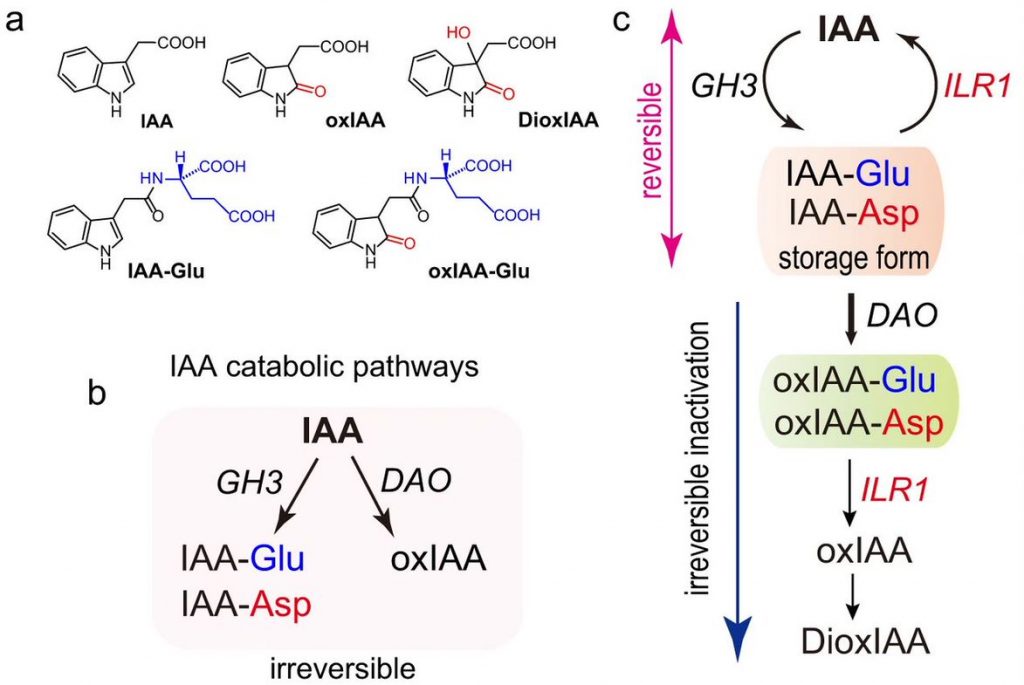
The main oxidative inactivation pathway of the plant hormone auxin (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin is a key hormone in almost all stages of the plant development and its main natural form is indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). In Arabidopsis, several gene families are involved in auxin homeostasis. In this work, Hayashi et al. focus on the roles of DIOXYGENASE FOR AUXIN OXIDATION 1 (DAO1) which converts…

A role for auxin in flag leaf angle in rice
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellAuthor et al. Huang et al. investigate the roles of auxin in flag leaf angle regulation. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab175
Guoqiang Huang
Joint International Research Laboratory of Metabolic & Developmental Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Hybrid Rice, SJTU-University of Adelaide…
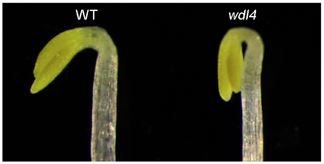
The role of the microtubule-associated protein WDL4 in apical hook opening
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellDeng and colleagues show how the microtubule-associated protein WDL4 contributes to apical hook opening to protect seedligns from damage by soil particles
By Jia Deng, Xiangfeng Wang, Ziqiang Liu, and Tonglin Mao, China Agricultural University
Background: When seedlings emerge through the soil…
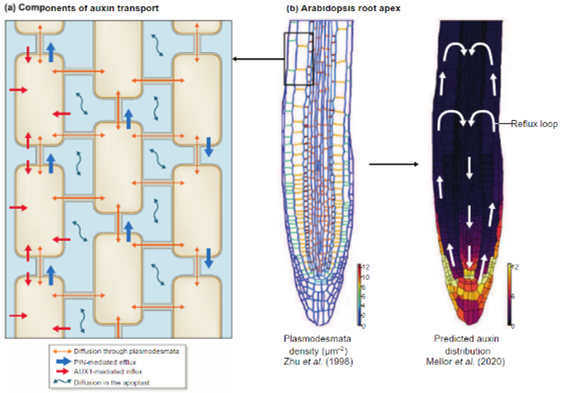
Review: Auxin fluxes through plasmodesmata (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata, the tubular connections that form continua between neighboring cells in plants, play vital roles in long-distance transport of ions, RNA, proteins, and small molecules. While it is known that plasmodesmata are permeable to phytohormones, including auxin, the physiological significance…

