. collected 210 soil samples from traditional…
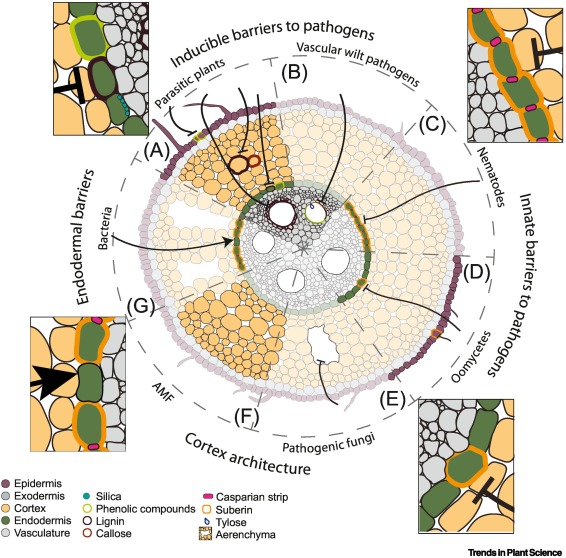
Review: Root cell types as an interface for biotic interactions (TIPS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyKawa and Brady review the contributions and responses of individual cell types and cell identities in plant biotic interactions, both pathogenic and commensal. The first step in these interactions is the perception of the microbes by root cells, which involves highly conserved microbe-associated molecular…
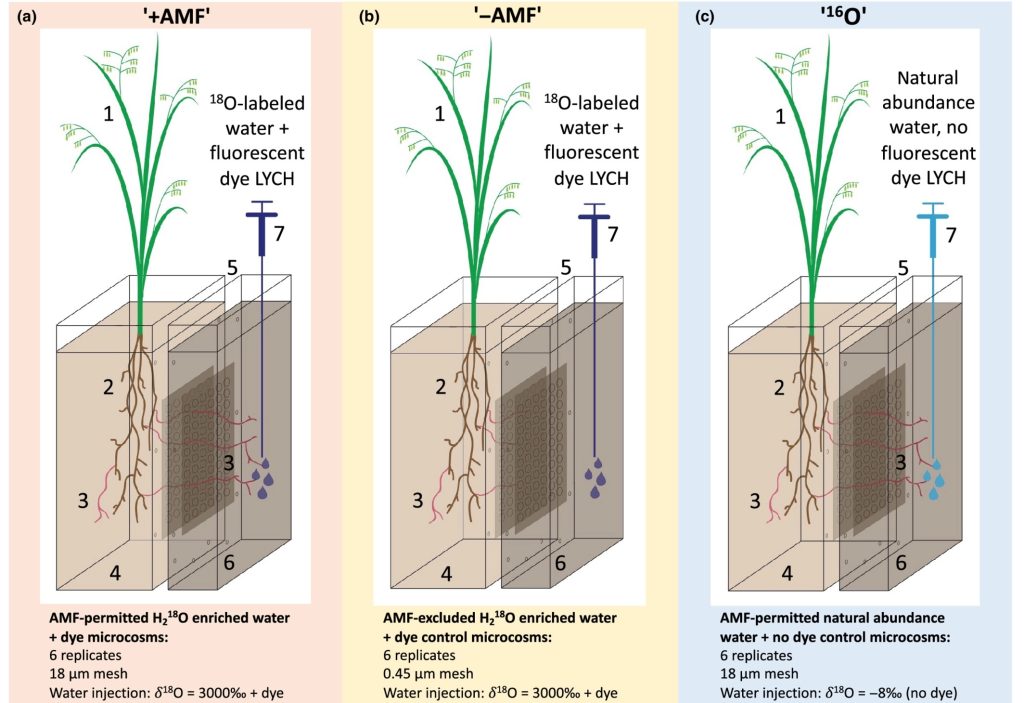
Tracking water transport to the host plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn spite of several years of observation of the symbiotic relationship between plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, we are still learning about the intricate mechanisms and processes behind their relationship. Symbiotic fungi provide nutrients (mainly phosphorus and nitrogen), stress tolerance, and…
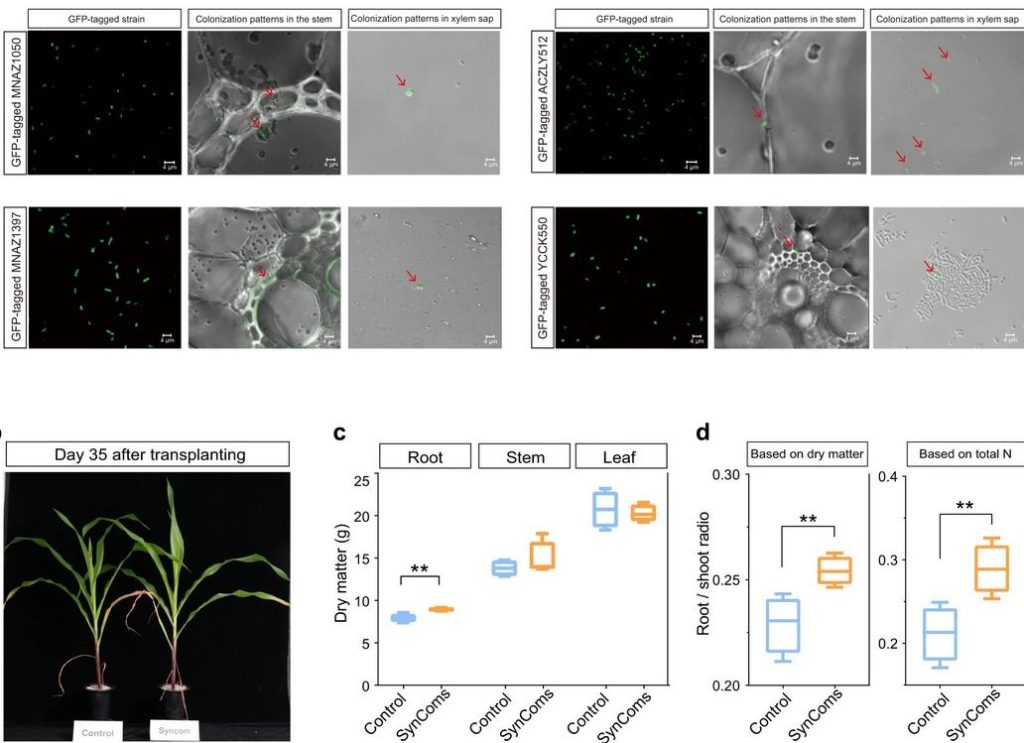
A highly conserved core bacterial microbiota with nitrogen-fixation capacity inhabits the xylem sap in maize plants (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants and microorganisms build complex associations that are essential for plant homeostasis. Studies have suggested that there is a ‘core microbiota’ that is particular to specific crops and that is inherited through generations. Targeted manipulation of crop microbiomes with the inoculation of…

