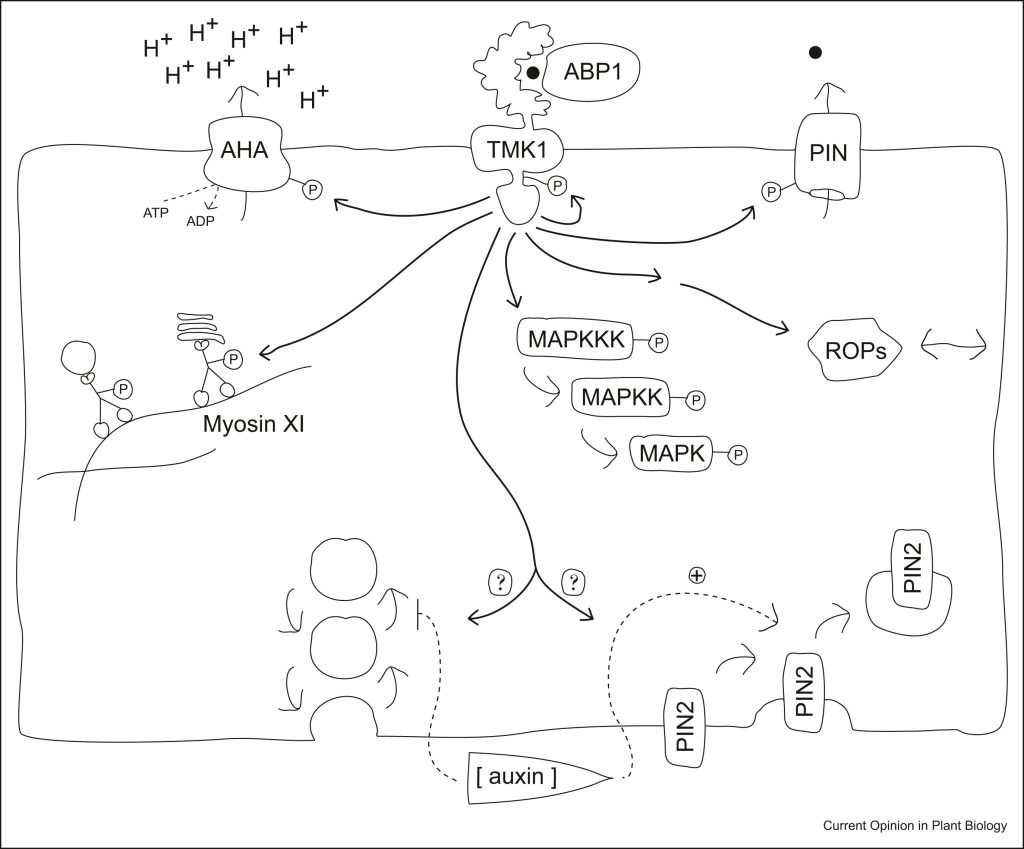
Review: Rapid auxin signaling: Unknowns old and new
Plant Science Research WeeklyYou might think you’ve read enough about auxin, but I recommend you take this opportunity to read one more article, this very interesting and enjoyable review by Fielder and Friml. Auxin has figured prominently in both the classical and molecular eras of plant biology. However, the exciting findings…
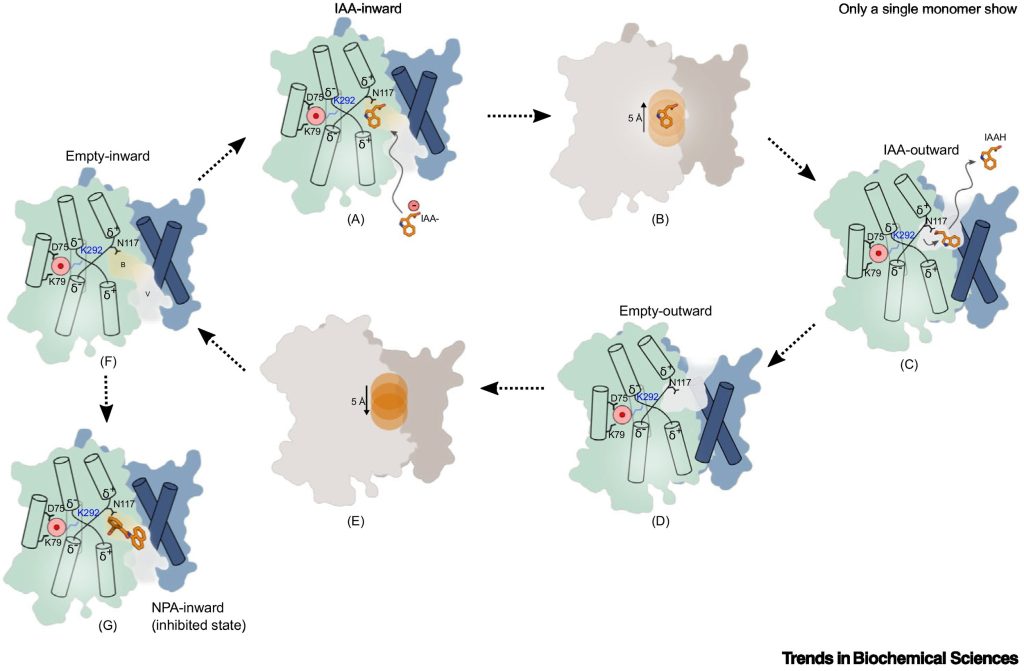
Review: Substrate recognition and transport mechanism of the PIN-FORMED auxin exporters
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe PIN-FORMED family of auxin transporters were first identified through genetic screens of Arabidopsis thaliana in the 1980s. Recessive pin mutants form a flowerless, pin-like inflorescence. Subsequent work showed that the encoded genes are membrane-localized auxin transporters and contribute to the…

Hormone distribution via hydraulic flux determines root branching
Plant Science Research WeeklyClimate change affects rain patterns and hydrological cycles all over the world, exacerbating water scarcity issues. Root branching is altered by local spatial differences in soil moisture. Indeed, when root tips temporarily lose contact with moisture, root branching stops until the appropriate moisture…
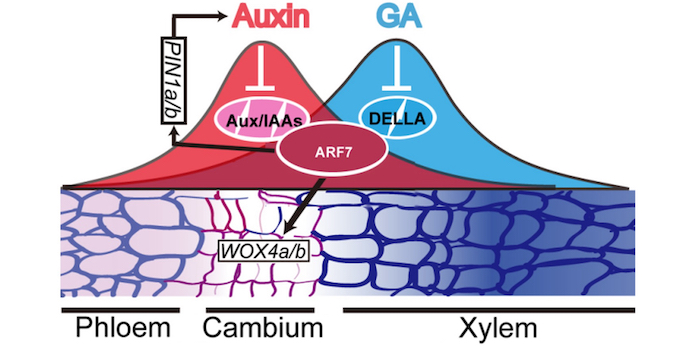
A handshake between auxin and gibberellin in the cambium
