tter gourd protein for defense against plant viral diseases
Plant Science Research WeeklyBitter gourds (or bitter melon) have been a childhood nightmare of mine. I remember that as a child, my grandparents used to force me to consume these really bitter gourds (Momordica charantia) telling me that they had ‘many benefits’. In addition to being a rich source of antioxidants, M. charantia…
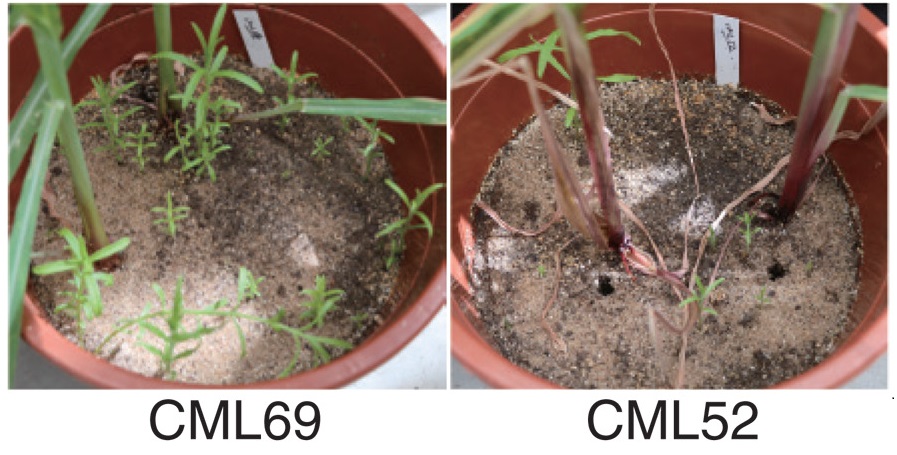

Weeding the witchweed by changing strigolactone biosynthesis in maize
Plant Science Research WeeklyStriga, commonly known as witchweed, compromises the yield of maize (Zea mays) especially in Africa. The seeds of Striga species remain dormant in the soil and are stimulated to germinate by a class of hormones called strigolactones (SL) exuded by the maize roots. Strigolactones are plant hormones with…
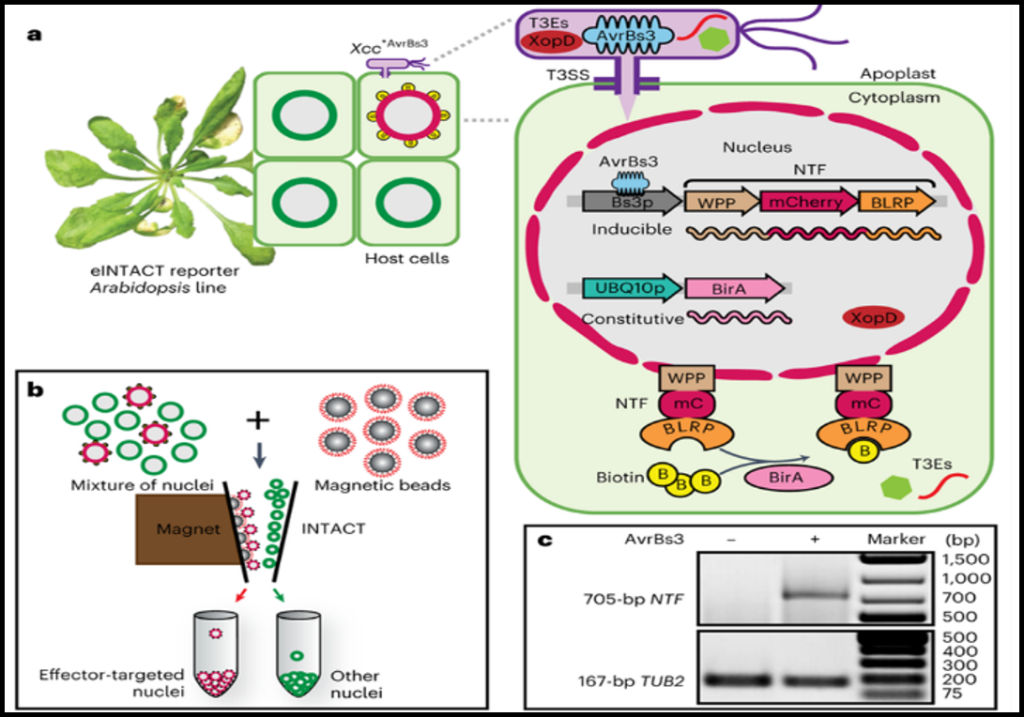
eINTACT – An effective system for isolating effector-recipient cells in plant tissues
