Rooting in salt: It’s not all about auxin
Yanxia Zhang1,2
1 Laboratory of Plant Physiology, Wageningen University & Research, The Netherlands
2 College of Agriculture, South China Agricultural University, China
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad317
Background: Soil salinity causes crop yield losses world-wide. Adjusting plant…
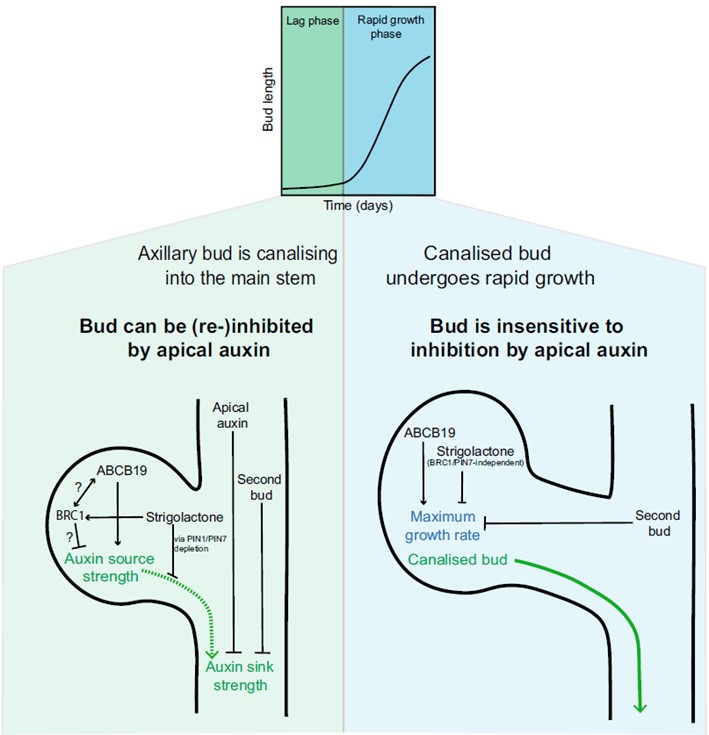
Lag, then leg it! An updated two-phase model for axillary bud activation and outgrowth in Arabidopsis
The mechanisms of apical dominance and bud outgrowth have puzzled generations of plant scientists, and over a century various hypotheses have been scrutinized. Two main hubs of regulation – auxin canalization (movement of auxin from a bud into the main stem) and the branching transcription factors…

RAF-like protein kinases mediate a deeply conserved, rapid auxin response
The definition of a phytohormone has not always been clear, though most plant biologists agree that phytohormones can be defined as endogenous molecules capable of triggering signaling cascades and associated responses by binding to specific receptors. They have been extensively studied in flowering…