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHu et al. demonstrate how the interactions of gibberellin and auxin signaling components regulate cambial activity during wood formation in poplar.
By Jian Hu, Changzheng Xu, and Keming Luo
Background: In trees, the vascular cambium is the population of stem cells that laterally divide and as…
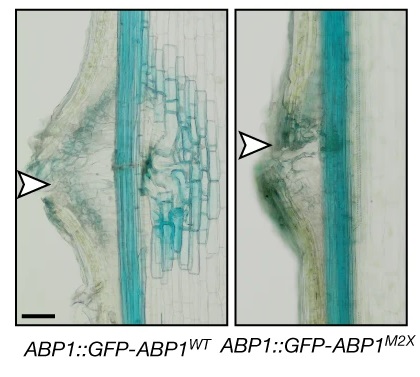
ABP1 (it’s back!) binds auxin and signals fast auxin responses (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the longstanding questions in plant biology concernes how auxin coordinates both gene expression in the nucleus and the so-called fast responses at the cell periphery including proton extrusion and cytoskeletal rearrangements. At this point the nuclear branch is well understood, but the cell periphery…
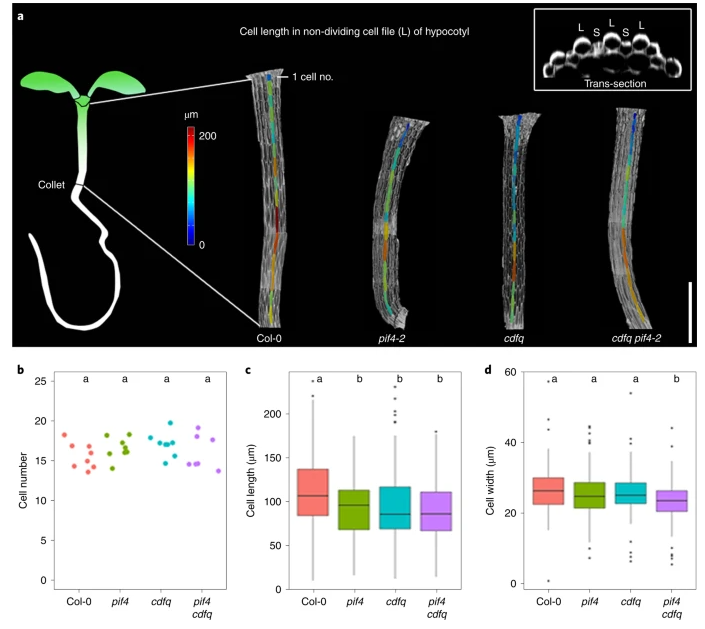
PIF4 enhances DNA binding of CDF2 to co-regulate target gene expression and promote Arabidopsis hypocotyl cell elongation (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResponses to environmental and internal signals require the recruitment of transcription factors (TFs). TFs recognize simple DNA sequences to activate specific genes that will accomplish the required functions. DOF (DNA-binding with one finger) is a large family of plant TFs that encloses the CYCLING…
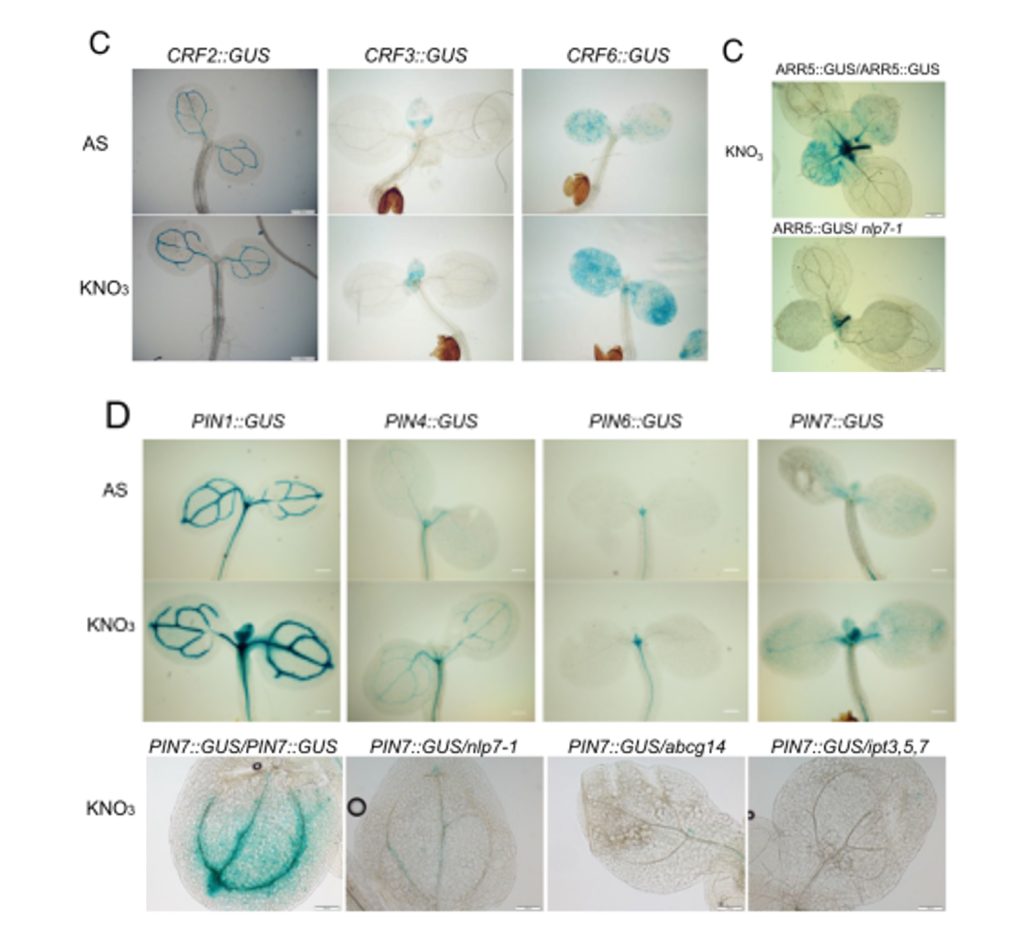