Plant Science Research WeeklyBacteria can cause plant diseases by secreting small molecules called effectors. Studies of these effectors on host plants mostly have not accounted for the cellular complexity of plant tissues. The difficulty of detecting and isolating effector-recipient cells means that scientists mostly use bulk-infected…
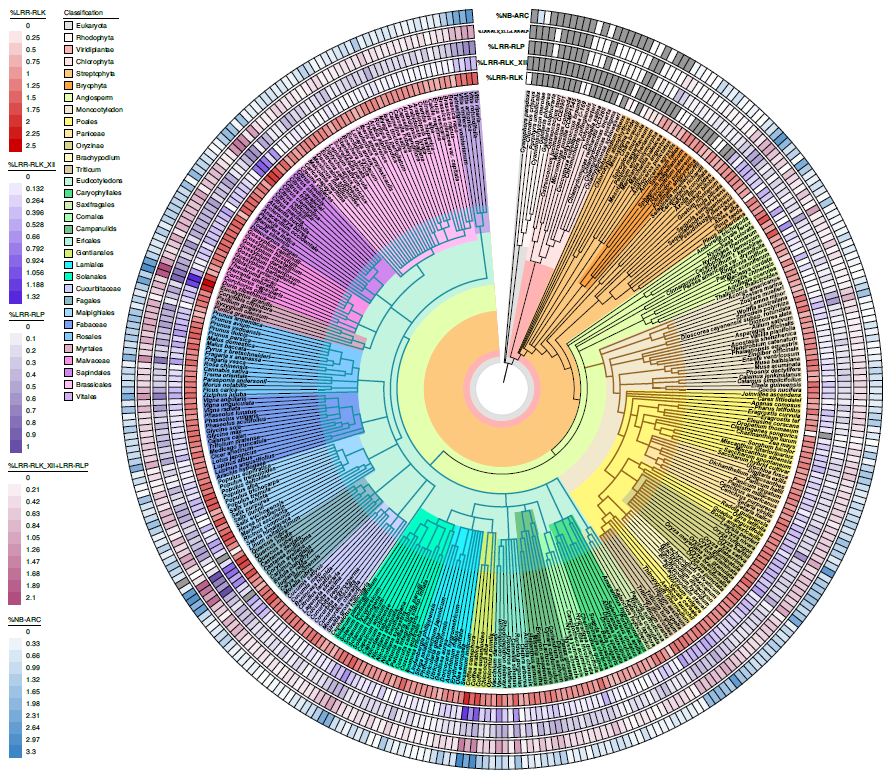
Concerted expansion and contraction of immune receptor gene repertoires in plant genomes (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant immunity is crucial for adaptation to pathogen attack and subsequent survival. Two systems support plant immunity. Cell-surface pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and prompt pattern-triggered immunity. Intracellular nucleotide-binding leucine-rich…
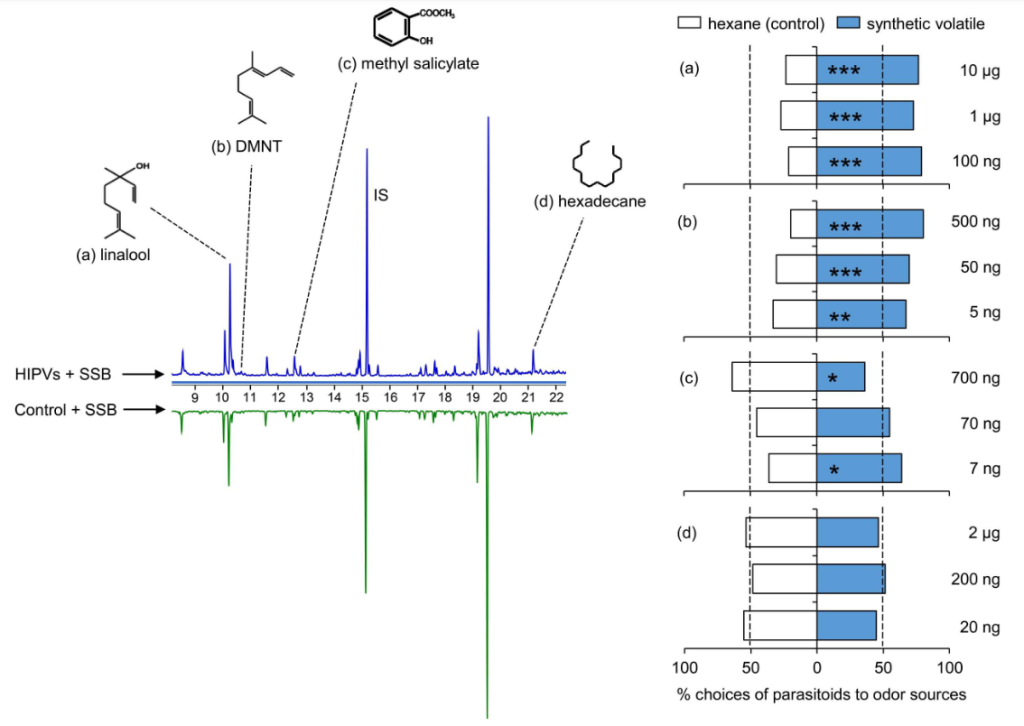
Stemborer-induced rice plant volatiles boost direct and indirect resistance in neighboring plants (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHerbivore attack can trigger release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in numerous plant species. These airborne compounds