Contribution of synthetic auxin conjugates to clonal propagation of woody species
From food and energy to paper and timber, many industries rely on clonal propagation of tree species. Successful propagation of cuttings depends on adventitious rooting ability, which is known to decline with tree age and to be naturally low in many species of interest. Propagators therefore employ naturally…
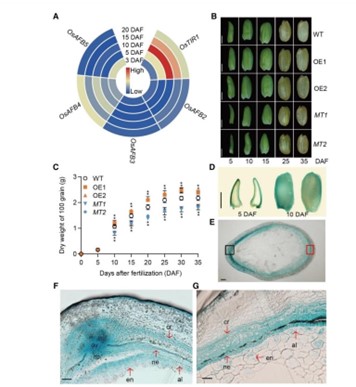
Auxin receptor OsTIR1 mediates auxin signaling during seed filling in rice
Throughout the world, cereal endosperm is a major source of food. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying the import of sugar into the endosperm of rice plants (Oryza sativa) and how these pathways relate to auxin signaling. In this paper, Wu et al. investigate the role of…
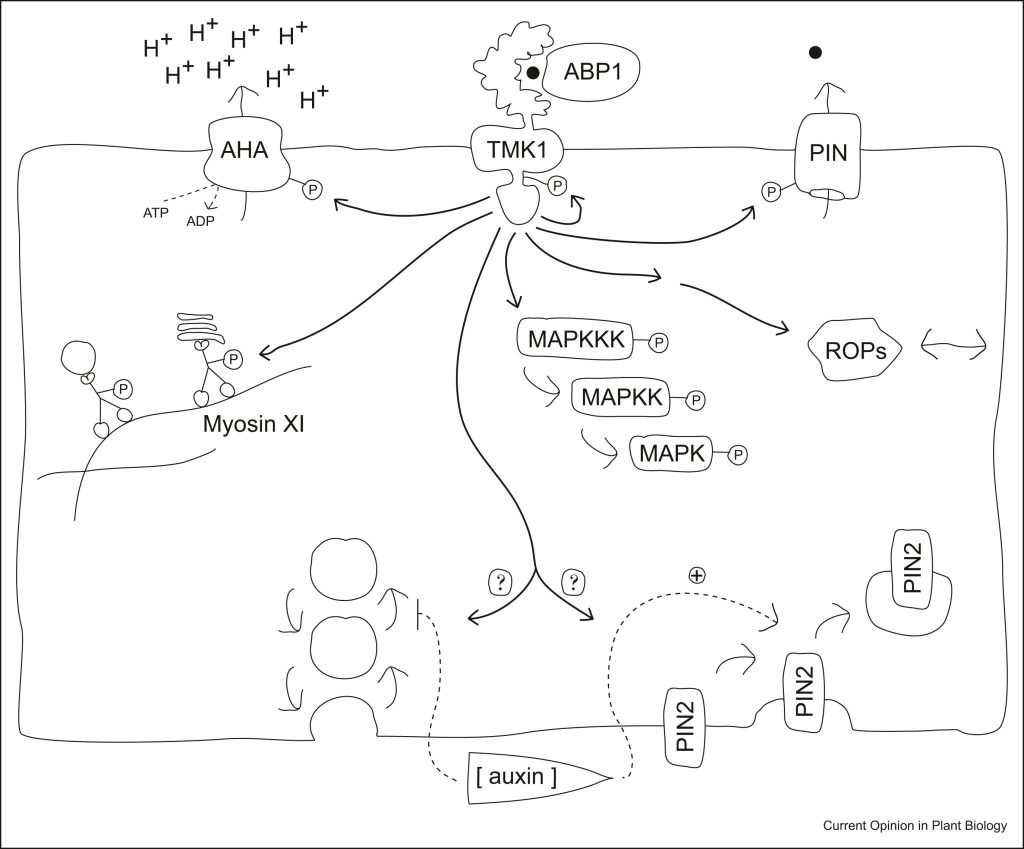
Review: Rapid auxin signaling: Unknowns old and new
You might think you’ve read enough about auxin, but I recommend you take this opportunity to read one more article, this very interesting and enjoyable review by Fielder and Friml. Auxin has figured prominently in both the classical and molecular eras of plant biology. However, the exciting findings…
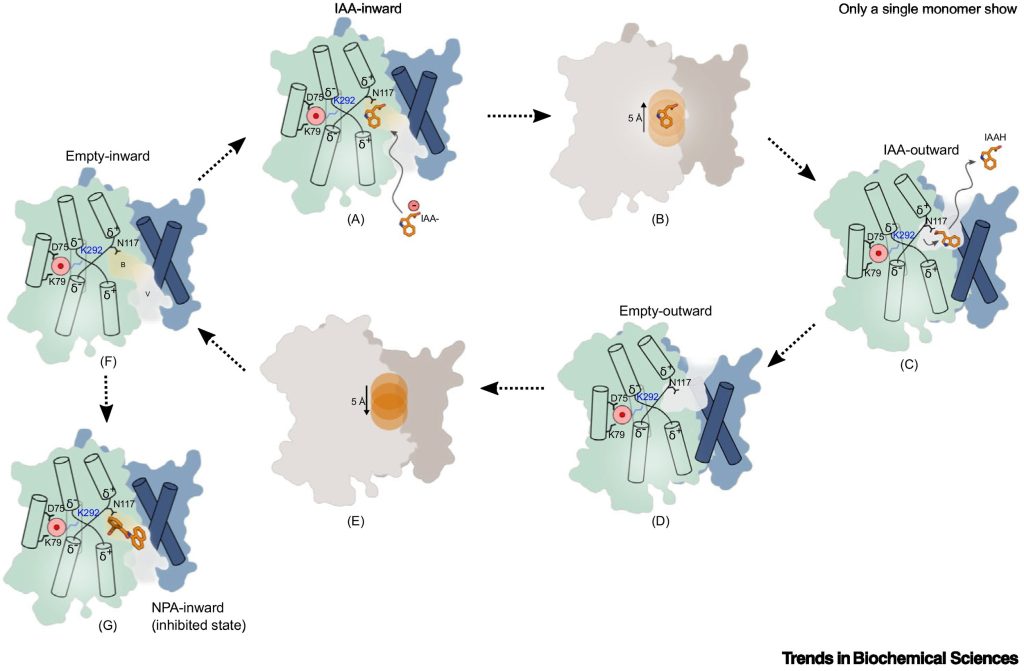