A boost to plant transformation: Agrobacterium expressing type III secretion system (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGene manipulation in most plant species faces two major hurdles, transformation efficiency of tissue and regeneration of callus. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation is the most common method of plant transformation. Transformation efficiency can range from more than half the tissue to less than…
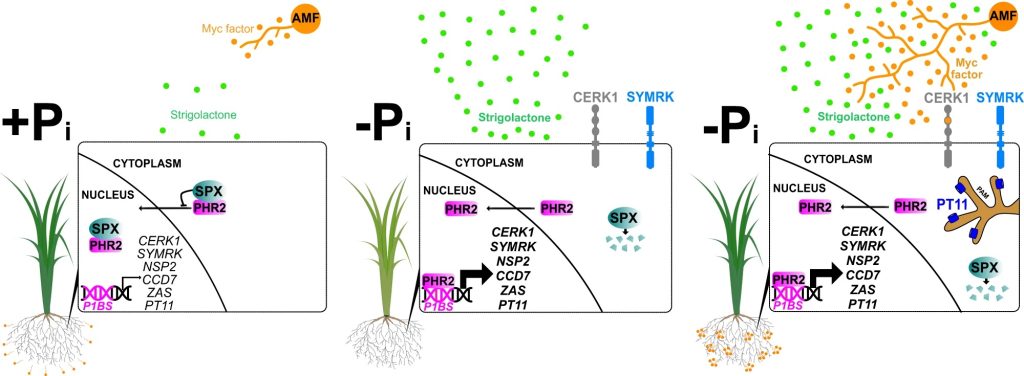
Plants’ PHR2-controlled phosphate starvation response regulates fungal symbiosis in rice (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants’ interaction with microbes in the rhizosphere affects their health and productivity. Plant-arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) fungi symbiosis is associated with almost 80% of land plants. The fungi provide phosphate, stress tolerance, and firmness to the soil in exchange for carbon. While low phosphate…
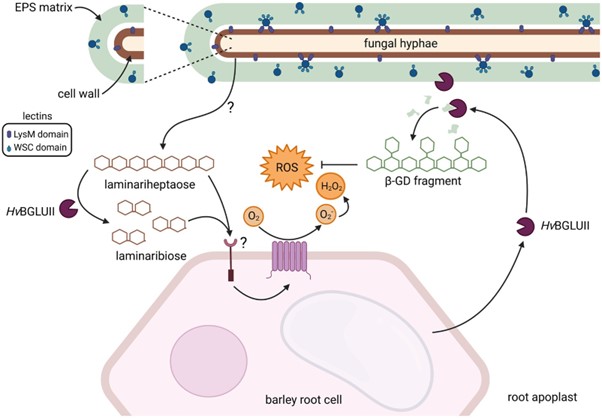
Fungal exopolysaccharide regulates plant-microbe interaction (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe studies on the apoplastic interactions of plants and fungi often focus on the fungal cell-wall, but recent studies indicate various plant colonizing fungi also have an exopolysaccharide (EPS) layer outside their cell wall. Chandrasekar et al. observed that the composition of this fungal EPS is distinct…