from an infected plant act as messengers in plant-plant interactions causing adaptation to the stress in adjacent plants. Globally, rice is a staple food for millions of people,…
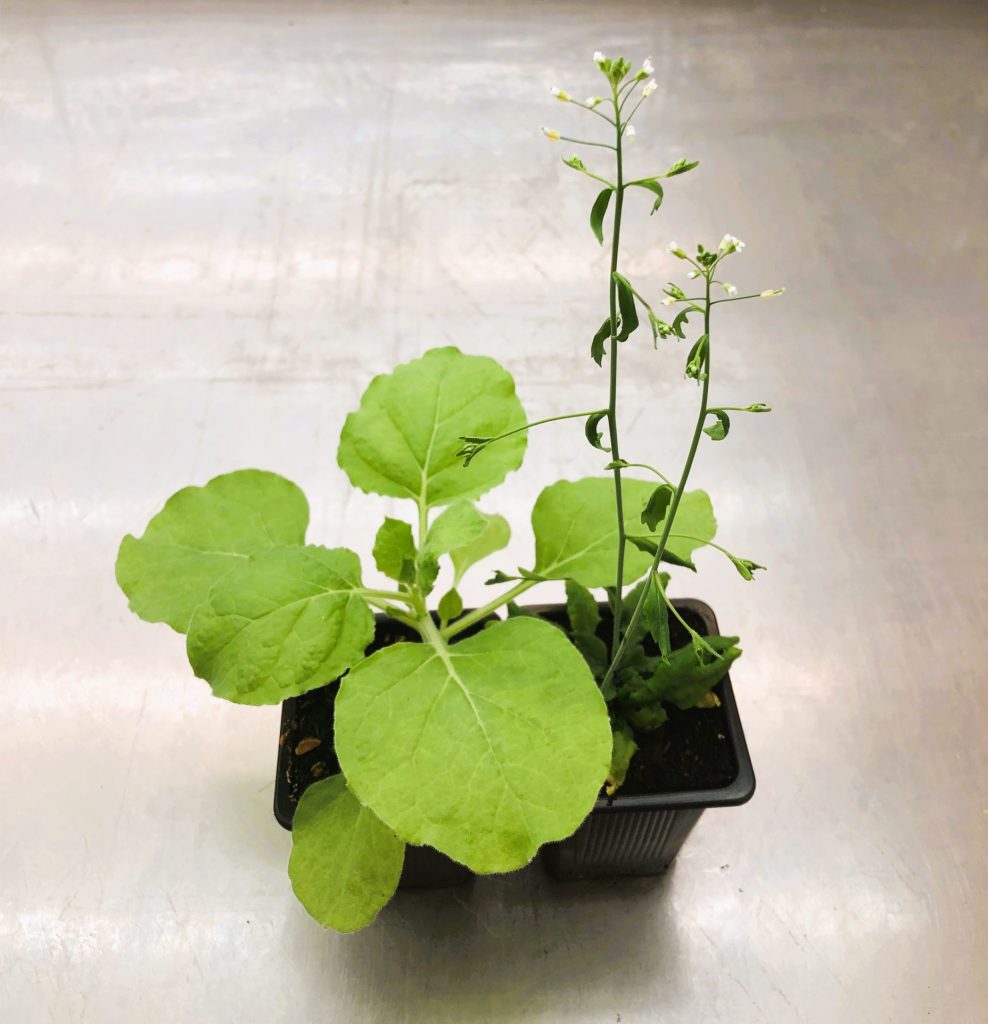

Plant immunity is wired differently in different plants (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn plants, microbial invasion is sensed by membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors. Our knowledge on the immune signaling that follows microbial recognition is mostly derived from studies on Arabidopsis thaliana. In this plant, receptor activation triggers immune responses that are distinct for each…
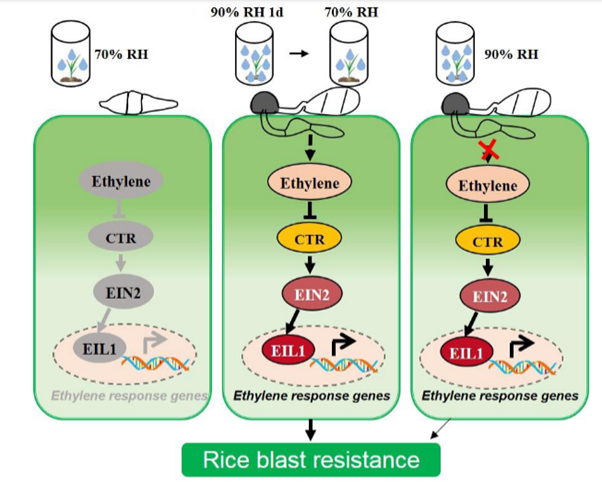
High humidity compromises plant immunity while promoting pathogen growth (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHumidity is considered a key component for the growth of fungal plant pathogens. For many infection assays we either maintain plants in high humidity, or wrap the infected area and keep spraying it with water. This is generally performed to facilitate fungal growth and the assumption that this may not…