Review: Substrate recognition and transport mechanism of the PIN-FORMED auxin exporters
The PIN-FORMED family of auxin transporters were first identified through genetic screens of Arabidopsis thaliana in the 1980s. Recessive pin mutants form a flowerless, pin-like inflorescence. Subsequent work showed that the encoded genes are membrane-localized auxin transporters and contribute to the…

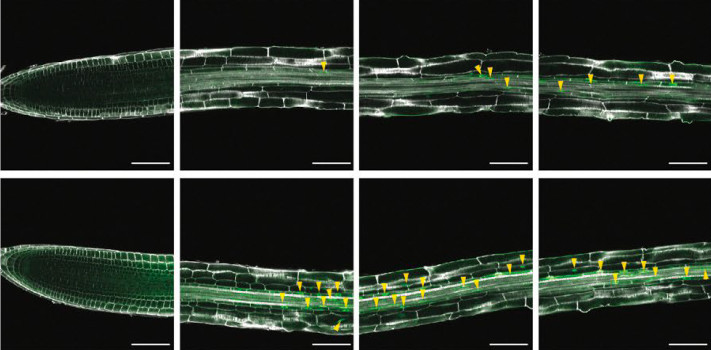
Hormone distribution via hydraulic flux determines root branching
Climate change affects rain patterns and hydrological cycles all over the world, exacerbating water scarcity issues. Root branching is altered by local spatial differences in soil moisture. Indeed, when root tips temporarily lose contact with moisture, root branching stops until the appropriate moisture…
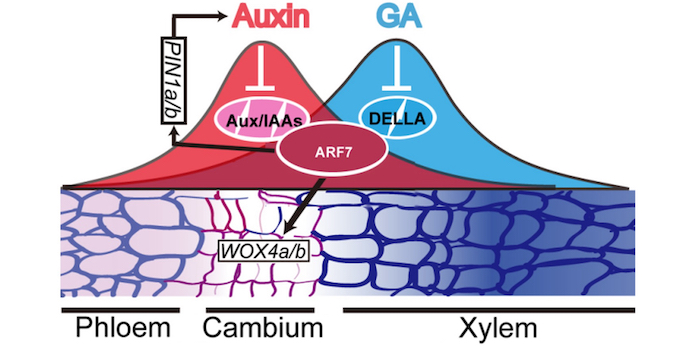
A handshake between auxin and gibberellin in the cambium
Hu et al. demonstrate how the interactions of gibberellin and auxin signaling components regulate cambial activity during wood formation in poplar.
By Jian Hu, Changzheng Xu, and Keming Luo
Background: In trees, the vascular cambium is the population of stem cells that laterally divide and as…