Natural Allelic Variation Improves Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang, Zhu, Shen, Ji et al. discover a way to enhance nitrogen use efficiency and grain yield in rice. The Plant Cell (2020) https://bit.ly/3s3bLb3
Background: Nitrogen (N), an essential element for crop growth, is provided to plants by external fertilizer application. However, the excessive use…
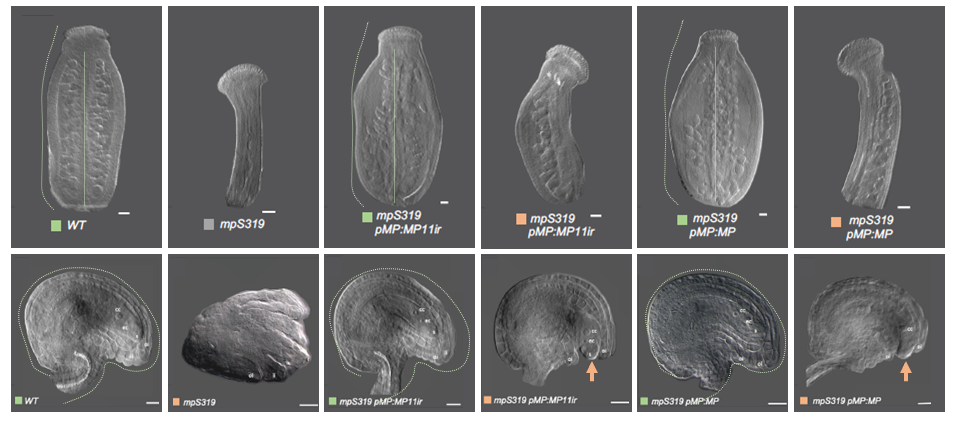
Alternative splicing generates a MONOPTEROS isoform required for ovule development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Auxin shapes the plant body and drives the formation of lateral organs such as roots and ovules. In the current model, AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORs (ARFs) are transcription factors that regulate plant growth by activating signaling in an auxin dose-dependent manner, regulated by Aux/IAA proteins. Here,…

A long shot: Photosynthesis-derived systemic signal controls lateral root emergence (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis, in addition to generating ‘food’ for plants, is also known to control root growth, although the mechanism has been unknown. Duan and co-workers identified CYCLOPHILIN38 (CYP38) as necessary for photosynthesis-mediated lateral root (LR) emergence. The chloroplast-localized CYP38 is…

SAURs protein antagonistically regulate a phosphatase activity during apical hook development and cotyledon opening (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Upon germination in dark, plants adopt a strategy known as skotomorphogenesis, or etiolation, to protect the shoot apical meristem and cotyledon from damage while the seedling moves through the soil. The seedlings de-etiolate when they perceive light and the apical hook and cotyledon open. Wang et…

Leaf position makes a difference: the ABCB19 auxin transporter affects light perception
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAuthor: David S. Favero1 (ORCID: 0000-0002-6879-0323)
[email protected]
Affiliation:
1RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science, Yokohama, Kanagawa, 230-0045 Japan
Main text:
As autotrophs, plants must maintain photosynthesis to thrive. In order for this to happen, a plant’s…