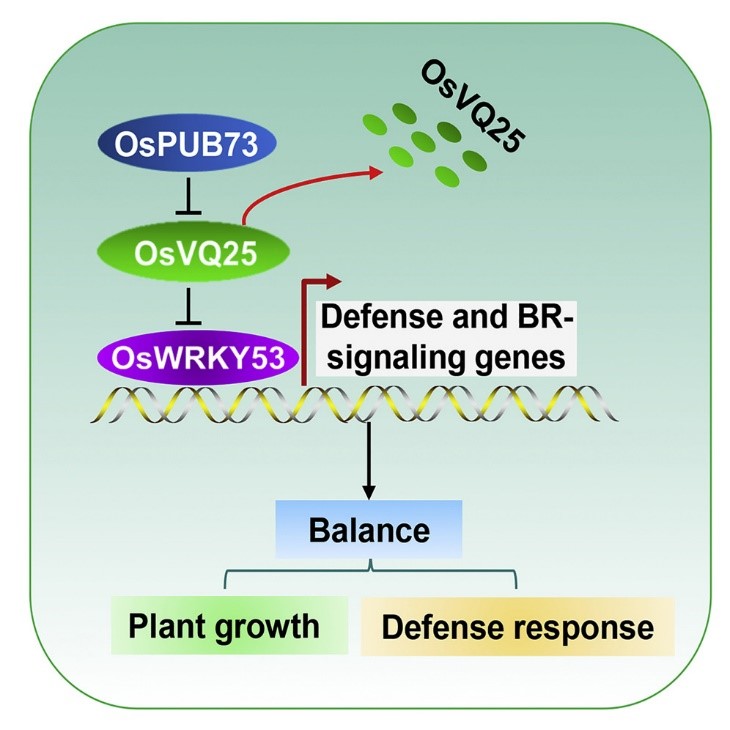
Identification of a cell signaling cascade that regulate s broad-spectrum resistance (Cell Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany different pathogens attack plants, and many genes have been identified that confer pathogen-specific resistance. In a recent study, Hao et al. identified a signaling cascade that regulates broad-spectrum disease resistance. This pathway is composed of a rice ubiquitin ligase OsPUB73, a VQ motif-containing…
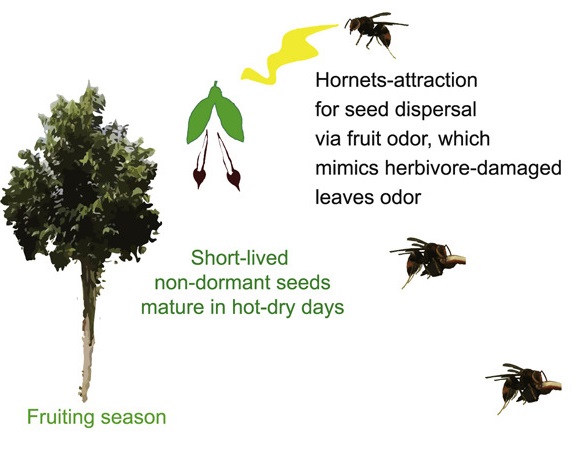
Agarwood harnesses hornets for rapid dispersal of non-dormant seeds (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe seeds of the Agarwood tree (Aquilaria sinensis) lose viability within a few hours of the fruit splitting, so need to reach the ground as soon as possible. Qin et al. report that agarwood achieves this by fooling hornets (Vespa spp.), which generally eat herbivore insects such as caterpillars. When…