NLP7-CRF-PIN, the nitrate-cytokinin-auxin crosstalk module, conveys root nitrate signals and regulates shoot growth adaptive responses (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrate, the prominent form of nitrogen used by most land plants, is a signal regulating plant growth and development. Nitrate sensing by roots not only regulates root development to facilitate nutrient foraging, but also the growth of distant plant organs. Cytokinin is a mobile signal coordinating nitrate…

KAI2 regulates seedling development by mediating light-induced remodeling of auxin transport (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed germination is can be described as having two phases depending on light availability, skoto- and photomorphogenesis. Skotomorphogenesis, which occurs while the seed is still buried, is characterized by the elongation of the coleoptile and the inhibition of the root system. When the seed reaches…
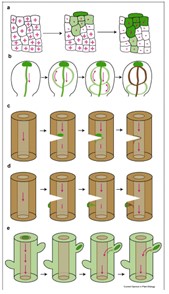
Review. Auxin canalization: From speculative models toward molecular players (Curr Opin Plant Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe versatility of roles that the hormone auxin plays led Paque and Weijers to suggest a new meaning to the acronym IAA (originally- Indole Acetic Acid)- ‘Influences Almost Anything’. It is known that PIN-FORMED (PIN) auxin exporters are responsible for cell-to-cell directional auxin flow and auxin…

